Cancer: How does doxorubicin work?
Many clinically available drugs are used without a clear understanding of how they work. This is particularly true in oncology, where powerful cytotoxic drugs are given to patients despite the fact that we do not fully understand their mechanism of action. Even targeted therapies such as rapamycins and receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors are active in only a subset of the tumours for which they were originally developed, which has led to calls for better methods to identify tumours that will respond to specific drugs. This issue is even more pressing for conventional cytotoxic agents because, in addition to being toxic to cancer cells, they can also be toxic to healthy cells. Now, writing in eLife, Brey Denard, Ching Lee and Jin Ye provide evidence that doxorubicin, a widely used cancer drug, induces cellular toxicity via a novel mechanism that involves the synthesis of ceramide followed by activation of a transcription factor called CREB3L1 (Denard et al., 2012).
This is a story that began 40 years ago with the introduction of doxorubicin and daunorubicin into clinical practice. Both of these compounds belong to a class of drugs called anthracyclines that are derived from bacteria belonging to the genus Streptomyces. Extensive clinical studies have demonstrated that they are active against a wide variety of tumours (Minotti et al., 2004). However, despite this, the clinical use of anthracyclines has been limited because of a significant risk for cardiac damage. The chances of this life-threatening side effect depend on cumulative dosage, and can occur decades after exposure (Kremer et al., 2001). Over the years, many mechanisms of action have been proposed for these drugs—including topoisomerase II inhibition, DNA intercalation, and free radical generation—but there has until recently been a lack of definitive evidence for all three of these mechanisms (Gewirtz, 1999).
Denard, Lee and Ye, who are based at the University of Texas Southwestern (UTSW) Medical Center, propose that doxorubicin can combat tumours via a mechanism called regulated intramembrane proteolysis. In this process, a membrane-bound protein is cleaved, liberating a soluble messaging molecule that can play a role in a variety of cellular processes, including apoptosis, lipid metabolism and the response to viral infection (Lal and Caplan, 2011).
In previous work, the UTSW group showed that CREB3L1—a membrane protein with a carboxy-domain inside the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum, and an amino-terminal domain that is in the cytoplasm of the cell—undergoes proteolytic cleavage during viral infection to release the amino-terminal domain, which then translocates to the nucleus and drives the transcription of genes that inhibit cellular proliferation (Denard et al., 2011). In the present study, Denard, Lee and Ye extend these results by treating multiple cell lines with doxorubicin and showing that the drug produces lipid molecules called ceramides that trigger the cleavage of CREB3L1 (see Figure 1). This is again followed by translocation of the resulting amino-terminal fragment to the nucleus and the increased expression of several genes (Denard et al., 2012). Importantly, the down-regulation of CREB3L1 diminishes doxorubicin-induced effects on cell proliferation, whereas overexpression of CREB3L1 makes tumour cells more sensitive to doxorubicin. Collectively, these observations provide the first evidence for a model in which the anthracycline-induced synthesis of ceramides leads to the cleavage of CREB3L1, resulting in altered expression of genes that might contribute to the effect of the drug.
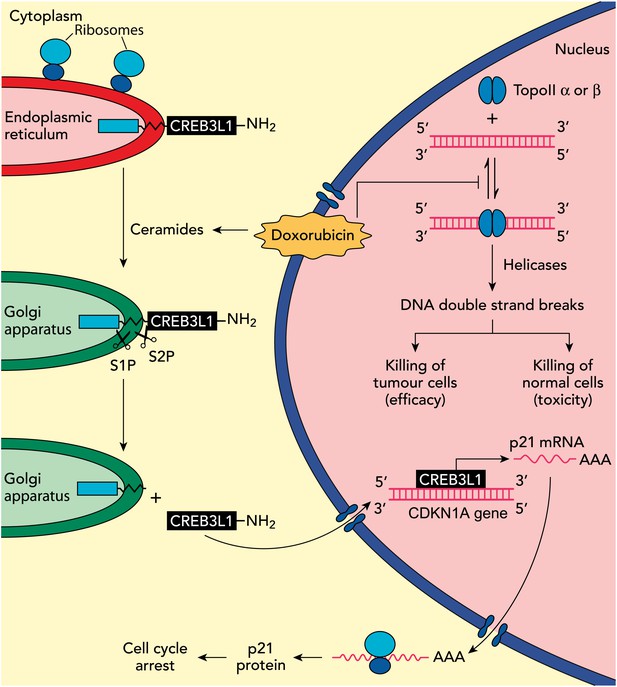
Understanding how the anticancer drug doxorubicin works is an important challenge in cancer research. Two independent groups have recently published evidence for two potential mechanisms that might be able to explain anti-tumour effects of doxorubicin. Zhang et al. showed diminished toxicity in cardiomyocytes from mice lacking the Top2b gene. These data are consistent with previous claims that doxorubicin helps to stabilize complexes containing double-stranded DNA and the enzyme topoisomerase II (top right of figure): this enzyme then cuts both of the DNA strands, which leads to the death of both normal cells (predominantly via topoisomerase IIβ) and in tumour cells that are susceptible to the drug (predominantly via topoisomerase IIα), thus accounting for both the toxicity and anti-tumour efficacy of doxorubicin. Denard et al. propose that doxorubicin increases the production of ceramides inside cells (top left), which leads to the latent transcription factor CREB3L1 translocating from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus. Two proteases (S1P and S2P) then cut the CREB3L1 protein; and its amino-terminal fragment then migrates into the nucleus, where it acts as a transcription factor to activate the CDNK1A locus and additional genes (bottom right). This leads to increased expression of the p21 protein along with other proteins that inhibit the proliferation of tumour cells.
While intriguing, these results represent only a first step in testing this model. In particular, as discussed by the authors, there are several open questions: Does ceramide alter CREB3L1 trafficking to the Golgi apparatus, where the intramembrane proteases are located? Does CDKN1A, one of the genes that is overexpressed when cells are treated with doxorubicin, have a critical role in the action of the drug? And does expression or activation of CREB3L1 correlate with doxorubicin sensitivity across a panel of cancer cell lines, such as the Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia (Barretina et al., 2012), or clinical specimens? In addition, it will be important to establish whether other chemo-therapeutic agents also induce proteolysis of CREB3L1 or other transmembrane proteins.
It will also be interesting to see whether the ideas put forward by the UTSW group can be integrated into existing models of doxorubicin action. Emerging data suggest that the enzyme topoisomerase IIβ has a critical role in the toxic effects of doxorubicin on cardiac tissue (see Figure 1), and it has been reported that the targeted deletion of the Top2b gene abolishes doxorubicin-induced effects on cardiac function (Zhang et al., 2012). By contrast, it has been suggested that the Top2a gene contributes to the anticancer effects of doxorubicin and other anthracyclines (Mao et al., 1999). This work, and also the work of the UTSW group, needs to be rigorously extended by studying in detail how doxorubicin kills cancer cells in appropriate cancer models and clinical samples.
The fact that doxorubicin remains the subject of intense study four decades after its introduction into the clinic is a reflection of its complex biology and its importance as a cancer drug. Hopefully, these recent studies will ultimately allow clinicians to better understand this important agent and to utilize it in a more targeted fashion.
References
-
Anthracycline-induced clinical heart failure in a cohort of 607 children: long-term follow-up studyJ Clin Oncol 19:191–196.
-
Regulated intramembrane proteolysis: signaling pathways and biological functionsPhysiology (Bethesda) 26:34–44.https://doi.org/10.1152/physiol.00028.2010
Article and author information
Author details
Publication history
- Version of Record published: December 18, 2012 (version 1)
Copyright
© 2012, Patel and Kaufmann
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use and redistribution provided that the original author and source are credited.
Metrics
-
- 8,469
- views
-
- 641
- downloads
-
- 70
- citations
Views, downloads and citations are aggregated across all versions of this paper published by eLife.
Download links
Downloads (link to download the article as PDF)
Open citations (links to open the citations from this article in various online reference manager services)
Cite this article (links to download the citations from this article in formats compatible with various reference manager tools)
Further reading
-
- Biochemistry and Chemical Biology
- Stem Cells and Regenerative Medicine
Molecules that facilitate targeted protein degradation (TPD) offer great promise as novel therapeutics. The human hepatic lectin asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGR) is selectively expressed on hepatocytes. We have previously engineered an anti-ASGR1 antibody-mutant RSPO2 (RSPO2RA) fusion protein (called SWEETS) to drive tissue-specific degradation of ZNRF3/RNF43 E3 ubiquitin ligases, which achieved hepatocyte-specific enhanced Wnt signaling, proliferation, and restored liver function in mouse models, and an antibody–RSPO2RA fusion molecule is currently in human clinical trials. In the current study, we identified two new ASGR1- and ASGR1/2-specific antibodies, 8M24 and 8G8. High-resolution crystal structures of ASGR1:8M24 and ASGR2:8G8 complexes revealed that these antibodies bind to distinct epitopes on opposing sides of ASGR, away from the substrate-binding site. Both antibodies enhanced Wnt activity when assembled as SWEETS molecules with RSPO2RA through specific effects sequestering E3 ligases. In addition, 8M24-RSPO2RA and 8G8-RSPO2RA efficiently downregulate ASGR1 through TPD mechanisms. These results demonstrate the possibility of combining different therapeutic effects and degradation mechanisms in a single molecule.
-
- Biochemistry and Chemical Biology
- Microbiology and Infectious Disease
Nonstructural protein 5 (Nsp5) is the main protease of SARS-CoV-2 that cleaves viral polyproteins into individual polypeptides necessary for viral replication. Here, we show that Nsp5 binds and cleaves human tRNA methyltransferase 1 (TRMT1), a host enzyme required for a prevalent post-transcriptional modification in tRNAs. Human cells infected with SARS-CoV-2 exhibit a decrease in TRMT1 protein levels and TRMT1-catalyzed tRNA modifications, consistent with TRMT1 cleavage and inactivation by Nsp5. Nsp5 cleaves TRMT1 at a specific position that matches the consensus sequence of SARS-CoV-2 polyprotein cleavage sites, and a single mutation within the sequence inhibits Nsp5-dependent proteolysis of TRMT1. The TRMT1 cleavage fragments exhibit altered RNA binding activity and are unable to rescue tRNA modification in TRMT1-deficient human cells. Compared to wild-type human cells, TRMT1-deficient human cells infected with SARS-CoV-2 exhibit reduced levels of intracellular viral RNA. These findings provide evidence that Nsp5-dependent cleavage of TRMT1 and perturbation of tRNA modification patterns contribute to the cellular pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.





