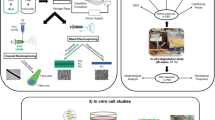
Abstract
Bone tissue engineering typically involves the use of porous, bioresorbable scaffolds to serve as temporary, three-dimensional scaffolds to guide cell attachment, differentiation, proliferation, and subsequent tissue regeneration. In this study we developed a composite membrane scaffold by phase inversion technique by using biodegradable polyester, Polycaprolactone (PCL), with hydroxyapatite (HA) in order to develop novel controlled nanostructured biomaterials for bone tissue engineering applications.After preparation, membrane scaffolds were characterized in order to evaluate its morphological, physico-chemical and mechanical properties and then used for the cell culture.
Our experimental design consists to apply the knowledge of natural bone tissue remodelling in an in vitro membrane biohybrid system. We used human mesenchymal stem cells for culture in the membrane scaffolds inducing the differentiation in osteoblasts and human monocytes to trigger osteoclastogenesis. Osteoclastic resorption of the scaffold material would lead to subsequent induction of osteoblasts and faster bone formation with mesenchymal stem cells. Our results show that osteoblasts and osteoclasts were successfully differentiated in the developed PCL-HA membrane scaffold. This membrane system will lead to insights in the creation of a controllable osteoinductive microenvironment based on the specific properties (e.g. basic composition, surface chemistry, architecture) and on the function (resorption coupled to proliferation and differentiation) of defined cellular systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Bose, M. Roy and A. Bandyopadhyay, Trends in Biotechnology 30, 11 (2012).
F. Zhao, Y.J. Yin, W.W. Lu, J.C. Leong, W. Zhang, J.Y. Zhang, M.F. Zhang and K.D. Yao, Biomaterials 23, 3227 (2002).
N.K. Vail, L.D. Swain, W.C. Fox, T.B. Aufdlemorte, G. Lee and J.W. Barlow, Materials for biomedical application, Materials & Design 20, 123 (1999).
M. Kellomaki, H. Niiranen, K. Puumanen, N. Ashammakhi, T. Waris, and P. Törmälä ;, Biomaterials 21, 2495 (2000)
M.A. Woodruff, D.W. Hutmacher, Progress in Polymer Science 35, 1217 (2010).
S.H. Oh, I.K. Park, J.M. Kim, JH. Lee, Biomaterials 28, 1664 (2007).
V. Guarino, F. Causa, P. Taddei, M. di Foggia, G. Ciapetti, D. Martini et al., Biomaterials 29, 3662 (2008).
CXF Lam, S.H. Teoh, D.W. Hutmacher, Polym Int. 56, 718 (2007).
CXF Lam, D.W. Hutmacher, J-T. Schantz, M.A. Woodruff, SH. Teoh, J Biomed Mater Res Part A 90, 906 (2008).
CXF Lam, M.M. Savalani, S.H. Teoh, D. Hutmacher, Biomed Mater; 3:1 (2008).
A.A. Sawyer, S.J. Song, E. Susanto, P. Chuan, CXF Lam, M.A. Woodruff et al., Biomaterials 30, 2479 (2009).
D.W. Hutmacher, Biomaterials 21, 2529 (2000).
S.A. Abbah, CFX Lam, D.W. Hutmacher, J.C.H. Goh, H-K Wong, Biomaterials 30, 5086 (2009).
I. Sopyana, M. Melb, S. Rameshc, K.A. Khalidd . Science and Technology of Advanced Materials 8, 116 (2007).
R. Ravichandran, J. R. Venugopal, S. Sundarrajan, S. Mukherjee and S. Ramakrishna Biomaterials 33, 846 (2012).
M.F. Pittenger, A.M. Mackay, S.C. Beck, R.K. Jaiswal, R. Douglas, J.D. Mosca, M.A. Moorman, D.W. Simonetti, S. Craig, D.R. Marshak . Science 284, 143 (1999).
Z. Gamie, G.T. Tran, G. Vyzas, N. Korres, M. Heliots., A. Mantalaris., E. Tsiridis . Expert Opin Biol Ther. 12, 713 (2012).
R.T. Franceschi . Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 10, 40 (1999).
J. Chen, K. Singh, B.B. Mukherjee, J. Sodek . Matrix 13, 113 (1993).
M. Amoui, S.M. Suhr, J.D. Baylink and K.H. William . Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 287, C874 (2004).
C. Minkin . Calcif. Tissue Int. 34, 285–290 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morelli, S., Facciolo, D., Messina, A. et al. Polycaprolactone-Hydroxyapatite Composite Membrane Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. MRS Online Proceedings Library 1502, 1215021006 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2013.567
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2013.567