Abstract
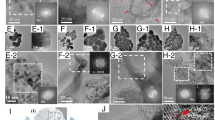
A wide variety of materials which are normally undamaged when exposed to a lOOkeV electron beam in a conventional transmission electron microscope can be modified on a nanometre scale by the high current density electron probe in a dedicated scanning transmission electron microscope (STEM). A stationary 100keV STEM electron probe can produce holes typically l-5nm diameter through crystalline Al, Si and MgO tens of nanometres in thickness, while a scanned electron beam can smooth surfaces on an atomic scale.
In Al the stationary electron probe in the STEM produces a row of facetted voids along the irradiated volume. The voids grow initially inwards from the electron exit surface, with each void typically 4nm in diameter and 12-24nm in length, separated by equal distances from one another. In contrast, continuous holes 1.2-1.6nm diameter form at the electron exit surface of Si when exposed to the focused electron beam. However, these holes form only at specific randomly distributed points separated from one another by 2-4nm over the surface of crystalline specimens of both n- and p-doped <001> and <111> Si.
Square cross-section holes with widths of about lnm can be formed by the stationary electron probe in MgO crystals. Rastering the probe over a restricted area of MgO initially results in the rapid development of surface islands and channels which are subsequently removed to leave an atomically smooth surface.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.A. Youngman, L.W. Hobbs and T.E. Mitchell, J. de Physique 41, C6-277 (1980)
G.W. Iseler, H.I. Dawson, A.S. Mehner and J.W. Kauffman, Phys. Rev. 146, 468 (1966)
J.W. Corbett and J.C. Bourgoin, in Point Defects in Solids, edited by J.H. Crawford, Jr., and L.M. Slifkin (Plenum Press, New York, 1975), Vol.2, ppl-161
G.M. Bond, I.M. Robertson, F.M. Zeides and H.K. Birnbaum, Philos. Mag. A, 55 (5), 669 (1987)
L.Reimer, Transmission Electron Microscopy, (Springer-Verlag, Berlin and London, 1989)
C.R. Bradley, Argonne National Laboratory Report ANL-88-48, 66 (1988)
M.L. Knotek and P.J. Feibelman, Surf. Sci., 90, 78 (1979)
R.E. Walkup and Ph. Avouris, Phys. Rev. Lett., 56, 524 (1986)
M.E. Mochel, C.J. Humphreys, J.A. Eades, J.M. Mochel and A.K. Petford, Appl. Phys. Lett., 42, 392 (1983)
S.D. Berger, I.G. Salisbury, R.H. Milne, D. Imeson and C.J. Humphreys, Philos. Mag. B, 55, 341 (1987)
R.W. Devenish, T.J. Bullough and C.J. Humphreys, presented at EMAG 89, London, 1989 (in press)
C.J. Humphreys, T.J. Bullough, R.W. Devenish, D.M. Maher and P.S. Turner, in Proc. 8th Pfefferkorn Conference on Fundamental Beam Interactions with Solids for Microscopy, Microanalysis and Microlithography, Utah, 1989 (in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bullough, T.J., Humphreys, C.J. & Devenish, R.W. Electron Beam Induced Nanometre Hole Formation and Surface Modification in Al, Si And MgO. MRS Online Proceedings Library 157, 323–328 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-157-323
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-157-323