Design of wide dynamic range MOS current mirror using nano dimension MOS field effect transistor
Authors
-
Astha Dadheech
*
 1
1
-
Nikhil Raj
 1
1
-
Divyang Rawal
 1
1
Abstract
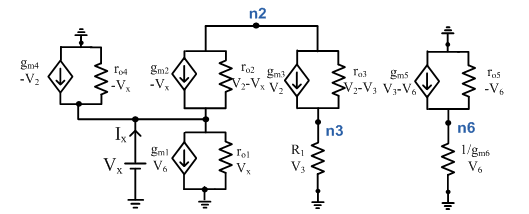
A nanoscale metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor based current mirror circuit operating in a sub volt supply for low power analog applications has been proposed in this paper. Current mirror is a fundamental block of current-mode circuits. In the proposed research, current mirror uses a level-shifted folded flipped voltage follower cell for class AB mode of operation. Usually at nano meter scale, the conventional architecture performance especially for analog gets deteriorates, so to meet the goal proposed design incorporates locally generated feedback & level shifter approach. It also shows improved wide current dynamic range with the use of folding transistors. The current mirroring is performed using folded MOS transistors along with feedback which increases the current mirroring range, results in low input resistance in megahertz range bandwidth. For improvement in output resistance, the architecture uses regulated cascode along with super transistor approach. The performance of the proposed current mirror has been validated small signal analysis and their simulations and corner analysis on Cadence. As observed, the current mirroring is performed with minimum error to 2 milli amperes consuming headroom of 0.14 volt. The input & output resistance is calculated as 1.35 ohm & 2.11 giga ohms respectively. The proposed current mirror is designed in 180 nano meter technology & operates at
0.5 volt.
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
References
[1] Sansen W., Steyaert M., Peluso V., Peeters E., (1998), Toward sub 1 V analog integrated circuits in submicron standard CMOS technologies, IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference ISSCC, pp. 186-187. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISSCC.1998.672428
[2] Azadmousavi T., Faraji Baghtash H., Najafi Aghdam E., (2018), A power efficient gain enhancing technique for current mirror, Iranian Journal of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, 14(2), 137-142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mejo.2014.11.003
[3] Dadheech A., Raj N., Rawal D., (2022), Design of Low Power High Gain Structure of Bulk Driven OTA, 2nd International Conference on Emerging Frontiers in Electrical and Electronic Technologies (ICEFEET), (pp. 1-6). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEFEET51821.2022.9848251
[4] Jalili S., Rafii-Tabar R., (2005), Electronic conductance through organic nanowires. J. Nano Dimens. 71: 410-419. https://doi.org/10.4103/0000-0000.0000
[5] Faraji M., Ghoreishi S. S., Yousefi R., (2018), Gate Structural Engineering of MOS-like Junctionless Carbon Nanotube Field Effect Transistor (MOS-like J-CNTFET). Int. J. Nano Dimens., 9(1): 32-40. https://doi.org/20.1001.1.20088868.2018.9.1.5.9
[6] Sadjadi M. S., Sadeghi B., Zare K., (2007), Natural bond orbital (NBO) population analysis of cyclic thionylphosphazenes, [NSOX (NPCl2) 2]; X= F (1), X= Cl (2), Journal of Molecular Structure: THEOCHEM, 817(1-3), 27-33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theochem.2007.04.015
[7] Ocampo-Hidalgo J. J., Alducín-Castillo J., Vazquez-Alvare I., Oliva-Moreno L. N., Molinar-Solís J. E., (2018), A CMOS low-voltage super follower using quasi-floating gate techniques, Journal of Circuits, Systems and Computers, 27(07), 1850111. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218126618501116.
[8] Raj N., Singh A. K., Gupta A. K., (2015), Low power circuit design techniques: a survey, International Journal of Computer Theory and Engineering, 7(3). https://doi.org/172-176.10.7763/IJCTE.2015.V7.951.
[9] Khateb F., (2014), Bulk-driven floating-gate and bulk-driven quasi-floating-gate techniques for low-voltage low-power analog circuits design, AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 68(1), 64-72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2013.08.019.
[10] Garde Luque M. P., López Martín A., Cruz Blas C. A. D. L., Carvajal R. G., Ramírez-Angulo J., (2020), Wide-swing class AB regulated cascode current mirror, IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), 2020, pp. 1-40. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISCAS45731.2020.918053
[11] Jindal C., Pandey R., (2021), A very low output resistance and wide-swing class-AB level-shifted folded flipped voltage follower cell, Integration, 81, 84-98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vlsi.2021.05.001
[12] Paul A., Ramírez-Angulo J., Torralba A., (2019), Analysis, comparison, and experimental validation of a class AB voltage follower with enhanced bandwidth and slew rate, IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 27(6), 1353-1364. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVLSI.2019.2903116
[13] Rajesh D., Tamil S., Raj N., Chourasia B., (2022), Low-voltage bulk-driven flipped voltage follower-based transconductance amplifier, Bulletin of Electrical Engineering and Informatics, 11(2), 765-771. https://doi.org/10.11591/eei.v11i2.3306.
[14] Bchir M., Aloui I., Hassen N., (2020), A bulk-driven quasi-floating gate FVF current mirror for low voltage, low power applications, Integration, 74, 45-54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vlsi.2020.04.002
[15] Jindal C., Pandey R., (2021), A high output resistance, wide bandwidth, and low input resistance current mirror using flipped voltage follower cell, International Journal of Circuit Theory and Applications, 49(10), 3286-3301. https://doi.org/10.1002/cta.3085
[16] Aggarwal B., Gupta M., Gupta A. K., Sangal A., (2016), A new low voltage level-shifted FVF current mirror with enhanced bandwidth and output resistance, International Journal of Electronics, 103(10), 1759-1775. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207217.2016.1138529
[17] Carvajal R.G., Ramirez-Angulo J., Lopez-Martin A.J., Torralba A., Galan J.A.G., Carlosena A., Chavero F.M., (2005), The flipped voltage follower: a useful cell for low-voltage low-power circuit design, IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers. 52: 1276-1291. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSI.2005.851387
[18] Ramírez-Angulo J., Paul A., Gangineni M., Hinojo-Montero J. M., Huerta-Chua J., (2023), Class AB Voltage Follower and Low-Voltage Current Mirror with Very High Figures of Merit Based on the Flipped Voltage Follower, Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications, 13(2), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea13020028
[19] Raj N., (2021), Low voltage FVF current mirror with high bandwidth and low input impedance, Iranian Journal of Electrical and Electronic Engineering. 17(3): 1972-1972. https://doi.org/10.22068/IJEEE.17.3.1972
[20] Raj N., (2021), Low-voltage wide-range high-impedance flipped voltage follower current mirror, Sādhanā, 46(3), 171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-021-01694-1
[21] Domala N., Sasikala G., (2021), Low power flipped voltage follower current mirror with improved input output impedances, Sādhanā, 46, 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-023-02205-4.
[22] Safari L., Minaei S., (2017), A low-voltage low-power resistor-based current mirror and its applications, Journal of Circuits, Systems and Computers, 26(11), 1750180. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218126617501808
[23] Domala N., Sasikala G., (2022), Low voltage quasi floating gate current mirror with improved output impedance, International Journal of Public Sector Performance Management, 10(4): 499-512. https://dx.doi.org/10.1504/IJPSPM.2022.126404
[24] Akbari M, Javid A., Hashemipour O., (2014), A high input dynamic range, low voltage cascode current mirror and enhanced phase-margin folded cascode amplifier, In: Proceedings of the Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering, pp. 77–81. https://doi.org/10.1109/IranianCEE.2014.6999507
[25] Kumar P. A., Tamil S., Raj N., (2021), Low voltage improved impedance wide bandwidth current mirror, International Journal of Information Technology, 13, 2411-2417. sshttps://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-021-00785-w.