Development: Unlocking the microbiome
Living peacefully within or on the surface of every multicellular organism is a community of microbes, known as a microbiome, that benefits the health of the host. In the human gut, for instance, these microbes help develop the immune system, provide protection against pathogens, and break down food for nutrition (Horrocks et al., 2023). Although scientists have made great strides in deciphering how these health benefits are achieved, identifying which microbes are responsible remains a major challenge in the field, particularly in higher organisms such as humans.
An alternative is to study organisms that have less complex microbiomes, such as fruit flies. Previous work has shown that four bacterial families make up 90% of the bacteria in the fruit fly microbiome, and only 14 families account for the other 10% (Chandler et al., 2011). Yeast are also an important part of the microbiome. Similar to bacterial populations, the diversity of yeast is also limited, with a single genus making up 59% of the yeast species present (Chandler et al., 2012). In natural habitats, wild fruit flies feed on fruit that is broken down, or ‘fermented’, by bacteria and yeast, which are then ingested by the fruit fly, causing them to become part of the fly’s microbiome. This community of microbes has been shown to generate nutrients that are critical for larval development (Shin et al., 2011; Storelli et al., 2011; Broderick and Lemaitre, 2012). Now, in eLife, Yukako Hattori from Kyoto University and JST FOREST – including Ayumi Mure as first author – report how individual members of the microbiome associated with the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster contribute to larval development (Mure et al., 2023).
To identify which microbes are present during larval development, the team (who are based at various institutes in Japan) placed freshly peeled bananas near their homes to attract wild fruit flies to lay eggs on the food. They then collected samples from the bananas two and a half days (early-stage food) and four to five days (late-stage food) into the fermentation process. Mure et al. found that the yeast and bacterial species that dominated the food changed from the early- to late-stage (Figure 1A). Notably, this transition in dietary microbes occurred even when D. melanogaster larvae were not present, suggesting that the shift is likely caused by other factors such as interactions among the microbes.
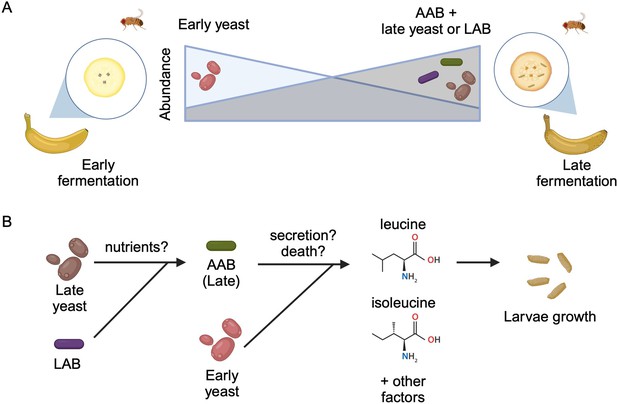
Interactions between diet, microbes, and flies.
(A) Fruit flies consume fermenting fruits containing various bacteria and yeast, which, as a result, become part of the fly’s microbiome. Early on during fermentation (left), a specific type of yeast dominates the food (early yeast). As fermentation progresses (right), the composition shifts, and the number of early yeast cells decreases while the number of acetic acid bacteria (AAB) increases, together with other species of yeast (late yeast) and/or lactic acid bacteria (LAB). (B) Both acetic acid bacteria (green) and the early yeast species (pink) support larvae growth by producing two branched-chain amino acids (leucine and isoleucine) and other, unknown factors. Initially, the early yeast cells provide these amino acids. As fermentation progresses, the rising number of lactic acid bacteria (purple) and late yeast cells (brown) increases the growth of acetic acid bacteria, which take over generating the amino acids and other factors the larvae need to grow. Exactly how these nutrients are provided is still unclear, but may involve active secretion by live cells or passive release through cell death.
Image credit: Figure created using BioRender.com.
Next, Mure et al. set out to determine which of the microbes they had identified were involved in larval development. Various species of bacteria and yeast were isolated from the fermented food, and added individually or in combination to a sterile culture medium that is prepared with bananas. Larvae that were free from microbes were then introduced to the cultures to see how ingestion of the different microbial species affected the rate and timing of pupariation, which is when larvae stop crawling and surround themselves with a pupal case before undergoing metamorphosis. Larvae fed on the yeast species that dominated early fermentation (Hanseniaspora uvarum) exhibited high rates of pupariation, whereas the yeast species from the late-stage (Pichia kluyveri and Starmerella bacillaris) were unable to effectively promote larval growth.
Mure et al. also observed high levels of pupariation when the acetic acid bacterium Acetobacter orientalis from late-stage food was provided in combination with yeast or lactic acid bacteria. Further experiments suggested that A. orientalis needs other microbes in order to grow to a high enough level to support larval development (Figure 1B). Indeed, Mure et al. found that larvae fed a daily dose of A. orientalis were able to effectively pupariate even in the absence of other microbes.
To further understand how yeast support larval growth, Mure et al. investigated how species from early- and late-stage food impact pupariation when they have been killed with heat, causing their nutrients and metabolites to leak out. Surprisingly, they found that yeast from the late-stage, which had previously not supported larval growth, could now promote development when introduced into the banana-like culture medium. This suggests that all of the studied yeast strains produce nutrients and metabolites that support larval growth, but those generated by the non-supportive yeast are less accessible to the larvae.
Analyzing the metabolites present in different yeasts revealed significantly higher levels of the branched-chain amino acids isoleucine and leucine in cultures of supportive species. Although supplementing the banana-like culture with these amino acids improved larval development, the larvae could still not fully grow into adulthood. This suggests that other unidentified nutrients provided by the supportive yeasts must be playing a role.
More studies identifying which microbes are responsible for certain biological effects will be fundamental to truly understand the impact microbial communities have on host health. Furthermore, this work highlights the complexity of interactions that occur between microbes from the diet and the host microbiome. In the future, knowledge created by these studies could be used to manipulate the composition of microbiomes for specific benefits, ranging from improving human health to altering the behavior of pollinating insects.
References
-
Gut-associated microbes of Drosophila melanogasterGut Microbes 3:307–321.https://doi.org/10.4161/gmic.19896
-
Yeast communities of diverse Drosophila species: comparison of two symbiont groups in the same hostsApplied and Environmental Microbiology 78:7327–7336.https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01741-12
Article and author information
Author details
Publication history
- Version of Record published: October 11, 2023 (version 1)
Copyright
© 2023, Ferreira and Antunes
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use and redistribution provided that the original author and source are credited.
Metrics
-
- 539
- views
-
- 61
- downloads
-
- 0
- citations
Views, downloads and citations are aggregated across all versions of this paper published by eLife.
Download links
Downloads (link to download the article as PDF)
Open citations (links to open the citations from this article in various online reference manager services)
Cite this article (links to download the citations from this article in formats compatible with various reference manager tools)
Further reading
-
- Developmental Biology
- Structural Biology and Molecular Biophysics
The receptor tyrosine kinase ROR2 mediates noncanonical WNT5A signaling to orchestrate tissue morphogenetic processes, and dysfunction of the pathway causes Robinow syndrome, Brachydactyly B and metastatic diseases. The domain(s) and mechanisms required for ROR2 function, however, remain unclear. We solved the crystal structure of the extracellular cysteine-rich (CRD) and Kringle (Kr) domains of ROR2 and found that, unlike other CRDs, the ROR2 CRD lacks the signature hydrophobic pocket that binds lipids/lipid-modified proteins, such as WNTs, suggesting a novel mechanism of ligand reception. Functionally, we showed that the ROR2 CRD, but not other domains, is required and minimally sufficient to promote WNT5A signaling, and Robinow mutations in the CRD and the adjacent Kr impair ROR2 secretion and function. Moreover, using function-activating and -perturbing antibodies against the Frizzled (FZ) family of WNT receptors, we demonstrate the involvement of FZ in WNT5A-ROR signaling. Thus, ROR2 acts via its CRD to potentiate the function of a receptor super-complex that includes FZ to transduce WNT5A signals.
-
- Developmental Biology
- Immunology and Inflammation
Cardiac macrophages are heterogenous in phenotype and functions, which has been associated with differences in their ontogeny. Despite extensive research, our understanding of the precise role of different subsets of macrophages in ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury remains incomplete. We here investigated macrophage lineages and ablated tissue macrophages in homeostasis and after I/R injury in a CSF1R-dependent manner. Genomic deletion of a fms-intronic regulatory element (FIRE) in the Csf1r locus resulted in specific absence of resident homeostatic and antigen-presenting macrophages, without affecting the recruitment of monocyte-derived macrophages to the infarcted heart. Specific absence of homeostatic, monocyte-independent macrophages altered the immune cell crosstalk in response to injury and induced proinflammatory neutrophil polarization, resulting in impaired cardiac remodeling without influencing infarct size. In contrast, continuous CSF1R inhibition led to depletion of both resident and recruited macrophage populations. This augmented adverse remodeling after I/R and led to an increased infarct size and deterioration of cardiac function. In summary, resident macrophages orchestrate inflammatory responses improving cardiac remodeling, while recruited macrophages determine infarct size after I/R injury. These findings attribute distinct beneficial effects to different macrophage populations in the context of myocardial infarction.






