Abstract
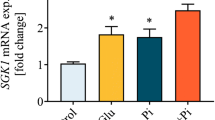
In this paper, we investigate the effect and the possible mechanism of high glucose levels on the calcification of human aortic smooth muscle cells (HASMCs). HASMCs were divided into four groups: normal glucose group (NG), osmolality control group (OC), high glucose group (HG, HASMCs culture medium containing 30 mmol/L glucose), and high glucose plus recombinant human Noggin protein (bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) antagonist) group (HN). The mRNA levels and the protein expressions of BMP-2 and core binding factor alpha-1 (Cbfα-1) were measured by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and Western blot. After induced by 10 mmol/L β-glycerol phosphoric acid, cells were harvested for assessments of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activities at Days 1, 2, and 3, and intracellular calcium contents at Days 7 and 14, respectively. High glucose levels increased the mRNA levels and the protein expressions of BMP-2 and Cbfα-1 (P<0.05). The expression of Cbfα-1 was partially blocked by Noggin protein (P<0.05), while BMP-2 was not (P>0.05). After being induced by β-glycerol phosphoric acid, high glucose levels increased the ALP activity [(48.63±1.03) vs. (41.42±2.28) U/mg protein, Day 3; P<0.05] and the intracellular calcium content [(2.76±0.09) vs. (1.75±0.07) μmol/mg protein, Day 14; P<0.05] in a time-dependent manner when compared with the NG group, while the ALP activity could not be blocked by Noggin protein [(48.63±1.03) vs. (47.37±0.97) U/mg protein, Day 3; P>0.05]. These results show that high glucose levels can evoke the calcification of HASMCs by inducing osteoblastic trans-differentiation and intracellular calcium deposition via the BMP-2/Cbfα-1 pathway, which can be partially blocked by Noggin protein.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attisano, L., Wrana, J.L., 2002. Signal transduction by the TGF-β superfamily. Science, 296(5573):1646–1647. [doi: 10.1126/science.1071809]
Busch, C., Drews, U., Eisele, S.R., Garbe, C., Oppitz, M., 2008. Noggin blocks invasive growth of murine B16-F1 melanoma cells in the optic cup of the chick embryo. Int. J. Cancer, 122(3):526–533. [doi:10.1002/ijc.23139]
Canalis, E., Economides, A.N., Gazzerro, E., 2003. Bone morphogenetic proteins, their antagonists, and the skeleton. Endocr. Rev., 24(2):218–235. [doi:10.1210/er.2002-0023]
Chen, N.X., O'Neill, K.D., Duan, D., Moe, S.M., 2002.Phosphorus and uremic serum up-regulate osteopontin expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. Kidney Int., 662 (5):1724–1731. [doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2002.00625.x]
Chen, N.X., Duan, D., O'Neill, K.D., Moe, S.M., 2006. High glucose increases the expression of Cbfα1 and BMP-2 and enhances the calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant., 221 (12):3435–3442. [doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfl429]
Conley, B.A., Smith, J.D., Guerrero-Esteo, M., Bernabeu, C., Vary, C.P., 2000. Endoglin, a TGF-β receptor-associated protein, is expressed by smooth muscle cells in human atherosclerotic plaques. Atherosclerosis, 153(2):323–335. [doi:10.1016/S0021-9150(00)00422-6]
Dhore, C.R., Cleutjens, J.P., Lutgens, E., Cleutjens, K.B., Geusens, P.P., Kitslaar, P.J., Tordoir, J.H., Spronk, H.M., Vermeer, C., Daemen, M.J., 2001. Differential expression of bone matrix regulatory proteins in human atherosclerotic plaques. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol., 21(12):1998–2003. [doi:10.1161/hq1201.100229]
Doherty, T.M., Fitzpatrick, L.A., Inoue, D., Qiao, J.H., Fishbein, M.C., Detrano, R.C., Shah, P.K., Rajavashisth, T.B., 2004. Molecular, endocrine, and genetic mechanisms of arterial calcification. Endocr. Rev., 25(4):629–672. [doi:10.1210/er.2003-0015]
Lee, K.S., Kim, H.J., Li, Q.L., Chi, X.Z., Ueta, C., Komori, T., Wozney, J.M., Kim, E.G., Choi, J.Y., Ryoo, H.M., et al., 2000. Runx2 is a common target of transforming growth factor-1 and bone morphogenetic protein 2, and cooperation between Runx2 and Smad5 induces osteoblast- specific gene expression in the pluripotent mesenchymal precursor cell line C2C12. Mol. Cell. Biol., 20(23):8783–8792. [doi:10.1128/MCB.20.23.8783-8792.2000]
Lehto, S., Niskanen, L., Suhonen, M., Rönnemaa, T., Laakso, M., 1996. Medial artery calcification a neglected harbinger of cardiovascular complications in non-insulin- dependent diabetes mellitus. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol., 16(8):978–983.
Moe, S.M., Chen, N.X., 2004. Pathophysiology of vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease. Circ. Res., 95(6): 560–567. [doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000141775.67189.98]
Moe, S.M., Duan, D., Doehle, B.P., O'Neill, K.D., Chen, N.X., 2003. Uremia induces the osteoblast differentiation factor Cbfα1 in human blood vessels. Kidney Int., 63(3):1003–1011. [doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00820.x]
Mori, K., Shioi, A., Jono, S., Nishizawa, Y., Morii, H., 1999. Dexamethasone enhances in vitro vascular calcification by promoting osteoblastic differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol., 19(9):2112–2118.
Otto, F., Lubbert, M., Stock, M., 2003. Upstream and downstream targets of RUNX proteins. J. Cell Biochem., 89(1): 9–18. [doi:10.1002/jcb.10491]
Parhami, F., Basseri, B., Hwang, J., Tintut, Y., Demer, L.L., 2002. High density lipoprotein regulates calcification of vascular cells. Circ. Res., 91(7):570–576. [doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000036607.05037.DA]
Shanahan, C.M., Cary, N.R., Metcalfe, J.C., Weissberg, P.L., 1994. High expression of genes for calcification-regulating proteins in human atherosclerotic plaques. J. Clin. Invest., 93(6):2393–2402. [doi:10.1172/JCI117246]
Shioi, A., Nishizawa, Y., Jono, S., Koyama, H., Hosoi, M., Morii, H., 1995. β-glycerophosphate accelerates calcification in cultured bovine vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol., 15(11):2003–2009.
Shioi, A., Katagi, M., Okuno, Y., Mori, K., Jono, S., Koyama, H., Nishizawa, Y., 2002. Induction of bone-type alkaline phosphatase in human vascular smooth muscle cells: roles of tumor necrosis factor-α and oncostatin M derived from macrophages. Circ. Res., 91(1):9–16. [doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000026421.61398.F2]
Steitz, S.A., Speer, M.Y., Curinga, G., Yang, H.Y., Haynes, P., Aebersold, R., Schinke, T., Karsenty, G., Giachelli, C.M., 2001. Smooth muscle cell phenotypic transition associated with calcification: upregulation of Cbfα1 and downregulation of smooth muscle lineage markers. Circ. Res., 89(12):1147–1154. [doi:10.1161/hh2401.101070]
Takayama, K., Suzuki, A., Manaka, T., Taguchi, S., Hashimoto, Y., Imai, Y., Wakitani, S., Takaoka, K., 2009. RNA interference for Noggin enhances the biological activity of bone morphogenetic proteins in vivo and in vitro. J. Bone Miner. Metab., 27(4):402–411. [doi:10.1007/s00774-009-0054-x]
Tintut, Y., Patel, J., Parhami, F., 2000. Tumor necrosis factor-α promotes in vitro calcification of vascular cells via the cAMP pathway. Circulation, 102(21):2636–2642.
Yuasa, S., Fukuda, K., 2008. Multiple roles for BMP signaling in cardiac development. Drug Discov. Today: Ther. Strategies, 5(4):209–214. [doi:10.1016/j.ddstr.2008.12.001]
Zhu, W., Kim, J., Cheng, C., Rawlins, B.A., Boachie-Adjei, O., Crystal, R.G., Hidaka, C., 2006. Noggin regulation of bone morphogenesis protein (BMP) 2/7 heterodimer activity in vitro. Bone, 39(1):61–71. [doi:10.1016/j.bone.2005.12.018]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The two authors contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, F., Zhong, H., Liang, Jy. et al. Effect of high glucose levels on the calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells by inducing osteoblastic differentiation and intracellular calcium deposition via BMP-2/Cbfα-1 pathway. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 11, 905–911 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1000119
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1000119
Key words
- Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)
- Core binding factor alpha-1 (Cbfα-1)
- Vascular smooth muscle cell
- Noggin protein