Published online Dec 29, 2022. doi: 10.5495/wjcid.v12.i3.76
Peer-review started: October 13, 2022
First decision: October 28, 2022
Revised: November 11, 2022
Accepted: December 7, 2022
Article in press: December 7, 2022
Published online: December 29, 2022
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) was first identified in Wuhan, China and then rapidly spread all over the world. The World Health Organization declared a pandemic on March 11, 2020 as a result of COVID-19. As it has caused substantial morbidity and mortality, most countries took several measures to control its spread, including India. As of now, India has witnessed three major waves of COVID-19. Several measures like nationwide lockdown, active case finding, con
Core Tip: Numerous steps were taken in response to the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic including nationwide lockdown, active case finding, contact tracing, screening, home isolation, transfer of patients to dedicated care centres, vaccination, and activities to generate disease awareness. Several challenges in the implementation of these steps at the grassroots level were overcome with the involvement of multiple governmental and private sectors. The grassroots workers were the backbone in the management of the pandemic in rural areas. Despite taking various steps to combat COVID-19, we may not have been able to prevent or control the waves of COVID-19.
- Citation: Chandra A. Steps taken to fight the COVID-19 pandemic at the grassroots level of rural India: Experience of a community physician. World J Clin Infect Dis 2022; 12(3): 76-84
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3176/full/v12/i3/76.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5495/wjcid.v12.i3.76
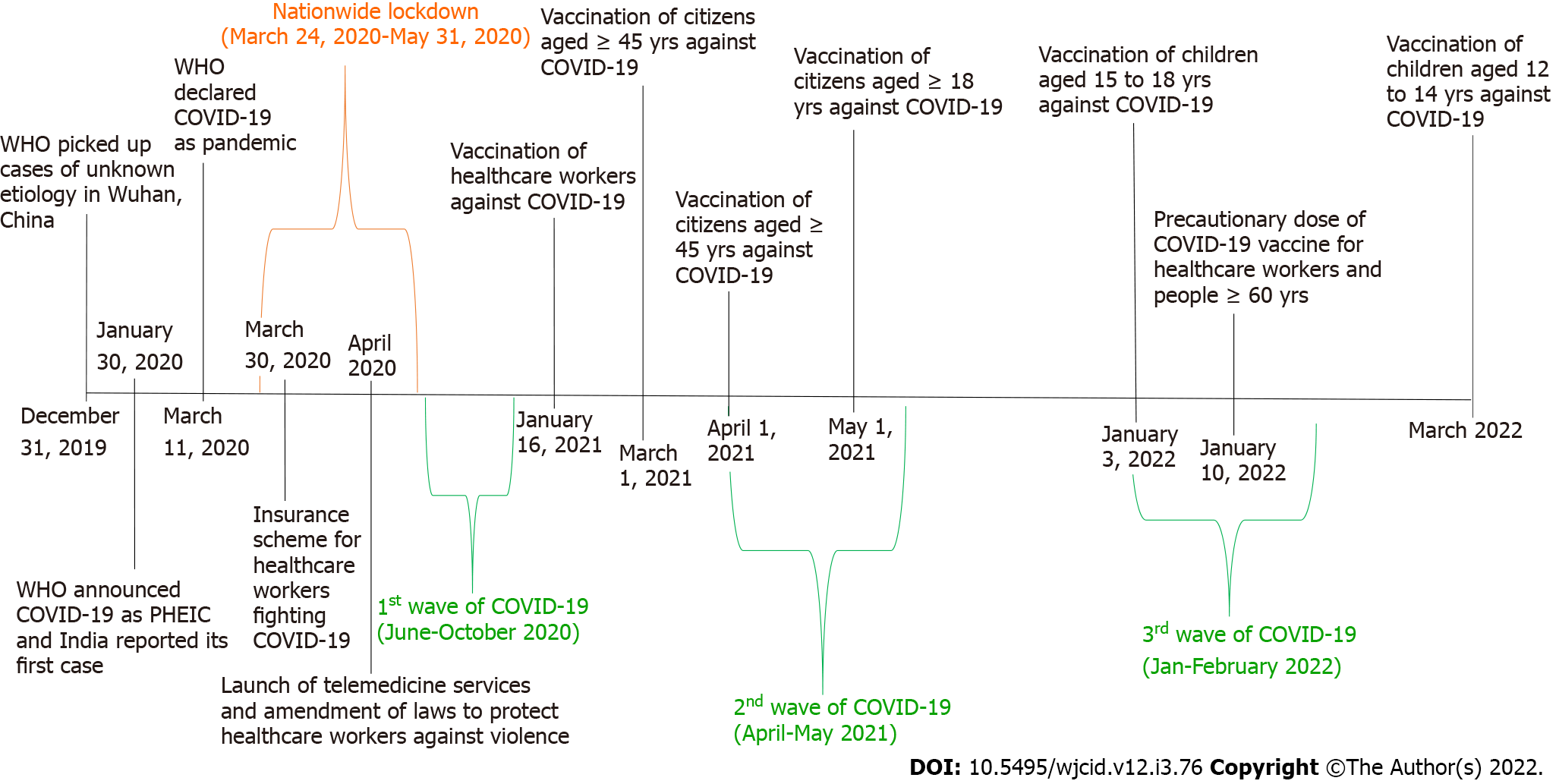
In December 2019, the World Health Organization learned of reports of a cluster of ‘viral pneumonia cases of unknown origin’ in Wuhan city, People’s Republic of China[1]. On January 30, 2020, the Director-General of the World Health Organization declared the outbreak of a novel coronavirus that was named 2019-nCoV at the time as a Public Health Emergency of International Concern[2]. On the same day in India, Kerala state’s Ministry of Health and Family Welfare reported the first case of 2019-nCoV from a student who had travelled from Wuhan city[3]. On March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization declared a pandemic as a result of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)[4]. On the same day, the Government of India requested state governments to invoke the ‘Epidemic Act 1897’ to address the COVID-19 emergency, and it was made a notifiable disease[5]. As of now, India has witnessed three major waves of COVID-19 in July to October 2020, April to May 2021, and January to February 2022[6]. India had a total of 44658365 COVID-19 positive cases and 530479 deaths (1%) through November 4, 2022[7].
The Indian health system in rural communities consists of a three-tier system with three levels of health care facilities: Primary level [includes sub-centres/health and wellness centres, and primary health centres (PHCs)]; secondary level (includes community health centres); and tertiary level (includes district hospital and medical colleges). During the period of the COVID-19 pandemic, I was posted as a postgraduate trainee at a PHC in a rural setting of Haryana state (India). The workforce at the PHC includes a medical officer-in-charge, staff nurses, lab technician, pharmacist, health supervisors, and supporting staff for sanitation and security. This PHC is affiliated with an academic institute. Therefore, it has undergraduate and postgraduate students posted for training purposes. Under this PHC there are 12 sub-centres. A subcentre is the most peripheral contact point and has a workforce of two multipurpose health workers [male multipurpose health worker (MPW) and female MPW]. Every village has Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHAs) who are honorary volunteers from the community and act as a link between the community and the healthcare system. This PHC caters to a population of around 50000 residing in the 17 villages and has 47 ASHAs. The medical officer’s role in COVID-19-related activities in a PHC were in planning and execution of active case detection and surveillance, contact tracing, monitoring/management of COVID-19-positive patients, and the vaccination program against COVID-19. I had the opportunity to closely see these steps taken and the challenges faced for the COVID-19 pandemic response at the grassroots level[8]. This article highlighted the issues faced along the journey and their outcomes.
In rapid response to the COVID-19 pandemic, one of the major steps that was taken by India was to implement a nationwide lockdown from March 24, 2020 to May 31, 2020[9]. This was prescribed by the National Disaster Management Authority of India in exercise of the powers under the Disaster Management Act of 2005[10]. It included travel restriction, shutting down educational institutes, offices, industries, shops, and places of worship, closure of hospitality, and restriction in gathering. The lockdown was released in a phased manner, starting on June 1, 2020[11]. Unlike the villages, a strict lockdown was enforced by the government in urban areas. The halt of public transport caused misery to many migrant daily wage workers who had come for crop harvesting and were stuck in rural Haryana. During the lockdown, most of the households had financial hardships as the economy in the rural setting is mostly informal and operates primarily with cash. Shops selling alcohol and tobacco were closed as they were non-essentials. People dependent on tobacco and alcohol had withdrawal symptoms and started purchasing them illegally. During the lockdown, we also saw an increase in the number of patients in primary health care due to the lockdown. PHCs attended many complicated cases, which were follow-up cases from tertiary health centres or that needed tertiary care.
During the pandemic, there was coordination with multiple sectors like the education department, police department, Ministry of women & child development, Ministry of Ayurveda, Yoga and Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha and Homeopathy, sanitation department, and local village council (panchayat). There was absolute cooperation and coordination between the government and private health sectors. The police department coordinated the execution of various plans like lockdown and cluster containment. The police department also extended its support in maintaining law and order during the conduction of community surveys, contact tracing, and isolation of patients. School and college teachers (from the education department) and Anganwadi workers (Ministry of women & child development) were also involved in conducting the active case-finding survey on COVID-19.
Due to the shortage of isolation facilities, a few of the schools and colleges were converted to COVID-19 care centres that were managed by medical officers. During the management of the COVID-19 pandemic, the traditional medicine system of India, which is Ayurveda, Yoga and Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha and Homeopathy, was also involved[12]. There was the distribution of ayurvedic medications in the community to boost immunity by the Ministry of Ayurveda, Yoga and Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha and Homeopathy. Yoga and Naturopathy were also promoted in the community for prevention and symptomatic management. Medical officers (Ayurveda) posted at the primary health care level worked in patient monitoring, contact tracing, and led the camps for COVID-19 testing and vaccination. For the first time, Ayurveda and Allopathy worked together at a mass level. Patients with influenza-like illness (ILI) also sought medical treatment from private labs, chemists, and non-government clinics. A list of these patients was maintained at these private facilities and was shared with the district administration to track and test these patients.
The community was involved in activities related to surveillance, restriction of movement, disinfection, and promoting COVID-19-appropriate behaviour. The community helped the administration by providing information related to any in-migration (travel from foreign regions) and cooperated during the symptomatic screening in the village. The village sarpanch (head of the locally elected village council) coordinated to prevent any public gathering in their village. To disinfect the public places in the villages, sodium hypochlorite solution was sprayed by workers of the panchayat (locally elected village council). Restrictions to enter the villages were made by the community to prevent virus spread. The people of the villages took the lead and guarded the entry and exit gates of their village. Occasionally free distribution of masks was led by community leaders and non-governmental organisations. We found that the people in the community preferred to wear a piece of cloth (household fabrics/ scarf/towel/handkerchief) around their faces over a surgical mask (procedure mask) or N95 mask. This could be due to the poor availability of masks (surgical or N95 masks) or due to the unaffordability[13,14]. This could also be due to the feeling of comfort in a piece of cloth, which can be easily recycled by washing[15]. In the community, mask hygiene and safe disposal of surgical masks and N95 mask was difficult[16].
Initially, the negative news in the media scared the community and increased the stigma against COVID-19. Diagnosis of COVID-19 was considered a death sentence. Community members tended to hide the ILI symptoms and would not show up for COVID-19 testing. Symptomatic people testing negative for rapid antigen test were advised to take an RTPCR test[17]. There were numerous revisions done to the testing strategy based on the evolution of testing facilities and community transmission of infection[18]. The uptake of RTPCR tests was limited due to distant government facilities to perform the test and the high cost of RTPCR in limited private facilities. Hence, the government has made the RTPCR sample collection facility available at the PHC to increase the uptake of the RTPCR test. Samples were collected at the PHC and were transferred to the tertiary centres equipped with facilities to run the test. The problems faced were the spillage or contamination of samples and delay in reporting results. There were several mass screening camps organised for COVID-19 testing in the villages. Medical mobile units were also deployed to reach the people in the villages, this was an example of delivering health through the principle of equity.
Microplanning was completed for the active case finding and a survey conducted by ASHAs, Anganwadi workers, MPWs, teachers, and volunteers from other departments. Large surveys were conducted in the villages where door-to-door screening for ILI symptoms or any history of recent travel to high-risk areas. If anyone was found positive for screening, then monitoring and testing for COVID-19 was done. For conducting these surveys several training sessions and planning were done. Contact tracing was another herculean task as it involves the enumeration of all the contacts of COVID-19-positive patients, monitoring of all the contacts for any development of symptoms and testing for COVID-19. It was challenging due to the stigma related to COVID-19 and higher social mixing in rural communities. We had to deal with all the queries and anxieties of the quarantined contacts. We had to convince them to be screened for COVID-19 and monitor them daily until the end of the quarantine period.
For the cluster of COVID-19 cases, there was the formation of a containment zone to avoid the spread of disease, which was accomplished by sealing the geographical area. In this area, daily house-to-house surveillance, contact tracing, monitoring of cases, and testing of symptomatic community members in the containment zone was done by the MPWs, ASHAs, and Anganwadi workers. This cluster containment strategy to break the chain of transmission was activated by the district administration through their chief medical officer and deputy commissioner[19].
In the first wave, patients who tested positive were transferred to isolation centres (dedicated COVID-19 care centres or hospitals) by a special ambulance, and their contacts were quarantined. All the ambulances posted at PHCs were called back to the district hospital and worked for the transportation of COVID-19 patients. They were made available through a district control room. Few people perceived the isolation in the centres as an impingement on their autonomy and liberty. There was a belief that the services and quality of these centres were subpar[20].
The household of a COVID-19-positive patient was labelled with a warning sticker, which created anxiety among the villagers. This was a tough situation for the members of the household because of the stigma towards them. After a while, this practice was withdrawn[21]. As the number of positive cases rose, the healthcare system was overburdened. Then, the concept of home isolation for mild cases was introduced. We formed a team and visited all the positive cases and distributed a home-based kit (containing a biomedical waste bag, masks, bleaching powder, vitamin C and paracetamol tablets, and a pamphlet with self-care guidelines). For COVID-19-related waste generated at the household of a COVID-19-positive patient, we tried to safely collect and dispose at our PHC through the arrangement made with the help of a sarpanch/caregiver/health staff.
Similarly, like many health programmes in India, ASHAs were given training and were actively involved in COVID-19-related activities like active case finding, contact tracing, surveillance, and patient monitoring. Later, ASHAs were provided with a pulse oximeter to monitor the home isolated patients.
In the villages, the panchayat took the lead in promulgating COVID-19-related messages. Efforts were made to raise general awareness about COVID-19 among the individuals visiting PHC through posters, pamphlet distribution, videos, and health talks. ASHAs and MPWs were trained to provide health education in the community during their field visits.
At the national and state level of health promotion, there were various strategies used for health promotion, which were used in other national health programmes too. Caller tunes were used, and messages were printed on daily use items like milk and curd packets. Awareness was created through television, newspapers, and radio. Help from the entertainment industry was also taken to create related music and videos. There was the use of designer masks and caps and placement of posters at public places (hospitals, traffic signals, and bus stops). Awareness was generated not only by the government but also by the non-government sector. Most mobile applications changed their icon to a facemask, which created a daily reminder for people to wear a facemask. There were websites and digital applications that provided COVID-19-related information, national and state toll-free helplines, and other various helplines were started on social platforms like Telegram, WhatsApp, and Facebook.
Reporting related to COVID-19 testing and the status of home isolation/quarantine was completed on a daily basis to several portals of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Indian Council of Medical Research, Integrated Disease Surveillance Programme and other portals. Several communications and daily reporting were done through WhatsApp and emails. As daily reporting was done in multiple online portals and to various authorities, there was a huge amount of work related to data entry and reporting. On April 13, 2020, the government of India rolled out ‘eSanjeevani OPD’ to provide telemedicine services to patients isolated/quarantined at home. Unfortunately, this had poor coverage[22], which could be due to low digital literacy.
There were numerous meetings and trainings conducted at various levels. With the concept of digital meetings, we did save some time. A technological solution for contact tracing and syndromic mapping like Araogya Setu mobile application was not useful in a rural setting where the digital literacy is quite low.
The launch of the covid vaccine intelligence network (Co-WIN) application for vaccination was laudable. This application serves the function of registration, scheduling an appointment at their nearest location, and generating a COVID-19 vaccination certificate. The data entry operator posted at PHC and MPWs in the field had to enter the detail of each vaccine beneficiary into this application. Through this application, authorities can monitor the real-time vaccine status, coverage of the vaccine, and immediate adverse effects reported by a health facility.
For the first time, several vaccines were developed against a single disease, and all of them were approved for emergency use in a short interval. India also developed and introduced its indigenous vaccine (Covaxin/BBV152) against COVID-19 in January 2021[23]. The majority of vaccinations were completed using Covishield and Covaxin vaccines. It was first given to healthcare workers from January 16, 2021 onwards. The vaccination was available for citizens who were aged ≥ 60 years and who were high risk from March 1, 2021 onwards. Other citizens were eligible for vaccination in phased manner (details in Figure 1)[24]. India became the first country to administer 1 billion doses of vaccine by the end of October 2021. This was done through conducting door-to-door vaccination (Har Ghar Dastak), mass vaccination camps/drives, and using the Co-WIN app. In the field, we did see vaccine hesitancy among the people. This hesitancy was reduced after the leaders and celebrities promoted the COVID-19 vaccination in our country. People also complied with vaccination against COVID-19 as it was made mandatory to produce vaccination certificates in several places for the purpose of travel, admission at events, and jobs.
In our healthcare centre, we started screening all patients for ILI symptoms and high temperature using an infrared thermometer. A separate flu clinic was started to segregate the patients with flu symptoms, and daily reporting was done to the district. We started daily disinfection of the PHC with sodium hypochlorite solution. This caused chemical damage to the furniture of the health facility. Initially, there was a shortage of personal protective equipment (PPE). As the lockdown ended, the supply of PPE improved. We ran 24 h emergency care services and routine services at the PHC using PPE. We trained all the healthcare workers on the utilisation PPE and its safe disposal. Female staff faced difficulty in maintaining menstrual hygiene during the prolonged use of PPE. COVID-19-related waste generated at the field/subcentre was brought back to the PHC for safe disposal.
At the grassroots level, we faced several challenges; some were managed and some were not. Initially many of the MPWs and ASHAs were hesitant to visit the households of any COVID-19-positive case. Many of the healthcare workers had comorbidities. The lead was taken by the medical officers and young healthcare workers in the field. Initially, to reduce the exposure we reduced the number of staff by half, and workdays were changed to alternate weeks. As the understanding of the disease improved, the involvement of the healthcare workers and the cooperation from the community increased. There were steps taken to protect all healthcare workers from COVID-19 such as the use of chemical prophylaxis (hydroxychloroquine tablets), PPE (gown, face shield, N95 mask, shoe cover, gloves, and head cover), and the introduction of the vaccines. Despite all these measures, the number of positive cases among healthcare workers rose substantially. This caused an acute shortage of staff. During this period, we learned task shifting and task sharing, which were done by training all the staff in COVID-19-related activities. Sometimes lab technicians and support staff were borrowed for a day from the neighbouring PHCs.
Later we trained our staff nurses in conducting rapid antigen tests and sample collection for RTPCR. The available trainees (students) at the PHC became involved in contact tracing and follow-up of home-isolated patients via telephone. Healthcare worker burnout and anxiety was real during the pandemic. To tackle this issue, a telephone helpline handled by a professional psychiatrist and psychologist was launched by the state government. This helpline also helped the staff, patients in isolation, and citizens to mitigate stress through online counselling. This was a commendable and well-appreciated initiative to provide psychosocial support. The government of India launched an insurance scheme for healthcare workers fighting COVID-19 (Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Package) to provide comprehensive personal accident coverage of INR 50 Lakh (USD 60446). The healthcare workers included community healthcare workers (ASHAs, MPWs), hospital staff (doctors, nurses, paramedics, technicians), and supporting staff of sanitation and helpers. This scheme was extended to private healthcare workers who may have been in direct contact or at risk of COVID-19[25].
After a few attacks of healthcare workers in India, there was the promulgation of an ordinance to amend the Epidemic Diseases Act of India, which was approved on April 22, 2020 to protect the health workers and property including their living/working premises against violence[26]. To boost the morale of healthcare workers, they received appreciation from the community, national leaders, and compliments from the media.
During community surveillance, we did receive a few false alarms raised by people. We started verifying the calls by the MPWs and ASHA. In a few areas, we did face some resistance to active case-finding surveys from the community. Help from the police and sarpanch were required to resolve the issues. Contact tracing and active case finding were highly resource-demanding activities, which were not useful in the later phase of the pandemic as community transmission had occurred. Despite knowing the fact that a substantial proportion of COVID-19 cases are asymptomatic[27], we continued the practice of symptomatic screening and contact tracing for a very long time. Moreover, the number of symptomatic cases during the peak of the COVID-19 wave were overwhelming for our healthcare workers to trace.
Home isolation also had its own challenges. In the villages, isolating a homemaker was a challenging task as women in villages are primarily involved in taking care of children and livestock. Isolating them for 1-2 wk was a major concern for their children and livestock, which are solely dependent on them. Furthermore, it was difficult to keep farmers away from their farmland because they needed to go to the field daily for irrigation and crop management. Thus, we asked for help from the village sarpanch, the patient’s neighbours, or relatives to provide food and basic needs to the dependents. Our MPWs also frequently visited the patient’s house to check on the dependent’s health. Not only that, but a daily phone call was made at the PHC to check the patient, and their family’s daily health status was updated over the phone. Home isolation was also challenging in cases where a patient did not have a caregiver, did not have a separate toilet in the house, had mental illness, or was experiencing homelessness. Hence, facility-based isolation was most suitable for these kinds of patients. Strict isolation was enforced by the head of the villages, police, and higher authorities as some of the quarantined patients and contacts were not following the isolation order.
We also found that a few patients provided the wrong address and mobile number during the COVID-19 testing, which caused problems in contact tracing later, if the result is positive. To tackle this, we started checking the address with a valid identity card at the time of testing. It was also found that COVID-19-positive patients were tested at multiple health facilities to get a negative report as soon as possible due to requirement to go back to work, double confirmation of diagnosis, a fear of COVID-19, and to confirm recovery. This also increased the burden on the healthcare system as their names were duplicated in the computer systems. Then, the government issued new guidelines stating that the retesting of COVID-19 was not required at the end of the isolation period. This solved the issue of multiple testing for COVID-19 and reduced the workload.
We faced a limitation of space at the PHC due to the creation of space for donning & doffing area for PPE as well as an isolated area for COVID-19 testing. Eventually, after a discussion with the higher authority, a separate COVID-19 testing booth was provided to overcome the limitation. With limited space, it was difficult to maintain physical distancing for the inpatient services and at the sites of COVID-19 testing and vaccination. We faced another challenge of training all the healthcare workers to use smartphones and various applications (like Co-WIN and WhatsApp), which were used for official communication/reporting, sharing the geo location, and vaccination details. For this, we conducted several training sessions for them at the PHC. In the initial period, there were various guidelines related to testing strategy, isolation and quarantine, clinical management of COVID-19, etc. issued by multiple institutions or organisations that created confusion among healthcare workers. Then there were national guidelines released, but all of these guidelines kept changing rapidly with advancing knowledge of the disease. We found it quite challenging to implement the newer guidelines in the community in a short period.
The above steps taken were to break the chain of transmission and to assess the extent of COVID-19 infection in the community. Frequent estimation of seropositivity was a crucial indicator[28]. In our rural setting of Haryana state, the seropositivity during April to May 2021 (the initial phase of vaccination against COVID-19) was 59.3%[29]. The seropositivity among vaccinated and unvaccinated groups during July-August 2021 was 65.4% and 57.8%, respectively[29]. When we look at the national level, the seropositivity in India during May-June 2020 was found to be 0.73%[30], and it increased exponentially to 20.7% in the first wave and to 69.2% during the second wave of COVID-19[31]. Even during the nationwide lockdown there was a substantial increase in the test positivity rate[32].
The major steps included nationwide lockdown and COVID-19 vaccination. The nationwide lockdown may have been effective in enhancing the preparation (procurement of resources and preparedness for logistics and health infrastructure) and capacity building. The collateral consequences of lockdown were seen in a few unpublished research studies that were conducted in our setting and found a significant reduction in the coverage of routine immunisation for children and a substantial reduction in the utilisation of maternal care services during the lockdown. It also affected the follow-up and medication adherence in patients with tuberculosis or non-communicable diseases. Vaccination against COVID-19 may have been effective in reducing the severity of the disease in an unexposed person. Currently, the evidence suggests a pressing need to revise this COVID-19 vaccination strategy in India[33]. In the race of the COVID-19 vaccination drive, the single best vaccine against COVID-19 was not selected. Acknowledging the effectiveness of natural immunity was not accomplished. The COVID-19 pandemic had a short-term positive effect on the environment[34] and was a boon for promoting digital platforms/interventions. Mass-level promotion of health and hygiene could have a direct or indirect effect for controlling other infectious diseases.
Despite taking various steps to combat COVID-19, we may have not been able to prevent or control the waves of COVID-19. COVID-19 exposed the weaker links of our healthcare system, which provides us with an opportunity to strengthen the rural healthcare system for the future. The subject of public health in India is dealt by the state, therefore there could be variations across the states of India. However, the strategy remained the same across the whole of India, which was a five-fold strategy of test-track-treat-vaccinate and COVID-19-appropriate behaviour. Perhaps a concurrent evaluation of each step/strategy would have provided better learning and understanding.
The COVID-19 pandemic affected all levels of healthcare. We witnessed the brink of the breakdown of the health system, especially during the second wave when there were shortages of medical oxygen and beds in hospitals. We faced several challenges but never stopped healthcare services and fieldwork. We saw a huge and active collaboration of multiple sectors to combat this disease. During the COVID-19 pandemic, we saw an approach involving an empowered community, and multisectoral coordination, which are said to be the pillars of primary health care. COVID-19 has taught numerous lessons to everyone.
Due to the selective focus on COVID-19-related activities, other routine healthcare services for maternal and child health and major illnesses like tuberculosis, and non-communicable diseases were affected. The pandemic affected physical health and other domains of health (psychosocial, spiritual). COVID-19 has also affected the education and financial system of our society. It does provide a picture of the extent a disease affects human life.
The current healthcare system of rural India was not adequate to contain the transmission of COVID-19 and was not able to manage the load of COVID-19 patients. There is a paramount need to strengthen the infrastructure, laboratory services, regional surveillance systems, medical care, and skilled workforce. Currently, the healthcare system in rural India is heavily dependent on grassroots workers like ASHAs and MPWs. During the pandemic, ASHAs played a pivotal role in the management COVID-19 pandemic in rural areas. Furthermore, improving the support and recognition of grassroots workers are needed.
I would like to thank my teachers and colleagues. I would like to express my gratitude to all the staff of the primary health centre and all the grassroots health workers.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Infectious diseases
Country/Territory of origin: India
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): D
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Cozma CT, Romania; Yusof NA, Malaysia S-Editor: Wang JJ L-Editor: Filipodia P-Editor: Wang JJ
| 1. | World Health Organization. Archived: WHO Timeline - COVID-19. [cited 15 September 2022]. Available from: https://www.who.int/zh/news/item/27-04-2020-who-timeline---covid-19. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 2. | World Health Organization. WHO Director-General’s statement on IHR Emergency Committee on Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV). [cited 15 September 2022]. Available from: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-statement-on-ihr-emergency-committee-on-novel-coronavirus. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 3. | Sharma A. India’s first coronavirus infection confirmed in Kerala. [cited 15 September 2022]. Available from: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/indias-first-coronavirus-infection-confirmed-in-kerala/article61638034.ece. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 4. | World Health Organization. WHO Director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19. [cited 15 September 2022]. Available from: https://vietnam.un.org/en/38806-who-director-generals-opening-remarks-media-briefing-covid-19. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 5. | Explained Desk. Explained: Govt invokes Epidemic Diseases Act, 1897 to fight coronavirus; what is it? [cited 15 September 2022]. Available from: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-what-is-the-epidemic-act-of-1897-govt-has-invoked-to-fight-coronavirus-6309925/. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 6. | Johns Hopkins University & Medicine. COVID-19 Dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU). [cited 15 September 2022]. Available from: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 7. | Worldmeter. Word/Counter/India, Coronavirus Cases, Death and Recovered. [cited 4 November 2022]. Available from: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/country/india/. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 8. | Ankit Suniyal vids. The COVID story - A battle with many lessons (from lockdown to unlock). [cited 15 September 2022]. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=94gDe9RI9DU. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 9. | Press Information Bureau, Government of India, Ministry of Home Affairs. Extension of Lockdown up to May 31, 2020. [cited 15 September 2022]. Available from: https://www.pib.gov.in/Pressreleaseshare.aspx?PRID=1624763. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 10. | Ministry of Home Affairs. Government of India issues Orders prescribing lockdown for containment of COVID-19 Epidemic in the country. [cited 15 September 2022]. Available from: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1607997. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 11. | Press Information Bureau, Government of India, Ministry of Home Affairs. New Guidelines to fight COVID-19 to be effective from 1st June 2020. [cited 15 September 2022]. Available from: https://pib.gov.in/Pressreleaseshare.aspx?PRID=1627965. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 12. | Government of India, Ministry of Ayush. Guidelines for AYUSH practioners for COVID-19. [cited 15 September 2022]. Available from: https://www.ayush.gov.in/ayush-guidelines.html. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 13. | LocalCircles. Despite COVID cases rising across the country, 95% Indians surveyed say mask and social distancing compliance is not happening in their city/district/area. [cited 15 September 2022]. Available from: https://www.localcircles.com/a/press/page/mask-and-social-distancing-covid-survey. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 14. | LocalCircles. As America rolls out “Masks for all”, 2 in 3 surveyed keen that India takes up a mission to get protective masks to every Indian. [cited 15 September 2022]. Available from: https://www.localcircles.com/a/press/page/protective-mask-for-all. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 15. | Taylor S, Asmundson GJG. Negative attitudes about facemasks during the COVID-19 pandemic: The dual importance of perceived ineffectiveness and psychological reactance. PLoS One. 2021;16:e0246317. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 156] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 113] [Article Influence: 37.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Sangkham S. Face mask and medical waste disposal during the novel COVID-19 pandemic in Asia. Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering. CSCEE. 2020;2:100052. [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 302] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 176] [Article Influence: 44.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Indian Council of Medical Research, Department of Health Research, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India. Advisory on Use of Rapid Antigen Detection Test for COVID-19. [cited 19 September 2022]. Available from: https://www.icmr.gov.in/pdf/covid/strategy/Advisory_for_rapid_antigen_test14062020.pdf. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 18. | Indian Council of Medical Research, Department of Health Research, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India. Advisory on Purposive Testing Strategy for COVID-19 in India (Version VII, dated 10th January 2022). [cited September 19 2022]. Available from: https://prsindia.org/files/covid19/notifications/Advisory_COVID_Testing_10012022.pdf. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 19. | Director Health Services, Haryana, Panchkula. Preparing cluster containment strategy in District for preparedness for COVIDl9 cases. [cited September 19 2022]. Available from: http://nhmharyana.gov.in/WriteReadData/userfiles/file/CoronaVirus/advisoryforwebsite1/03.03.2020%20Preparing%20Cluster%20Containment%20Strategy%20in%20District%20for%20Prepardness%20for%20COVID-19%20Cases.pdf. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 20. | Thacker T. Covid-19 spread: Poor conditions of quarantine facilities come into focus in India. [cited 19 September 2022]. Available from: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/politics-and-nation/poor-conditions-of-quarantine-facilities-come-into-focus/articleshow/74738682.cms. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 21. | Mishra A. Haryana government does away with the practice of marking houses of Covid-19 patients. [cited 19 September 2022]. Available from: http://www.hindustantimes.com/gurugram/haryana-government-does-away-with-the-practice-of-marking-houses-of-covid-19-patients/story-oUFzH3J9mUGr9TeP8f2FiL.html. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 22. | Press information Bureau. More than Half a Crore patients served by the National Telemedicine Service (eSanjeevani) during the COVID-19Pandemic. [cited 15 September 2022]. Available from: https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1718221. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 23. | Ella R, Reddy S, Blackwelder W, Potdar V, Yadav P, Sarangi V, Aileni VK, Kanungo S, Rai S, Reddy P, Verma S, Singh C, Redkar S, Mohapatra S, Pandey A, Ranganadin P, Gumashta R, Multani M, Mohammad S, Bhatt P, Kumari L, Sapkal G, Gupta N, Abraham P, Panda S, Prasad S, Bhargava B, Ella K, Vadrevu KM; COVAXIN Study Group. Efficacy, safety, and lot-to-lot immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (BBV152): interim results of a randomised, double-blind, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;398:2173-2184. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 189] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 196] [Article Influence: 65.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India. COVID-19 Vaccine FAQs. [cited 19 September 2022]. Available from: https://www.mohfw.gov.in/covid_vaccination/vaccination/index.html. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 25. | Press information Bureau. “Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Package: Insurance Scheme for Health Workers fighting COVID-19”, extended for a further period of 180 days. [cited 15 September 2022]. Available from: https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1817977. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 26. | Press information Bureau. Promulgation of an Ordinance to amend the Epidemic Diseases Act, 1897 in the light of the pandemic situation of COVID-19. [cited 15 September 2022]. Available from: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1617327. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 27. | Ma Q, Liu J, Liu Q, Kang L, Liu R, Jing W, Wu Y, Liu M. Global Percentage of Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infections Among the Tested Population and Individuals With Confirmed COVID-19 Diagnosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4:e2137257. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 170] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 238] [Article Influence: 79.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | World Health Organization. A Coordinated Global Research Roadmap. [cited 15 September 2022]. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/a-coordinated-global-research-roadmap. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 29. | Misra P, Kant S, Guleria R, Rai SK, Kishore S, Baidya S, Singh AK, Chinnakali P, Medigeshi, Guruprasad R, Chaturvedi PK, Joshi HS, Mandal S, Sangral M, Yadav K, Bairwa M, Haldar P, Kardam P, Patil S, Jha S. Serological prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibody among children and young age group (between 2 and 17 years) in India: An interim result from a large multicentric population-based seroepidemiological study. J Family Med Prim Care. 2022;11:2816-2823. [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 8] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Murhekar MV, Bhatnagar T, Selvaraju S, Rade K, Saravanakumar V, Vivian Thangaraj JW, Kumar MS, Shah N, Sabarinathan R, Turuk A, Anand PK, Asthana S, Balachandar R, Bangar SD, Bansal AK, Bhat J, Chakraborty D, Rangaraju C, Chopra V, Das D, Deb AK, Devi KR, Dwivedi GR, Salim Khan SM, Haq I, Laxmaiah A, Madhuka, Mahapatra A, Mitra A, Nirmala AR, Pagdhune A, Qurieshi MA, Ramarao T, Sahay S, Sharma YK, Shrinivasa MB, Shukla VK, Singh PK, Viramgami A, Wilson VC, Yadav R, Girish Kumar CP, Luke HE, Ranganathan UD, Babu S, Sekar K, Yadav PD, Sapkal GN, Das A, Das P, Dutta S, Hemalatha R, Kumar A, Narain K, Narasimhaiah S, Panda S, Pati S, Patil S, Sarkar K, Singh S, Kant R, Tripathy S, Toteja GS, Babu GR, Kant S, Muliyil JP, Pandey RM, Sarkar S, Singh SK, Zodpey S, Gangakhedkar RR, S Reddy DC, Bhargava B. Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection in India: Findings from the national serosurvey, May-June 2020. Indian J Med Res. 2020;152:48-60. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 155] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 135] [Article Influence: 33.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Jahan N, Brahma A, Kumar MS, Bagepally BS, Ponnaiah M, Bhatnagar T, Murhekar MV. Seroprevalence of IgG antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in India, March 2020 to August 2021: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Infect Dis. 2022;116:59-67. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 8] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Kharya P, Koparkar AR, Dixit AM, Joshi HS, Rath RS. Impact of Nonpharmacological Public Health Interventions on Epidemiological Parameters of COVID-19 Pandemic in India. Cureus. 2021;13:e15393. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Rai SK, Kant S, Jha S. Pressing need to revise the COVID-19 vaccination strategy in India. Indian J Prevent Social Med. 2022;53:165-167. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 34. | Soni P. Effects of COVID-19 lockdown phases in India: an atmospheric perspective. Environ Dev Sustain. 2021;23:12044-12055. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 45] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 23] [Article Influence: 7.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |