Abstract
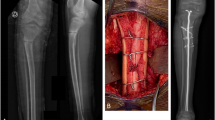
Background: Children with osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) can suffer from frequent fractures and limb deformities, resulting in impaired ambulation. Osteopenia and thin cortices complicate orthopedic treatment in this group. This study evaluates the clinical results of a bone splint technique for the treatment of lower limb deformities in children with type I OI. The technique consists of internal plating combined with cortical strut allograft fixation.
Materials and Methods: We prospectively followed nine children (five boys, four girls) with lower limb deformities due to type I Ol, who had been treated with the bone splint technique (11 femurs, fourtibias) between 2003 and 2006. The fracture healing time, deformity improvement, ambulation ability and complications were recorded to evaluate treatment effects.
Results: At the time of surgery the average age in our study was 7.7 years (range 5–12 years). The average length of followup was 69 months (range 60–84 months). All patients had good fracture healing with an average healing time of 14 weeks (range 12–16 weeks) and none experienced further fractures, deformity, or nonunion. The fixation remained stable throughout the procedure in all cases, with no evidence of loosening or breakage of screws and the deformity and mobility significantly improved after surgery. Of the two children confined to bed before surgery, one was able to walk on crutches and the other needed a wheelchair. The other seven patients could walk without walking aids or support like crutches.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that the bone splint technique provides good mechanical support and increases the bone mass. It is an effective treatment for children with Ol and lower limb deformities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alanay Y, Avaygan H, Camacho N, Utine GE, Boduroglu K, Aktas D, et al. Mutations in the gene encoding the RER protein FKBP65 cause autosomal-recessive osteogenesis imperfecta. Am J Hum Genet 2010;86:551–9.
Stynowick GA, Tobias JD. Perioperative care of the patient with osteogenesis imperfecta. Orthopedics 2007;30:1043–9.
Enright WJ, Noonan KJ. Bone plating in patients with type III osteogenesis imperfecta: Results and complications. Iowa Orthop J 2006;26:37–40.
Luhmann SJ, Sheridan JJ, Capelli AM, Schoenecker PL. Management of lower-extremity deformities in osteogenesis imperfecta with extensible intramedullary rod technique: A 20-year experience. J Pediatr Orthop 1998;18:88–94.
Gamble JG, Strudwick WJ, Rinsky LA, Bleck EE. Complications of intramedullary rods in osteogenesis imperfecta: Bailey-Dubow rods versus nonelongating rods. J Pediatr Orthop 1988;8:645–9.
Nicolaou N, Bowe JD, Wilkinson JM, Fernandes JA, Bell MJ. Use of the Sheffield telescopic intramedullary rod system for the management of osteogenesis imperfecta: Clinical outcomes at an average followup of nineteen years. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2011;93:1994–2000.
Barden B, Fitzek JG, Huttegger C, Loer F. Supportive strut grafts for diaphyseal bone defects in revision hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2001;387:148–55.
Emerson RH Jr, Malinin TI, Cuellar AD, Head WC, Peters PC. Cortical strut allografts in the reconstruction of the femur in revision total hip arthroplasty. A basic science and clinical study. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1992;285:35–44.
Springer BD, Berry DJ, Lewallen DG. Treatment of periprosthetic femoral fractures following total hip arthroplasty wth femoral component revision. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2003;85:2156–62.
Wang JW, Weng LH. Treatment of distal femoral nonunion with internal fixation, cortical allograft struts and autogenous bone-grafting. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2003;85:436–40.
Donati D, Di Liddo M, Zavatta M, Manfrini M, Bacci G, Picci P, et al. Massive bone allograft reconstruction in high-grade osteosarcoma. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2000;377:186–94.
Sillence DO, Senn A, Danks DM. Genetic heterogeneity in osteogenesis imperfecta. J Med Genet 1979;16:101–16.
Glorieux FH, Bishop NJ, Plotkin H, Chabot G, Lanoue G, Travers R. Cyclic administration of pamidronate in children with severe osteogenesis imperfecta. N Engl J Med 1998;339:947–52.
Abulsaad M, Abdelrahman A. Modified Sofield-Millar operation: Less invasive surgery of lower limbs in osteogenesis imperfecta. Int Orthop 2009;33:527–32.
Zeitlin L, Fassier F, Glorieux FH. Modern approach to children with osteogenesis imperfecta. J Pediatr Orthop B 2003;12:77–87.
Saldanha KA, Saleh M, Bell MJ, Fernandes JA. Limb lengthening and correction of deformity in the lower limbs of children with osteogenesis imperfecta. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2004;86:259–65.
Joseph B, Rebello G, BCK. The choice of intramedullary devices for the femur and the tibia in osteogenesis imperfecta. J Pediatr Orthop B 2005;14:311–9.
Kaur S, Kulkarni KP, Kochar IS, Narasimhan R. Management of lower limb deformities in children with osteogenesis imperfecta. Indian Pediatr 2011;48:637–9.
Cho TJ, Kim JB, Lee JW, Lee K, Park MS, Yoo WJ, et al. Fracture in long bones stabilised by telescopic intramedullary rods in patients with osteogenesis imperfecta. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2011;93:634–8.
Cho TJ, Choi IH, Chung CY, Yoo WJ, Lee KS, Lee DY. Interlocking telescopic rod for patients with osteogenesis imperfecta. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2007;89:1028–35.
Yoneda M, Terai H, Imai Y, Okada T, Nozaki K, Inoue H, et al. Repair of an intercalated long bone defect with a synthetic biodegradable bone-inducing implant. Biomaterials 2005;26:5145–52.
Head WC, Malinin TI. Results of onlay allografts. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2000;371:108–12.
Poyrazoglu S, Gunoz H, Darendeliler F, Bas F, Tutunculer F, Eryilmaz SK, et al. Successful results of pamidronate treatment in children with osteogenesis imperfecta with emphasis on the interpretation of bone mineral density for local standards. J Pediatr Orthop 2008;28:483–7.
El-Sobky MA, Hanna AA, Basha NE, Tarraf YN, Said MH. Surgery versus surgery plus pamidronate in the management of osteogenesis imperfecta patients: A comparative study. J Pediatr Orthop B 2006;15:222–8.
Astrom E, Magnusson P, Eksborg S, Soderhall S. Biochemical bone markers in the assessment and pamidronate treatment of children and adolescents with osteogenesis imperfecta. Acta Paediatr 2010;99:1834–40.
Lowing K, Astrom E, Oscarsson KA, Soderhall S, Eliasson AC. Effect of intravenous pamidronate therapy on everyday activities in children with osteogenesis imperfecta. Acta Paediatr 2007;96:1180–3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, D., Zhai, W., Lian, K. et al. Results of a bone splint technique for the treatment of lower limb deformities in children with type I osteogenesis imperfecta. IJOO 47, 377–381 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.114922
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.114922