Abstract
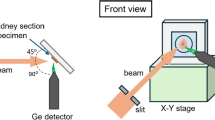
Knowledge about the spatial distribution and the local concentration of trace elements in tissues is of great importance, since trace elements are involved in many biological functions of living organisms. However, there are few methods available to measure the spatial (two (three)-dimensional) elemental distribution in animal brain. X-ray microfluorescence with synchrotron radiation is a multielemental mapping technique, which was used in this work to determine the topographic of iron, zinc and copper in coronal sections of female Wistar rats of different ages. Young (14 days old) and middle-aged (20 months old) rats (n = 8) were analyzed. The measurements were carried out at the XRF beam line at the Synchrotron Light National Laboratory (Campinas, Brazil). Two-dimensional scanning was performed in order to study the tendency of elemental concentration variation. The acquisition time for each pixel was 10 s/step and the step size was 300 mm/step in both directions. It was observed that the iron distribution was more conspicuous in the cortical area, thalamus and bellow the thalamus. On the other hand, the zinc distribution was more pronounced in the hippocampus. The iron, copper and zinc levels increased with advancing age. Therefore, this study reinforces the idea that these elements are involved in the chemical mechanisms of the brain that induce some neurological diseases, since they are also present in high levels in specific areas of the brain, such as the hippocampus and the substantia nigra of patients with these disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Bohic, A. Simionovici, R. Ortega, D. Heymann, C. Schroer, and A. Snigirev, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B, 2001, 181, 728.
T. Takahashi, S. Hatashita, and Y. Taba, J. Neurosci. Methods, 2000, 100, 53.
C. Sergeant, M. H. Vesvres, G. Devès, and F. Guillou, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B, 2005, 231, 234.
R. A Floyd and K. Hensley, Neurobiol. Aging, 2002, 23, 795.
G. Hebbrecht, W. Maenhaut, and J. De Reuck, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B, 1999, 150, 208.
T. G. M. H. Dickhoff, M. Prins, and L. J. B. Hoffman, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B, 1982, 197, 129.
M. Lankosz, M. Szcerbowska-Boruchowska, J. Chwiej, J. Ostachowicz, A. Simionovici, and S. Bohic, Spectrochim. Acta, Part B, 2004, 59, 1517.
F. Watt, T. Lee, P. S. P. Thong, and M. Tang, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B, 1995, 104, 361.
M. Szcerbowska-Boruchowska, M. Lankosz, and D. Ostachowicz, J. Phys. IV, 2003, 104, 325.
M. Szcerbowska-Boruchowska, M. Lankosz, and D. Ostachowicz, X-Ray Spectrom., 2004, 33, 3.
R. Ortega, M. Deves, and M. Bonnin-Mosbah, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B, 2001, 181, 485.
W. M. Kwiatek, A. L. Hanson, and M. Paluszkiewicz, J. Alloys Compd., 2004, 362, 83.
A. Ide-Ektessabi, T. Kawakami, and F. Watt, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B, 2004, 213, 590.
U. Lindh, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B, 1995, 104, 285.
Quantitative X-ray Analysis System (QXAS) software package, IAEA, Vienna.
M. Prins, J. A. Van der Heide, and A. J. J. Boss, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 1983, 30, 1243.
A. Ektessabi, S. Yoshida, and K. Takada, X-Ray Spectrom., 1999, 28, 456.
B. Singh, D. Dhawan, B. Chand, P. C. Mangal, and P. N. Trehan, Appl. Radiat. Isot., 1995, 46, 59.
J. M. Graham, M. N. J. Paley, R. A. Grünewald, N. Hoqqard, and P. D. Griffiths, Brain, 2000, 123, 2423.
E. Kienzl, L. Puchinger, K. Jellinger, H. Stachelberger, and R. F. Jameson, J. Neurol. Sci., 1995, 134, 69.
W. R. Markesbery, W. D. Ehmann, M. Alauddin, and T. J. M. Hossain, Neurobiol. Aging, 1984, 5, 19.
C. W. Levenson, Physiol. Behav., 2005, 86, 399.
H. Shim and Z. L. Harris, J. Nutr., 2003, 133, 1527.
R. Palm, G. Wahlström, and G. Hallmans, Lab. Anim., 1990, 240.
C. L. Keen and L. S. Hurley, Mech. Aging Dev., 1980, 13, 161.
T. Tarohda, M. Yamamoto, and R. Amano, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2004, 380, 240.
E. Mocchegiani, M. Muzzioli, C. Cipriano, and R. Giacconi, Mech. Aging Dev., 1998, 106, 183.
D. W. Choi, M. Yokoyama, and J. Koh, Neuroscience, 1988, 24, 67.
A. Takeda, J. Sawashita, and S. Okada, Brain Res., 1995, 695, 53.
C. J. Frederickson, W. I. Manton, M. H. Frederickson, G. A. Howell, and M. A. Mallory, Brain Res., 1982, 246, 338.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serpa, R.F.B., de JESUS, E.F.O., Anjos, M.J. et al. Topographic Trace-Elemental Analysis in the Brain of Wistar Rats by X-ray Microfluorescence with Synchrotron Radiation. ANAL. SCI. 24, 839–842 (2008). https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.24.839
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.24.839