Abstract
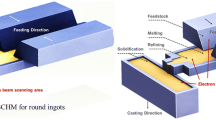
The purpose of this work is, based on CAFE method, to study the microstructure evolution and optimize the quality of the large-scale titanium slab ingot during EBCHM. The nucleation parameters of the microstructure simulation of titanium ingot are determined based on one of the actual experimental results. For the determined parameters, our theoretical results are agreement with other experimental results. The effects of pouring temperature and pulling speed on the microstructure are presented based on CAFE method. The quantitative analyses of the simulated results show that with the pulling speed increasing, the number of grains decreases, whereas the mean grain radius increases under identical thermal condition; with the pouring temperature increasing, the mean grain radius increases under the given pulling speed. Our results are very important to obtain the optimal structure of the ingots by controlling pulling speed and pouring temperature.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 1:
-
Electron beam cold hearth melting (EBCHM)
- 2:
-
Vacuum arc remelting (VAR)
- 3:
-
Monte Carlo method (MC)
- 4:
-
Finite element coupling the cellular automaton method (CAFE)
- 5:
-
Kurz, Giovanola, and Trivediand model (KGT)
References
R.R. Boyer: An overview on the use of titanium in the aerospace industry. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 213, 103–114 (1996).
S. Seok, C.D. Onal, K.J. Cho, and R.J. Wood: A peristaltic soft robot with antagonistic nickel titanium coil actuators. IEEE ASME Trans. Mechatron. 18, 1485–1497 (2013).
A. Mitchell: The electron beam melting and refining of titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 263, 217–223 (1999).
K. Vutova and V. Donchev: Electron beam melting and refining of metals: Computational modeling and optimization. Materials 6, 4626–4640 (2013).
T. Tatsuhiko, H. Kanayama, and T. Onoye: Temperature measurement of molten metal surface in electron beam melting of titanium alloys. ISIJ Int. 32, 593–599 (1992).
Q.L. Liu, X.M. Li, and Y.H. Jiang: Research progress of electron beam clod hearth melting for titanium and titanium alloys. Hot Work. Technol. 45, 9–14 (2016).
J.R. Wood: Producing Ti-6Al-4V plate from single-melt EBCHM ingot. JOM 54, 56–58 (2002).
K. Vutova, E. Koleva, and G. Mladenov: Simulation of thermal transfer process in cast ingot at electron beam melting and refining. Int. Rev. Mech. Eng. 5, 257–265 (2009).
E. Koleva, K. Vutova, and G. Mladenov: The role of ingot crucible thermal contact in mathematical modelling of the heat transfer during electron beam melting. Vacuum 62, 189–196 (2001).
A.N. Kalinyuka, N.P. Triguba, V.N. Zamkova, and O.M. Ivasishin: Microstructure, texture, and mechanical properties of electron-beam melted Ti–6Al–4V. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 346, 178–188 (2003).
R.C. Atwood, P.D. Lee, and R.S. Minisandram: Multiscale modelling of microstructure formation during vacuum arc remelting of titanium 6-4. J. Mater. Sci. 39, 7193–7197 (2004).
M. Rappaz and Ch.A. Gandin: Probabilistic modelling of microstructure formation in solidification processes. Acta Metall. Mater. 41, 345–360 (1993).
S.P. Wu, D.R. Liu, J.J. Guo, C.Y. Li, and Y.Q. Su: Numerical simulation of microstructure evolution of Ti–6Al–4V alloy in vertical centrifugal casting. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 426, 240–249 (2006).
Ch.A. Gandin and M. Rappaz: A coupled finite element-cellular automaton model for the prediction of dendritic grain structures in solidification processes. Acta Metall. Mater. 42, 2233–2246 (1994).
Ch.A. Gandin, M. Rappaz, and R. Tintillier: Three-dimensional probabilistic simulation of solidification grain structures: Application to superalloy precision castings. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 24, 467–479 (1993).
T. Carozzani, H. Digonnet, and C. Gandin: 3D CAFE modeling of grain structures: Application to primary dendritic and secondary eutectic solidification. Modell. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 20, 15010–15028 (2012).
M. Rappaz, C.A. Gandin, J.L. Desbiolles, and P. Thévoz: Prediction of grain structures in various solidification processes. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 27, 695–705 (1996).
F.J. Tian, Z.G. Li, and J.X. Song: Solidification of laser deposition shaping for TC4 alloy based on cellular automation. J. Alloys Compd. 676, 542–550 (2016).
A. Burbelko, J. Falkus, W. Kapturkiewicz, K. Sołek, P. Drożdż, and M. WróbeL: Modeling of the grain structure formation in the steel continuous ingot by cafe method. Arch. Metall. Mater. 57, 379–384 (2012).
Q.L. Liu, X.M. Li, X.F. Chen, N.T. Geng, and Y.H. Jiang: Numerical simulation of electron beam cold hearth melting for the large scale titanium slab ingot during solidification process. Spec. Cast. Nonferrous Alloys 3, 244–249 (2017).
W. Kurz, B. Giovanola, and R. Trivedi: Theory of microstructural development during rapid solidification. Acta Metall. Mater. 34, 823–830 (1986).
H.C. Kou, Y.J. Zhang, P.F. Li, R. Hu, J.S. Li, and L. Zhou: Numerical simulation of titanium alloy ingot solidification structure during VAR process based on three-dimensional CAFE method. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 43, 1537–1542 (2014).
J.L. Wang, F.M. Wang, Y.Y. Zhao, J.M. Zhang, and W. Ren: Numerical simulation of 3D-microstructures in solidification processes based on the CAFE method. Int. J. Miner., Metall. Mater. 16, 640–645 (2009).
Q.L. Liu, X.M. Li, and Y.H. Jiang: Numerical simulation of EBCHM for the large-scale TC4 alloy slab ingot during the solidification process. Vacuum 141, 1–9 (2017).
M. Rappaz, Ch. Charbon, and R. Sasikumar: About the shape of eutectic grains solidifying in a thermal gradient. Acta Metall. Mater. 42, 2365–2374 (1994).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work is supported By Applied Basic Research Program of Yunnan Province (No. 2013FC001), Science and Technology Project of Yunnan Province (No. 2016FB089), and Startup Foundation for Advanced Talents of Kunming University of Science and Technology (No. KKSY201551034).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, QL., Li, XM. & Jiang, YH. Microstructure evolution of large-scale titanium slab ingot based on CAFE method during EBCHM. Journal of Materials Research 32, 3175–3182 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.174
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.174