Abstract
Background
Development of biosimilars requires physicochemical and biologic characterization to show comparability with a reference product. Zarzio® (filgrastim) is a biosimilar recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) that has been approved in the EU using Neupogen® as its reference product.
Objective
The aim of this study was to compare the drug identity, purity, and bioactivity of Zarzio® (300 and 480μg/0.5mL solution) with Neupogen®, using a broad range of standard and advanced analytical methods.
Methods
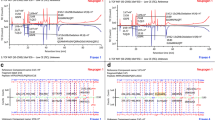
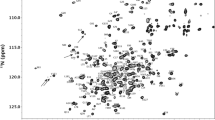
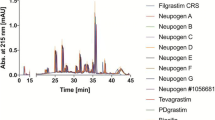
Peptide mapping with UV detection and mass determination, circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography electrospray ionization (LC-ESI) mass spectrometry were among the analyses used to compare primary and higher-order protein structure. Cation-exchange chromatography (CEX) and reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) were used to compare polarity and charge. Biologic characterization included comparison of G-CSF receptor binding affinity by surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy, an in vitro cell proliferation assay, and Western blot immunologic binding.
Results
The primary structures of Zarzio® and Neupogen® were shown to be identical by peptide mapping and other tests. CD and NMR spectroscopy demonstrated that the two products have comparable secondary and tertiary structures. RP-HPLC and other methods showed that the products have similar purity profiles. Comparable affinity with the G-CSF receptor GCSFR/CD114 was obtained using surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy, and comparable in vitro bioactivity was shown in a cell proliferation assay.
Conclusion
These results show the physicochemical and biologic comparability of Zarzio® and its reference product, Neupogen®.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kelly C, Mir F. Economics of biological therapies. BMJ 2009; 339: b3276
Roger SD. Biosimilars: how similar or dissimilar are they? Nephrology 2006; 11: 341–6
Schellekens H. Biosimilar therapeutics: what do we need to consider? NDT Plus 2009; 2Suppl. 1: i27–36
Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Medicines Agency. Guideline on similar biological medicinal products [CHMP/437/04]. London: European Medicines Agency, 2005 Oct 30 [online]. Available from URL: http://www.emea.europa.eu/pdfs/human/biosimilar/043704en.pdf [Accessed 2009 Oct 8]
Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Medicines Agency. Guideline on similar biological medicinal products containing biotechnology-derived proteins as active substance: quality issues [EMEA/CHMP/BWP/49348/2005]. London: European Medicines Agency, 2006 Feb 22 [online]. Available from URL: http://www.emea.europa.eu/pdfs/human/biosimilar/4934805en.pdf [Accessed 2009 Oct 8]
Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Medicines Agency. Annex to guideline on similar biological medicinal products containing biotechnology-derived proteins as active substance: non-clinical and clinical issues. Guidance on similar medicinal products containing recombinant granulocyte-colony stimulating factor [EMEA/CHMP/BMWP/31329/2005]. London: European Medicines Agency, 2006 Feb 22 [online]. Available from URL: http://www.emea.europa.eu/pdfs/human/biosimilar/3132905en.pdf [Accessed 2009 Oct 8]
Chirino AJ, Mire-Sluis A. Characterizing biological products and assessing comparability following manufacturing changes. Nat Biotechnol 2004; 22: 1383–91
Brockmeyer C, Seidl A. Binocrit: assessment of quality, safety and efficacy of biopharmaceuticals. EJHP Practice 2009; 15: 34–40
Filgrastim concentrated solution [monograph no. 07/2010:2206]. In: European Pharmacopoeia. 6th ed. Suppl. 6.8. Strasbourg: European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & HealthCare (EDQM), 2010
Locatelli F, Del Vecchio L, Pozzoni P. Pure red-cell aplasia “epidemic”: mystery completely revealed? Perit Dial Int 2007; 27Suppl. 2: S303–7
Gascon P, Fuhr U, Sörgel F, et al. Development of a new G-CSF product based on biosimilarity assessment. Ann Oncol 2010 Jul; 21(7): 1419–29
Acknowledgments
All analyses were funded by Sandoz. Study design, management, analysis, and interpretation of analytical data were done by the authors and other Sandoz personnel. Fritz Sörgel has conducted analytical and clinical research as a consultant funded by Sandoz. Helmut Lerch and Thomas Lauber are employees of Sandoz. Medical writing support was provided by Andy Bond of Spirit Medical Communications Ltd, supported by Sandoz.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sörgel, F., Lerch, H. & Lauber, T. Physicochemical and Biologic Comparability of a Biosimilar Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor with its Reference Product. BioDrugs 24, 347–357 (2010). https://doi.org/10.2165/11585100-000000000-00000
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/11585100-000000000-00000