Assesment of physico-chemical analysis of pond water in Newara village
Gayatri Neelam Shashtri1 , N.K. Singh1 and C. Das1 *
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.12944/CWE.3.1.36
In present study the water quality of the Newara village pond was evaluated by analyzing physcio-chemical characteristics. The values obtained for various physico-chemical parameters like temperature, pH, Chloride, Total hardness, DO, BOD, COD were measured. The values of these parameters are summarized in table, which shows enormous growth of phytoplanktons throughout the year.
Copy the following to cite this article:
Shashtri G.N, Singh N.K, Das C. Assesment of physico-chemical analysis of pond water in Newara village. Curr World Environ 2008;3(1):211-212 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.12944/CWE.3.1.36
Copy the following to cite this URL:
Shashtri G.N, Singh N.K, Das C. Assesment of physico-chemical analysis of pond water in Newara village. Curr World Environ 2008;3(1):211-212. Available from: http://www.cwejournal.org/?p=817
Download article (pdf) Citation Manager Publish History
Select type of program for download
| Endnote EndNote format (Mac & Win) | |
| Reference Manager Ris format (Win only) | |
| Procite Ris format (Win only) | |
| Medlars Format | |
| RefWorks Format RefWorks format (Mac & Win) | |
| BibTex Format BibTex format (Mac & Win) |
Article Publishing History
| Received: | 2008-04-23 |
|---|---|
| Accepted: | 2008-06-27 |
Human being requires more water as compared to any other terrestrial organism. Hence the great human civilizations have developed near the fresh water bodies. Therefore the aspect of water use, as every one have become aware of water as a limited natural resources as precious if not yet as scared as gold or oil.
The Pond is selected in the outskirts of village Newara, which is 22 km. away from Bilaspur towards Bilaspur-Kota road.
The present study reveals the assessment of pond water in Newara village with respect to some physico-chemical parameters.
The study was carried out for the month of January to December during the year 2006. The water samples ware collected from surface near the margins of the pond between 8.30 am. to 10.30 am. The analysis of physico-chemical parameters were made by following APHA-AWWA-WPCF 1985.
The physico-chemical parameters of pond water are given in Table 1. The pond water temperature was observed minimum 18.6°C in the month of February and maximum 31°C in the month of Jun. Ph had very little variation in the values throughout the year however the value ranged from 7.21 to 8.87, Chloride content had showed a values change in the all months, the values ranged from 117.74 to 469.9 mg./-1. The maximum value of 905.76 mg./-1, total Hardness was obtained in the month of February, while lowest value of 87.67 mg/-1 in September Dissolve oxygen was ranged from 1.06 to 8.61 mg/-1. The minimum value was recorded in the month of the May and Jun maximum in December it was resulted due to greater consumption of oxygen by organism during the summer months, May and Jun as compared to December. BOD values were ranged from 9.18 mg./-1 to 36.6mg./-1. The minimum value was record in the month of Jun and maximum in January. The higher in the month of Jun infers the greater rate of biological oxidation in prevailing higher temperature of the pond water. Minimum values of COD was noted in the month of August 240 mg./-1 and maximum value of the month of April. The higher value of COD during the summer was due to higher rate of evaporation.
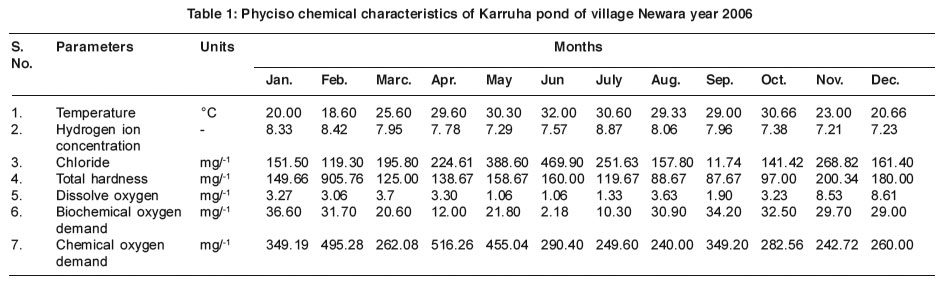 |
Table 1: Phyciso chemical characteristics of Karruha pond of village Newara year 2006 Click here to view table |
The analysis of physico-chemical parameter had indicated the wider human activity and in flux of domestic wastes in ponds which Caused the eutrophication ponda of the century. So the pond has showed enormous growth of phytoplankton throughout the study period.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to principal Dr. V.K. Shrivastava, Head Department of Botany Dr. Asha Kaushik for providing avaialble library and laboratory facilities time to time along with giving invaluable suggestion during the course of carrying out the experimental work. Further the author is also thankfur to M.F.K. Khokkar, Retired Principal, Govt. Collage Masturi for his intellectual support and encouragement.
References
1. APHA-AWINA and WPCE: Standard method for the Examination of water and waste water 16th edition Amer. Publ. Health, Assoc, INC., Newyork (1985).
2. Baruah, B.K., Talukdar, S. and Brothokur: Area of Kamrup Distt. Assam. Env. Eco., 8 Conc (1984) 16(2): 254-256.
3. Chona, M.K., Physico-chemical complexes of a polluted pond at Halomagra (Chandigarh), Himalayan J. Environ, Zoo., (1991) 5(1): 42-44.
4. Grewal., Water quality in Punjab, JIWWA 4275-279 (1976).
5. Hutchinson, G.E., A Treatise on Limnology. Vol. 1, John Wiley and Sons, INC. Newyork (1967).
6. Kalostra, B.L., Sheikh, H.N., Abrof, S.L., Mehta, B.L. and Kumar, R., Inorganic content in water of Sinkichhapri and Baba Sidhgoria ponds in Jammu Distt. Indian J. of Environ Prot., (1996) 16(2): 81-84.
7. Kaur, H., Dhillon, S.S., Bhatt, K.S. and Mander, G., Abiotic and biotic Components of fresh water pond of Patiala (Punjab).
8. Kanungo, V.K., Verma, J.N. and Patel, D.K., Physico-chemical characteristics of Doodhadahri pond of Raipur (Chattisgarh), Eco. Env. and Cons, (2006) 12(2): 207-209.







