Abstract
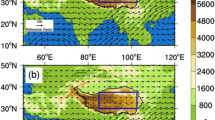
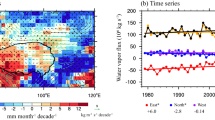
Using ERA-Interim and ERA-5 reanalysis datasets combined with measurements from the Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS), we divided the Tibetan Plateau (TP) into three regions to analyse the long-term trends of water vapor in the upper troposphere and its possible mechanisms. The conclusions are as follows. The water vapor at 200 hPa in the summers from 1979 to 2016 over Region 1 (34°N-40°N, 80°E-100°E) shows a positive trend, which is caused by the rising surface temperature and the northward shift of the South Asian High (SAH). The positive trend of water vapor over Region 2 (28°N-33°N, 80°E-90°E) is attributed to the enhanced South Asian summer monsoon, which leads to increases in horizontal transport of water vapor and vertical water vapor flux. The increase in the vertical transport of water vapor is responsible for the increase in water vapor over the Region 2. The negative trend of water vapor over Region 3 (27°N-30°N, 93°E-98°E) is mainly due to the weakening of water vapor transport caused by the weakening of convective activities.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bi Y., Chen Y., Zhou R. et al.: Study on H2O and CH4 Distributions and Variations over Qinghai-Xizang Plateau Using HALOE Data. PLATEAU METEOROLOGY. pp. 249–258 (2008) (in Chinese)
Bian J., Pan L.L., Paulik L. et al.: In situ water vapor and ozone measurements in Lhasa and Kunming during the Asian summer monsoon. Geophys Res Lett. 39(19) (2012)
Chen, F., Chen, J., Huang, W.: A discsussion on the westerly-dominated climate model in mid-latitude Asia during the modern interglacial period. Front. Earth Sci. 16(6), 023–032 (2009)
Chen, B., Xu, X.D., Yang, S., et al.: Climatological perspectives of air transport from atmospheric boundary layer to tropopause layer over Asian monsoon regions during boreal summer inferred from Lagrangian approach. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 12(13), 5827–5839 (2012)
Dee D. P., Uppala S. M., Simmons A. J., et al.: The ERA-Interim reanalysis: configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 137:553–597 (2011).
Diallo, M., Riese, M., Birner, T., et al.: Response of stratospheric water vapor and ozone to the unusual timing of El Niño and the QBO disruption in 2015–2016. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 18(17), 13055–13073 (2018)
Fu, R., Hu, Y., Wright, J.S., et al.: Short circuit of water vapor and polluted air to the global stratosphere by convective transport over the Tibetan plateau. P NATL ACAD SCI USA. 103(15), 5664–5669 (2006)
Gettelman A., Kinnison D.E., Dunkerton T.J. et al.: Impact of monsoon circulations on the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere. J Geophys Res-Atmos. 109(D22) (2004)
Hegglin M. I., Tegtmeier S., Anderson J. et al.: SPARC Data Initiative: Comparison of water vapor climatologies from international satellite limb sounders. J Geophys Res-Atmos. Pp, 11824–11846 (2013)
Held I. M. and Soden B. J.: Water vapor feedback and global warming1. ANNU REV ENERG ENV. pp. 441–475 (2000)
Hoffmann, L., Günther, G., Li, D., et al.: From ERA-interim to ERA5: the considerable impact of ECMWF's next-generation reanalysis on Lagrangian transport simulations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 19, 3097–3124 (2019)
Huang, R., Liu, Y., Du, Z., et al.: Differences and links between the east Asian and south Asian summer monsoon systems: characteristics and variability. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 34(10), 1204–1218 (2017)
IPCC: Summary for Policymakers of Climate change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK (2007)
IPCC.: Summary for Policymakers of Climate change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change,” Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK (2013)
Jain, S., Kar, S.C.: Transport of water vapor over the Tibetan plateau as inferred from the model simulations. J Atmos Sol-Terr Phy. 161, 64–75 (2017)
Jiang J.H., Su H., Zhai C. et al.: An assessment of upper-troposphere and lower-stratosphere water vapor in MERRA, MERRA2 and ECMWF reanalyses using Aura MLS observations. J Geophys Res-Atmos. 120(22) (2015)
Lacis A.A., Hansen J.E., Russell G.L. et al.: The role of long-lived greenhouse gases as principal LW control knob that governs the global surface temperature for past and future climate change. Tellus B, 65 (2013)
Lin, H., You, Q., Zhang, Y., et al.: Impact of large-scale circulation on the water vapour balance of the Tibetan plateau in summer. Int. J. Climatol. 36(13), 4213–4221 (2016)
Livesey N. J., Read W. G., Wagner P. A., et al.: Version 4.2 x Level 2 data quality and description document. JPL D-33509 Rev. C. (2017)
Luo, J., Pan, L.L., Honomichl, S.B., et al.: Space–time variability in UTLS chemical distribution in the Asian summer monsoon viewed by limb and nadir satellite sensors. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 18(16), 12511–12530 (2018)
Nützel, M., Dameris, M., Garny, H.: Movement, drivers and bimodality of the south Asian high. Atmos Chem. Phys. 16(22), 14755–14774 (2016)
Oltmans, S.J., Hofmann, D.J.: Increase in lower-stratospheric water vapour at a mid-latitude northern hemisphere site from 1981 to 1994. Nature. 374(6518), 146–149 (1995)
Park M., Randel W.J., Gettelman A. et al.: Transport above the Asiansummer monsoon anticyclone inferred from Aura Microwave LimbSounder tracers. J Geophys Res-Atmos. 112(D16) (2007)
Park M., Randel W.J., Emmons L.K. et al.: Transport pathways of carbon monoxide in the Asian summer monsoon diagnosed from Model of Ozone and Related Tracers (MOZART). J Geophys Res-Atmos. 114(D8) (2009)
Randel W.J., Park M.: Deep convective influence on the Asian summer monsoon anticyclone and associated tracer variability observed with Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS). J Geophys Res-Atmos. 111(D12) (2006)
Randel W.J., Park M., Emmons L. et al.: Asian Monsoon Transport of Pollution to the Stratosphere. Science. 328 (2010)
Read W.G., Wu D.L., Waters J.W. et al.: Dehydration in the tropical tropopause layer: Implications from the UARS Microwave Limb Sounder. J Geophys Res-Atmos. 109(D6) (2004)
Ren, C., Bian, J., Fan, Q.: The impact of the South Asia high bimodality on the chemical composition of the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere. Atmos. Oceanic Sci Lett. 4(4), 229–234 (2011)
Schmidt, G.A., Ruedy, R.A., Miller, R.L., et al.: Attribution of the present-day total greenhouse effect. J Geophys Res-Atmos. 115, D20 (2010)
Shang G., Matthes K., Wang W. et al.: Validation of COSMIC water vapor data in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere using MLS, MERRA and ERA-Interim. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques Discussions, pp. 1–28 (2016)
Shi, X., Shi, X.: Climatological Characteristics of Summertime Moisture Budget over the Southeast Part of Tibetan Plateau with Their Impacts. J. Appl. Meteor. Sci. (in Chinese). 19(1), 41–46 (2008)
Sinha, A., Harries, J.E.: Water vapor and greenhouse trapping: the role of far infrared absorption. Geophys. Res. Lett. 16, 2147–2150 (1995)
Solomon, S., Rosenlof, K.H., Portmann, R.W., Daniel, J.S., Davis, S.M., Sanford, T.J., Plattner, G.K.: Contributions of stratospheric water vapor to decadal changes in the rate of global warming. Science. 327(5970), 1219–1223 (2010)
Sridharan S., Sandhya M.: Long-term (2004–2015) tendencies and variabilities of tropical UTLS water vapor mixing ratio and temperature observed by AURA/MLS using multivariate regression analysis. J ATMOS SOL-TERR PHY. pp, 156–165 (2016)
Sun Y., Chen Q., Gui K. et al.: Characteristics of Water Vapor in the UTLS over the Tibetan Plateau Based on AURA/MLS Observations. Adv Meteorol. Pp, 1–13 (2017)
Tabazadeh, A.: Quantifying Denitrification and its effect on ozone recovery. Science. 288(5470), 1407–1411 (2000)
Tian, W., Chipperfield, M.P., Huang, Q.: Effects of the Tibetan plateau on total column ozone distribution. Tellus B. 60(4): 622-635 (2008)
Tian, W., Chipperfield, M.P., Lü, D.: Impact of increasing stratospheric water vapor on ozone depletion and temperature change. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 26(3): 423–437 (2009)
Tian, W., Tian, H., Dhomse, S., et al.: A study of upper troposphere and lower stratosphere water vapor above the Tibetan plateau using AIRS and MLS data. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 12(2), 233–239 (2011)
Tian H., Tian W., Luo J. et al.: Climatology of cross-tropopause mass exchange over the Tibetan Plateau and its surroundings. Int J Climatol. Pp, 3999–4014 (2017)
Tu H., Tian H., Xu X., Zhang R.: Influence of the South-North Displacement of South Asia High on the Distribution of Atmospheric Composition in the Upper Troposphere-Lower Stratosphere over the Asian Monsoon Region.Plat Meteorol. 39(2), 333-346. (2020) (in Chinese)
Turner, A.G., Annamalai, H.: Climate change and the south Asian summer monsoon. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2(8), 587–595 (2012)
Uma, K.N., Das, S.K., Das, S.S.: A climatological perspective of water vapor at the UTLS region over different global monsoon regions: observations inferred from the Aura-MLS and reanalysis data. Climate Dyn. 43(1–2), 407–420 (2014)
Vogel, B., Günther, G., Müller, R., et al.: Impact of different Asian source regions on the composition of the Asian monsoon anticyclone and of the extratropical lowermost stratosphere. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 15(23), 13699–13716 (2015)
Wagner T., Beirle S., Grzegorski M. et al.: Global trends (1996–2003) of total column precipitable water observed by Global Ozone Monitoring Experiment (GOME) on ERS-2 and their relation to near-surface temperature. J Geophys Res-Atmos. vol. 111 (2006)
Wang, K., Jiang, H., Zhao, H.: Atmospheric water vapor transport from westerly and monsoon over the Northwest China. Adv Water Resour (in Chinese). 03, 461 (2005)
Webster, P.J., Yang, S.: Monsoon and ENSO: selectively interactive systems. Quart J Roy Meteor Soc. 118(507), 877–926 (1992)
Wu, M.L.C., Schubert, S., Huang, N.E.: The development of the south Asian summer monsoon and the Intraseasonal oscillation. J. Clim. 12(7), 2054–2075 (1999)
Wei W., Zhang R., Wen M.: Meridional Variation of South Asian High and Its Relationship with the Summer Precipitation over China. J. Appl. Meteor. Sci. (in Chinese). 23(6), 650-659 (2012).
Xie F., Tian W., Li J.: The Effect of ENSO Activity on Lower Stratospheric Water Vapor and Circulation. Atmos Chem Phys. Pp, 4141–4166 (2011)
Xie F., Li J., Tian W., Zhou X, Ma X.: The Variations in Middle and Upper Stratospheric Water Vapour over the Past Two Decades. SOLA 12(12), 127–134 (2016)
Xie F., Zhou X., Li J., Chen Q., Zhang J., Li Y., Ding R., Xue J., Ma X.: Effect of the Indo-Pacific Warm Pool on Lower-Stratospheric Water Vapor and Comparison with the Effect of ENSO. J. Clim. 31, 929–943 (2018)
You Q., Jiang Z., Bao Y. et al.: Trends in upper tropospheric water vapour over the Tibetan Plateau from remote sensing. Int J Climatol. Pp, 4862–4872 (2016)
Zhang, Q., Wu, G., Qian, Y.: The bimodality of the 100 hPa South Asia high and its relationship to the climate anomaly over East Asia in summer. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 80, 733–744 (2002)
Zhang Y.: Studies on the Changing Characteristics of South Asia High and the Relation with Relevant Impact Factors. Lanzhou University. (in Chinese).424. (2012).
Zhang, Y., Wang, D., Zhai, P., et al.: Spatial distributions and seasonal variations of tropospheric water vapor content over the Tibetan plateau. J. Clim. 26(15), 5637–5654 (2013)
Zhang, P., Liu, Y., He, B.: Impact of east Asian summer monsoon heating on the interannual variation of the south Asian high. J. Clim. 29(1), 151106072625005 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA17010106) and the National Science Foundation of China (41875046).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Maeng-Ki Kim.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Tian, H., Qie, K. et al. A Study on the Trend of the Upper Tropospheric Water Vapor over the Tibetan Plateau in Summer. Asia-Pacific J Atmos Sci 57, 277–288 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-020-00191-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-020-00191-5