Abstract
Polyphenon E 10% ointment, which contains a mixture of green tea catechins, is indicated for the treatment of external genital and perianal warts (Condylomata acuminata) in immunocompetent patients aged ≥18 years.
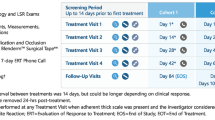
In two double-blind, multinational studies in adults with external genital and perianal warts, polyphenon E 10% ointment for up to 16 weeks was significantly more effective than vehicle with regard to the complete clearance of all warts (i.e. those at baseline and newly appearing during treatment) [primary endpoint]. In gender subgroup analyses, polyphenon E 10% ointment was more effective than vehicle in both men and women in one of two individual studies, and in pooled data from both studies.
Polyphenon E 10% ointment was also significantly more effective than vehicle with regard to several secondary endpoints, including the complete clearance of baseline warts and partial clearance of at least 50% of all warts in both studies.
Rates of recurrence of any warts or development of new warts were low (<9%) in both treatment arms during a 12-week follow-up period in both studies.
Polyphenon E 10% ointment was generally well tolerated in adults with external genital and perianal warts. According to pooled data from the two clinical studies, the majority of adverse events associated with polyphenon E 10% ointment involved application site and local skin reactions at the treatment site.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meltzer SM, Monk BJ, Tewari KS. Green tea catechins for treatment of external genital warts. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2009; 200 (3): 233.e1–7
Huh WK. HPV and management of external genital warts: an update. Contemporary Ob Gyn 2008; (Suppl Nov): 1–11
Health Protection Agency. Infection reports. Health Protection Report 2011 Apr 28; 5 (17): 1–13
Cox JT, Huh W, Mayeaux Jr EJ, et al. Management of external genital and perianal warts (EGW): proceedings of an Expert Panel Meeting. OBG Management The Female Patient 2011 Dec; Suppl.: 1–12
Beutner KR, Reitano MV, Richwald GA, et al. External genital warts: report of the American Medical Association Consensus Conference. AMA Expert Panel on External Genital Warts. Clin Infect Dis 1998 Oct; 27 (4): 796–806
Wagstaff AJ, Perry CM. Topical imiquimod: a review of its use in the management of anogenital warts, actinic keratoses, basal cell carcinoma and other skin lesions. Drugs 2007; 67 (15): 2187–210
Veregen 10% ointment: summary of product characteristics. Martinsried: MediGene AG, 2011
MediGene. MediGene: Veregen® marketing approval process initiated for 17 additional European countries [online]. Available from URL: http://www.medigene.com/ [Accessed 2011 Feb 23]
MediGene. Medigene’s drug Veregen® obtains market approval in Switzerland [online]. Available from URL: http://www.medigene.com/presse-investoren/news/pressemitteilungen/medigenes-drug-veregen-obtains-market-approvalin-switzerl [Accessed 2012 Apr 10]
Bradley Pharmaceuticals Inc. Veregen® (sinecatechins) ointment 15% [online]. Available from URL: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2008/021902s017lbl.pdf [Accessed 2012 Feb 14]
Tyring SK. Sinecatechins: effects on HPV-induced enzymes involved in inflammatory mediator generation. J Clin Aesthetic Dermatol 2012 Jan; 5 (1): 19–26
Tyring SK. Effect of sinecatechins on HPV-activated cell growth and induction of apoptosis. J Clin Aesthetic Dermatol 2012 Feb; 5 (2): 34–41
Stockfleth E, Beti H, Orasan R, et al. Topical polyphenon® E in the treatment of external genital and perianal warts: a randomized controlled trial. Br J Dermatol 2008; 158 (6): 1329–38
Tatti S, Swinehart JM, Thielert C, et al. Sinecatechins, a defined green tea extract, in the treatment of external anogenital warts: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2008; 111 (6): 1371–9
Tatti S, Stockfleth E, Beutner KR, et al. Polyphenon E®: a new treatment for external anogenital warts. Br J Dermatol 2010; 162 (1): 176–84
MediGene. Data on file. 2012
MediGene. Medigene: Veregen® receives positive decision on marketing approval for 17 additional European countries [online]. Available from URL: http://www.medigene.com/presse-investoren/news/pressemitteilungen/medigene-veregen-receives-positive-decision-on-marketing-a [Accessed 2012 Apr 10]
Acknowledgments and Disclosures
The manuscript was reviewed by: T. Cai, Department of Urology, University of Florence, Florence, Italy; M.A. Stanley, Department of Pathology, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK.
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding. During the peer review process, the manufacturer of the agent under review was offered an opportunity to comment on this article. Changes resulting from comments received were made by the author on the basis of scientific and editorial merit.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoy, S.M. Polyphenon E 10% Ointment. Am J Clin Dermatol 13, 275–281 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2165/11209370-000000000-00000
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/11209370-000000000-00000