Summary
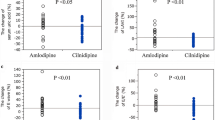
The new calcium antagonist felodipine with a pronounced arteriolar dilating capacity was used to treat 11 patients with severe hypertension resistant to treatment (4 with essential hypertension, 5 with renoparechymatous hypertension, 2 with renovascular hypertension). Mean glomerular filtration rate for 10 patients was 34 ± 27 ml/min/1.73m2 body surface area (51Cr- EDTA clearance) before felodipine. One patient was on haemodialysis treatment. Mean arterial blood pressure in the outpatient clinic was 206 ± 39/ 119 ± 18mm Hg in spite of treatment with 3 or more antihypertensive drugs. All but 2 patients had been given an angiotensin converting- enzyme inhibitor without success. All vasodilating agents were discontinued and the following morning 5 to 10mg felodipine was given orally. This resulted in a reduction of average supine blood pressure from 190/ 110mm Hg to 150/90mm Hg during the first hour. The antihypertensive effect was unchanged during 6 hours and the drug was subsequently administered twice or three times a day. Mean systolic and diastolic blood pressure after 1 month was 155 ± 19/91 ± 12mm Hg. Eight patients showed a favourable long term response with a mean systolic and diastolic blood pressure of 154 ± 17/89 ± 6mm Hg after 6 months. One patient died from his underlying disease after 2 months and 1 patient discontinued treatment because of ankle oedema after 6 weeks. In the long term treated patients with glomerular filtration rates > 15 ml/min/1.73m2 all but 1 showed an improved renal function by 26 ± 19% (n = 5) after initiation of felodipine therapy. In 2 cases with very low glomerular filtration rate (6 to 7 ml/min/1.73m2) the deterioration of renal function continued after felodipine, but at a slower rate.
It is concluded that felodipine decreased blood pressure dramatically in patients with severe hypertension where a majority of the cases had been resistant to a previous therapy. The drug appeared safe also in advanced renal insufficiency.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson, O.; Granérus, G. and Hedner, T.: Felodipine: A calcium-inhibiting vasodilator in refractory hypertension. Drugs 29 (Suppl. 2): 102–108 (1985).
Bröchner-Mortensen, J.: A simple method for determination of glomerular filtration rate. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation 30: 271–274 (1972).
Bühler, F.R. and Hulthen, L.: Calcium channel blockers: A pathophysiologically based antihypertensive treatment concept for the future. European Journal of Clinical Investigation 12: 1–3 (1982).
Edgar, B.; Elmfeldt, D.; Jonsson, G.; Lundborg, P.; Nyberg, G.; Raner, S. and Rönn, O.: Diuretic-natriuretic properties of single doses of felodipine in man. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 17: 191–192 (1984).
Erne, P.; Bürgisser, E.; Bolli, P. and Bühler, F.: Free calcium concentration in platelets closely related to blood pressure in normal and essential hypertensive subjects. New England Journal of Medicine 310: 1084–1088(1984).
Garthoff, B.; Kazda, S.; Knorr, A. and Günther, T.: Factors involved in the antihypertensive action of calcium antagonists. Hypertension 5 (Suppl.): 34–38 (1983).
Hulsemann, J.L.; Wilcox, C.S.; McKenzie, D.E. and Sterzel, R.B.: Antihypertensive and natriuretic effect of nitrendipine in rats with chronic infusion of angiotensin II. IXth International Congress of Nephrology, Los Angeles (1984).
Klütsch, K.; Schmidt, P. and Grosswenot, J.: Der Einfluss von BAY a 1040 auf die Nierenfunktion des Hypertonikers. Arzneimittel-Forschung 22: 377–380 (1972).
Lederballe Pedersen, O.: Calcium blockade in arterial hypertension. Hypertension 5 (Suppl.): 74–79 (1983).
Leonetti, G.; Fruscio, M.; Terzoli, L.; Rupoli, L.; Gradnik, R.; Sampieri, L.; Cuspidi, C.; Boselli, L.; Bolla, G. and Zanchetti, A.: Antihypertensive and water and sodium balance effects of felodipine, a new vasodilating calcium antagonist, in hypertensive patients. Drugs 29 (Suppl. 2): 185–191 (1985).
Nordlander, M.; DiBona, G.; Ljung, B.; Yao, T. and Thorén, P.: Renal and cardiovascular effects of acute and chronic administration of felodipine to SHR. European Journal of Pharmacology (In press 1985).
Raemsch, K.D. and Sommer, J.: Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of nitrendipine. Hypertension 5 (Suppl.): 18–24 (1983).
Stornello, M; Di Rao, G.; Iachello, M.; Pisani, R.; Scapellato, L.; Pedrinelli, R. and Satvetti, A.: Hemodynamic and humoral interactions between captopril and nifedipine. Hypertension 5 (Suppl.): 154–156 (1983).
Zidek, W.; Vetter, H.; Darst, K.G.; Zumkley, H. and Losse, H.: Intracellular Na+ and Ca2+ activities in essential hypertension. Clinical Science 63: 41–43 (1982).
Vierhapper, H. and Waldhäusl, W.: Reduced pressor effect of angiotensin II and of noradrenaline in normal man following the oral administration of the calcium-antagonist nifedipine. European Journal of Clinical Medicine 12: 263–267 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herlitz, H., Aurell, M., Björck, S. et al. Renal Effects of Felodipine in Hypertensive Patients with Reduced Renal Function. Drugs 29 (Suppl 2), 192–197 (1985). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-198500292-00034
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-198500292-00034