Abstract
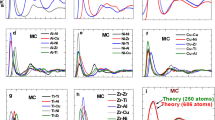
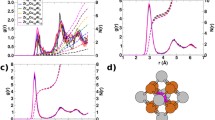
We used reverse Monte Carlo (RMC) modeling to simulate the atomic structure of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass (BMG), incorporating short-range structural data from the electron diffraction total reduced density function G(r) and medium-range structural data from fluctuation electron microscopy (FEM). Including the FEM data created within the model loosely ordered planar atomic arrangements covering regions ∼1 nm in diameter without degrading the agreement with G(r). RMC refinement against only G(r) produced no agreement with FEM. Improved simulations are needed to create fully realistic BMG structures, but these results show that including FEM in RMC further constrains the structure compared with G(r) data alone and that the FEM signal in real materials is likely to arise from pseudo-planar arrangements of atoms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Slipenyuk and J. Eckert: Correlation between enthalpy change and free volume reduction during structural relaxation of Zr55 Cu30Al10Ni5 metallic glass. Scr. Mater. 50, 39 (2004).
P.K. Cang Fan, T.W. Liaw, W. Wilson, W. Dmowski, H. Choo, C.T. Liu, J.W. Richardson, and Th. Proffen: Structural model for bulk amorphous alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 111905 (2006).
A.S. Argon: Plastic deformation in metallic glasses. Acta Metall. 27, 47 (1979).
M.L. Falk and J.S. Langer: Dynamics of viscoplastic deformation in amorphous solids. Phys. Rev. E 57, 7192 (1998).
A.C. Schuh, T.C. Hufnagel, and U. Ramamurty: Mechanical behavior of amorphous alloys. Acta Mater. 55, 4067 (2007).
G. Adam and J.H. Gibbs: On the temperature dependence of cooperative relaxation properties in glass-forming liquids. J. Chem. Phys. 43, 139 (1965).
D. Kivelson, S.A. Kivelson, X.L. Zhao, Z. Nussinov, and G. Tarjus: A thermodynamic theory of supercooled liquids. Physica A 219, 27 (1995).
H.W. Sheng, W.K. Luo, F.M. Alamgir, J.M. Mai, and E. Ma: Atomic packing and short-to-medium-range order in metallic glasses. Nature 439, 419 (2006).
T. Schenk, D. Holland-Moritz, V. Simonet, R. Bellissent, and D.M. Herlach: Icosahedral short-range order in deeply undercooled metallic melts. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 075507 (2002).
G.W. Lee, A.K. Gangopadhyay, K.F. Kelton, R.W. Hyers, T.J. Rathz, J.R. Rogers, and D.S. Robinson: Difference in icosahedral short-range order in early and late transition metal liquids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 037802 (2004).
D.B. Miracle: A structural model for metallic glasses. Nat. Mater. 3, 697 (2004).
H.E. Fischer, A.C. Barnes, and P.S. Salmon: Neutron and x-ray diffraction studies of liquids and glasses. Rep. Prog. Phys. 69, 233 (2006).
J. Hafner, T. Egami, S. Aur, and B.C. Giessen: The structure of calcium-aluminium glasses: X-ray diffraction and computer simulation studies. J. Phys. F: Met. Phys. 17, 1807 (1987).
T. Takagi, T. Okubo, Y. Hirotsu, B.S. Murty, K. Hono, and D. Shindo: Local structure of amorphous Zr70Pd30 alloy studied by electron diffraction. Appl. Phys. Lett. 79, 485 (2001).
H.W. Sheng, H.Z. Liu, Y.Q. Cheng, J. Wen, P.L. Lee, W.K. Luo, S.D. Shastri, and E. Ma: Polyamorphism in a metallic glass. Nat. Mater. 6, 192 (2007).
P.M. Voyles and J.R. Abelson: Medium-range order in amorphous silicon measured by fluctuation electron microscopy. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 78, 85 (2003).
J.J. Rehr and R.C. Albers: Theoretical approaches to x-ray absorption fine structure. Rev. Mod. Phys. 72, 621 (2000).
Y. Waseda: Anomalous X-Ray Scattering for Materials Characterization (Springer, Berlin, 2002).
S.R. Elliot: Medium-range structural order in covalent amorphous solids. Nature 354, 445 (1991).
P.H. Gaskell and D.J. Wallis: Medium-range order in silica, the canonical network glass. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 66 (1996).
D. Ma, A.D. Stoica, and X-L. Wang: Power-law scaling and fractal nature of medium-range order in metallic glasses. Nat. Mater. 8, 30 (2009).
B.S. Murty and K. Hono: Nanoquasicrystallization of Zr-based metallic glasses. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 312, 253 (2001).
A. Hirata, Y. Hirotsu, T.G. Nieh, T. Ohkubo, and N. Tanaka: Direct imaging of local atomic ordering in a Pd–Ni–P bulk metallic glass using Cs-corrected transmission electron microscopy. Ultramicroscopy 107, 116 (2007).
M.M.J. Treacy, J.M. Gibson, L. Fan, D.J. Paterson, and I. McNulty: Fluctuation microscopy: A probe of medium range order. Rep. Prog. Phys. 68, 2899 (2005).
J.M. Gibson, M.M.J. Treacy, and P.M. Voyles: Atom pair persistence in disordered materials from fluctuation microscopy. Ultramicroscopy 83, 169 (2000).
J. Hwang, H. Cao, and P.M. Voyles: Nanometer-scale structural relaxation in Zr-based bulk metallic glass. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 1048, Z05–04 (2008).
T.C. Hufnagel, C. Fan, R.T. Ott, J. Li, and S. Brennan: Controlling shear band behavior in metallic glasses through microstructural design. Intermetallics 10, 1163 (2002).
D.J. Sordelet, R.T. Ott, M.Z. Li, S.Y. Wang, C.Z. Wang, M.F. Besser, A.C.Y. Liu, and M.J. Kramer: Structure of Zrx Pt100-x (73 ≤x ≤77) metallic glasses. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 39, 1908 (2008).
J. Wen, Y.Q. Cheng, J.Q. Wang, and E. Ma: Distinguishing medium-range order in metallic glass using fluctuation electron microscopy: A theoretical study using atomic models. J. Appl. Phys. 105, 043519 (2009).
W.G. Stratton, J. Hamann, J.H. Perepezko, X. Mao, S.V. Khare, and P.M. Voyles: Aluminum nanoscale order in amorphous Al92Sm8 measured by fluctuation electron microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 141910 (2005).
P.M. Voyles, N. Zotov, S.M. Nakhmanson, D.A. Drabold, J.M. Gibson, M.M.J. Treacy, and P. Keblinski: Structure and physical properties of paracrystalline atomistic models of amorphous silicon. J. Appl. Phys. 90, 9 (2001).
D.A. Keen and R.L. Mcgreevy: Structural modelling of glasses using reverse Monte Carlo simulation. Nature 344, 423 (1990).
R.L. McGreevy: Reverse Monte Carlo modeling. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 13, R877 (2001).
P. Biswas, R. Atta-Fynn, and D.A. Drabold: Reverse Monte Carlo modeling of amorphous silicon. Phys. Rev. B 69, 195207 (2004).
P. Biswas, D.N. Tafen, R. Atta-Fynn, and D. Drabold: The inclusion of experimental information in first principles modelling of materials. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 16, S5173 (2004).
D. Wang, H. Tan, and Y. Li: Multiple maxima of GFA in three adjacent eutectics in Zr–Cu–Al alloy system: A metallographic way to pinpoint the best glass forming alloys. Acta Mater. 53, 2969 (2005).
H. Chen and J-M. Zuo: Structure and phase separation of Ag–Cu alloy thin films. Acta Mater. 55, 1617 (2007).
E.J. Kirkland: Advanced Computing in Electron Microscopy (Plenum, NY, 1998).
D.J.H. Cockayne and D.R. Mckenzie: Electron diffraction analysis of polycrystalline and amorphous thin films. Acta Crystallogr., Sect. A 44, 870 (1988).
P.M. Voyles: Fluctuation Electron Microscopy of Medium-Range Order in Amorphous Silicon (Dissertation, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 2001).
J. Puthoff and D.S. Stone: Unpublished data.
D.B. Miracle: The efficient cluster packing model: An atomic structural model for metallic glasses. Acta Mater. 54, 4317 (2006).
L.E. Hall and D.R. Mckenzie: Coordination number determination in binary alloys using electron diffraction. Philos. Mag. A 80, 525 (2000).
R.K. Dash, P.M. Voyles, J.M. Gibson, M.M.J. Treacy, and P. Keblinski: A quantitative measure of medium-range order in amorphous materials from transmission electron micrographs. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 15, S2425 (2003).
P.M. Voyles and D.A. Muller: Fluctuation microscopy in the STEM. Ultramicroscopy 93, 147 (2002).
W.G. Stratton and P.M. Voyles: Comparison of fluctuation electron microscopy theories and experimental methods. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 19, 455203 (2007).
L.A. Freeman, A. Howie, A.B. Mistry, and P.H. Gaskell: The Structure of Non-Crystallized Materials (Taylor and Francis, London, UK, 1976).
W.G. Stratton and P.M. Voyles: A phenomenological model of fluctuation electron microscopy for a nanocrystal/amorphous composite. Ultramicroscopy 108, 727 (2008).
L.A. Freeman, A. Howie, A.B. Mistry, and P.H. Gaskell: The Structure of Non-Crystallized Materials (Taylor and Francis, London, UK, 1976).
W.G. Stratton and P.M. Voyles: A phenomenological model of fluctuation electron microscopy for a nanocrystal/amorphous composite. Ultramicroscopy 108, 727 (2008).
G. Opletal, T.C. Petersen, D.G. McCulloch, I.K. Snook, and I. Yarovsky: The structure of disordered carbon solids studies using a hybrid reverse Monte Carlo algorithm. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 17, 2605 (2005).
G. Zhao, P.R. Buseck, A. Rougée, and M.M.J. Treacy: Mediumrange order in molecular materials: Fluctuation electron microscopy for detecting fullerenes in disordered carbons. Ultramicroscopy 109, 177 (2009).
Y. Suzuki, J. Haimovich, and T. Egami: Bond-orientational anisotropy in metallic glasses observed by x-ray diffraction. Phys. Rev. B 35, 2162 (1987).
M.I. Mendelev, D.J. Sordelet, and M.J. Kramer: Using atomistic computer simulations to analyze x-ray diffraction data from metallic glasses. J. Appl. Phys. 102, 043501 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, J., Clausen, A.M., Cao, H. et al. Reverse Monte Carlo structural model for a zirconium-based metallic glass incorporating fluctuation microscopy medium-range order data. Journal of Materials Research 24, 3121–3129 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2009.0386
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2009.0386