Abstract
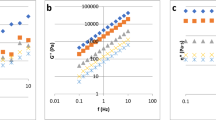
The aim of the study was to quantify sugar profile and rheological behaviour of four Indian honey varieties (Cotton, Coriander, Dalbergia, and Murraya). The effect of temperature (5, 10, 20 and 30 °C) on rheological behaviour of these honey varieties was also studied. Fourteen sugars (three monosaccharides, six disaccharides, four trisaccharides, and one oligosaccharide) were quantified. The concentration of glucose and fructose varied from 33.40–34.06% to 36.86–41.15%, respectively. Result indicated that monosaccharides were the dominant sugars among all the honey samples. Low amounts of turanose, trehalose, melibiose, and raffinose were present in the range of 0.02–0.03%, 0.11–0.26%, 0.09–0.18% and 0.06–0.12%, respectively in the analyzed honey varieties. The rheological behaviour of all four honey varieties was analysed at different temperatures i.e. 5, 10, 20 and 30 °C followed an Arrhenius model. In analysed honey varieties storage modulus (G′) was less than loss modulus (G″) which confirmed the Newtonian behaviour of all honey samples.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Jdayil B, Ghzawi A, Al-Malah KIM, Zaitoun S (2002) Heat effect on rheology of light and dark-coloured honey. J Food Eng 51:33–38
Ahmed J, Prabhu S, Raghavan G, Ngadi M (2007) Physico-chemical, rheological, calorimetric and dielectric behaviour of selected Indian honey. J Food Eng 79:1207–1213
Al-Malah KIM, Abu-Jdayil B, Zaitoun S, Al-Majeed Ghzawi A (2001) Application of WLF and Arrhenius kinetics to rheology of selected dark-colored honey. J Food Eng 24:341–357
Bentabol Manzanares A, Hernandez Garcia Z, Rodriguez Galdon B, Rodriguez Rodriguez E, Diaz Romero C (2011) Differentiation of blossom and honeydew honeys using multivariate analysis on the physicochemical parameters and sugar composition. Food Chem 126:664–672
Codex Alimentarius Commission (2001) Revised standards for honey. Codex Standard 12-1981. Rev 1 (1987), Rev 2 (2001), Rome, FAO, 2001
Costa PA, Moraes ICF, Bittante AMQB, Sobral PJA, Gomide CA, Carrer CC (2013) Physical properties of honeys produced in the Northeast of Brazil. Int J Food Stud 2:118–125
Cotte JF, Casabianca H, Chardon S, Lheritier J, Grenier-Loustalot MF (2003) Application of carbohydrate analysis to verify honey authenticity. J Chromatogr A 1021:145–155
De la Fuente E, Ruiz-Matute AI, Valencia-Barrera RM, Sanz J, Martinez-Castro I (2011) Carbohydrate composition of Spanish unifloral honeys. Food Chem 129:1483–1489
Dobre I, Georgescu LA, Alexe P, Escuredo O, Seijo MC (2012) Rheological behaviour of different honey types from Romania. Food Res Int 49:126–132
Escuredo O, Miguez M, Fernandez-Gonzalez M, Seijo MC (2013) Nutritional value and antioxidant activity of honeys produced in a European Atlantic area. Food Chem 138:851–856
Escuredo O, Dobre I, Fernandez-Gonzalez M, Seijo MC (2014) Contribution of botanical origin and sugar composition of honeys on the crystallisation phenomenon. Food Chem 149:84–90
Junzheng P, Changying J (1998) General rheological model for natural honeys in China. J Food Eng 36:165–168
Juszczak L, Fortuna T (2006) Rheology of selected polish honeys. J Food Eng 75:43–49
Juszczak L, Socha R, Roznowski J, Fortuna T, Nalepka K (2009) Physicochemical properties and quality parameters of herb honeys. Food Chem 113:538–542
Kamboj R, Bera MB, Nanda V (2013a) Evaluation of physico-chemical properties, trace metal content and antioxidant activity of Indian honeys. Int J Food Sci Technol 48:578–587
Kamboj R, Bera MB, Nanda V (2013b) Chemometric classification of Northern India unifloral honey. Acta Aliment Hung 42:540–551
Khalafi R, Goli SAH, Isfahani MB (2016) Characterization and classification of several monofloral Iranian honeys based on physicochemical properties and antioxidant activity. Int J Food Prop 19:1065–1079
Laos K, Kirs E, Pall R, Martverk K (2011) The crystallisation behaviour of Estonian honeys. Agron Res 9:427–432
Lazaridou A, Biliaderis CG, Bacandritsos N, Sabatini AG (2004) Composition, thermal and rheological behaviour of selected Greek honeys. J Food Eng 64:9–21
Nayik GA, Nanda V (2016) A Chemometric approach to evaluate the phenolic compounds, antioxidant activity and mineral content of unifloral honey types from Kashmir, India. LWT-Food Sci Technol 74:504–513
Nayik GA, Dar BN, Nanda V (2016) Physico-chemical, rheological and sugar profile of different unifloral honeys from Kashmir valley of India. Arab J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2015.08.017
Nozal MJ, Bernal JL, Toribio L, Alamo M, Diego JC (2005) The use of carbohydrate profiles and chemometrics in the characterisation of natural honeys of identical geographical origin. J Agric Food Chem 53:3095–3100
Ouchemoukh S, Schweitzer P, Bachir Bey M, Djoudad-Kadji H, Louaileche H (2010) HPLC sugar profiles of Algerian honeys. Food Chem 121:561–568
Patil U, Muskan K (2009) Essentials of biotechnology. International Publishing House, New Delhi
Persano Oddo L, Piro R (2004) Main European unifloral honeys: descriptive sheets. Apidologie 35:38–81
Primorac L, Flanjak I, Kenjeric D, Bubalo D, Topolnjak Z (2011) Specific rotation and carbohydrate profile of croatian unifloral honeys. Czech J Food Sci 29:515–519
Rybak-Chmielewska H, Szczesna T, Was E, Jaskiewicz K, Teper D (2013) Characteristics of Polish unifloral honeys IV honeydew honey, mainly Abies alba L. J Apic Sci 57:51–59
Sanz ML, Polemis N, Morales V, Corzo N, Drakoularakou A, Gibson GR et al (2005) In vitro investigation into the potential prebiotic activity of honey oligosaccharides. J Agric Food Chem 53:2914–2921
Saxena S, Panicker L, Gautam S (2014) Rheology of Indian honey: effect of temperature and gamma radiation. Int J Food Sci. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/935129
Senyuva HZ, Gilbert J, Silici S, Charlton A, Dal C, Gurel N, Cimen D (2009) Profiling Turkish honeys to determine authenticity usingphysical and chemical characteristics. J Agric Food Chem 57:3911–3919
Sopade PA, Halley PJ, D’Arcy BR, Bhandari B, Caffin N (2004) Dynamic and steady-state rheology of Australian honeys at subzero temperatures. J Food Process Eng 27:284–309
Szczesna T, Rybak-Chmielewska H, Was E, Kachaniuk K, Teper D (2011) Characteristics of Polish unifloral honeys. I. Rape honey (Brassica napus L. var. Oleifera Metzger). J Apic Sci 55:111–119
Von der Ohe W, Persano Oddo L, Piana ML, Morlot M, Martin P (2004) Harmonized methods of melissopalynology. Apidologie 35:S18–S25
Wei Z, Wang J, Wang Y (2010) Classification of monofloral honeys from different floral origins and geographical origins based on rheometer. J Food Eng 96:469–479
Witczak M, Juszczak L, Gałkowska D (2011) Non-Newtonian behaviour of heather honey. J Food Eng 104:532–537
Zaitoun S, Ghzawi AA, Al-Malah KIM, Abu-Jdayil B (2001) Rheological properties of selected light coloured Jordanian honey. Int J Food Prop 4:139–148
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to local beekeepers of Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, and Rajasthan (India) for providing honey samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamboj, R., Nayik, G.A., Bera, M.B. et al. Sugar profile and rheological behaviour of four different Indian honey varieties. J Food Sci Technol 57, 2985–2993 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04331-7
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04331-7