Abstract
Background
Patellar instability is a common problem in Down syndrome patients since their childhood. Several treatment have been proposed, but relapses are frequent and not all surgeries are suitable for growing patients. The aim of the present study is to evaluate the clinical and radiographic outcomes of a modified Roux-Goldthwait technique, for the management of patellar instability in children with Down syndrome at minimum 5-year followup.
Materials and Methods
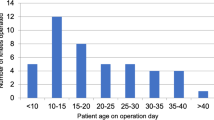
19 patients (23 knees) affected by Down syndrome surgically treated for patellar dislocation, between 2000 and 2012 were included in this study. The mean age of patients was 9.5 years (range 3.7 – 15 years) and had a Dugdale Grade III, I V, and V patellar dislocation. Trochlear groove dysplasia was present in 15 patients. Each patient was clinically evaluated considering relapse rate, pre- and postoperative range of motion (ROM), Kujala score, and modified Lysholm score. Radiographic examination was performed on standard X-ray considering patellar height, trochlear angle, and patellofemoral congruence angle.
Results
The mean followup was 134 months (range 62–206 months). No case of relapse of dislocation was registered with an improved ROM (significant for knee extension, P < 0.05). The Kujala score showed significant improvement from a mean preoperative value of 39 ± 6.3 to a mean postoperative value of 92.7 ± 3.4 (P < 0.05) at final followup such as the modified Lysholm score (from mean preoperative 55.6 ± 6.3 to mean postoperative of 94.2 ± 2.6). Radiographs performed at latest followup showed a tendency to normalization of all the parameters considered, with a restored patellofemoral congruence and trochlear groove shape and without signs of osteoarthritis.
Conclusion
The present study showed that the Roux-Goldthwait procedure is a valid surgical option for the treatment of patellar dislocation in children with Down syndrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Joo SY, Park KB, Kim BR, Park HW, Kim HW. The ‘four-in-one’ procedure for habitual dislocation of the patella in children: Early results in patients with severe generalised ligamentous laxity and aplasis of the trochlear groove. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2007;89:1645–9.
Vavken P, Wimmer MD, Camathias C, Quidde J, Valderrabano V, Pagenstert G, et al. Treating patella instability in skeletally immature patients. Arthroscopy 2013;29:1410–22.
Bettuzzi C, Lampasi M, Magnani M, Donzelli O. Surgical treatment of patellar dislocation in children with down syndrome: A 3- to 11-year followup study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2009;17:334–40.
Diamond LS, Lynne D, Sigman B. Orthopedic disorders in patients with down’s syndrome. Orthop Clin North Am 1981;12:57–71.
Benoit B, Laflamme GY, Laflamme GH, Rouleau D, Delisle J, Morin B, et al. Long term outcome of surgically-treated habitual patellar dislocation in children with coexistent patella alta. Minimum followup of 11 years. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2007;89:1172–7.
Dugdale TW, Renshaw TS. Instability of the patellofemoral joint in down syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1986;68:405–13.
Kujala UM, Jaakkola LH, Koskinen SK, Taimela S, Hurme M, Nelimarkka O, et al. Scoring of patellofemoral disorders. Arthroscopy 1993;9:159–63.
Tegner Y, Lysholm J. Rating systems in the evaluation of knee ligament injuries. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1985;198:43–9.
Thévenin-Lemoine C, Ferrand M, Courvoisier A, Damsin JP, Ducou le Pointe H, Vialle R, et al. Is the caton-deschamps index a valuable ratio to investigate patellar height in children? J Bone Joint Surg Am 2011;93:e35.
Merchant AC, Mercer RL, Jacobsen RH, Cool CR. Roentgenographic analysis of patellofemoral congruence. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1974;56:1391–6.
Rebouças Moreira TA, Demange MK, Gobbi RG, Mustacchi Z, Pécora JR, Passarelli Tírico LE, et al. Trochlear dysplasia and patellar instability in patients with down syndrome. Rev Bras Ortop 2015;50:159–63.
Fondren FB, Goldner JL, Bassett FH 3rd. Recurrent dislocation of the patella treated by the modified roux-goldthwait procedure. A prospective study of forty-seven knees. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1985;67:993–1005.
Grannatt K, Heyworth BE, Ogunwole O, Micheli LJ, Kocher MS. Galeazzi semitendinosus tenodesis for patellofemoral instability in skeletally immature patients. J Pediatr Orthop 2012;32:621–5.
Savarese E, Bisicchia S, Carotenuto F, Ippolito E. A technique for treating patello-femoral instability in immature patients: The tibial tubercle periosteum transfer. Musculoskelet Surg 2011;95:89–94.
Zhao J, Huangfu X, He Y, Liu W. Recurrent patellar dislocation in adolescents: Medial retinaculum plication versus vastus medialis plasty. Am J Sports Med 2012;40:123–32.
Palmu S, Kallio PE, Donell ST, Helenius I, Nietosvaara Y. Acute patellar dislocation in children and adolescents: A randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2008;90:463–70.
Kocon H, Kabacyj M, Zgoda M. The results of the operative treatment of patellar instability in children with Down’s syndrome. J Pediatr Orthop B 2012;21:407–10.
Saccomanno MF, Sircana G, Fodale M, Donati F, Milano G. Surgical versus conservative treatment of primary patellar dislocation. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Orthop 2016;40:2277–87.
Sever R, Fishkin M, Hemo Y, Wientroub S, Yaniv M. Surgical treatment of congenital and obligatory dislocation of the patella in children. J Pediatr Orthop 2017;Mar 21. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000000973 [Epub ahead of print]
Deie M, Ochi M, Sumen Y, Yasumoto M, Kobayashi K, Kimura H, et al. Reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament for the treatment of habitual or recurrent dislocation of the patella in children. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2003;85:887–90.
Ronga M, Oliva F, Longo UG, Testa V, Capasso G, Maffulli N, et al. Isolated medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction for recurrent patellar dislocation. Am J Sports Med 2009;37:1735–42.
Lind M, Enderlein D, Nielsen T, Christiansen SE, Faunø P. Clinical outcome after reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament in paediatric patients with recurrent patella instability. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2016;24:666–71.
Petershofer A, Fingernagel T, Trieb K. Patellofemoral instability in trisomy 21: MPFL-reconstruction as a single procedure. Orthopade 2015;44:643–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruzzini, L., Donati, F., Russo, R. et al. Modified Roux-Goldthwait Procedure for Management of Patellar Dislocation in Skeletally Immature Patients with Down Syndrome. JOIO 53, 122–127 (2019). https://doi.org/10.4103/ortho.IJOrtho_505_17
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/ortho.IJOrtho_505_17