Abstract
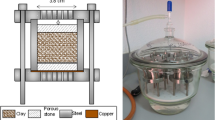
Packed columns of canister packing material containing 25% bentonite and 75% quartz or basalt sand, were exposed to water vapor at temperatures of up to 260°C. The permeabilities of the columns were subsequently measured after complete saturation with liquid water in a pressurized system. Exposure to water vapor caused irreversible increases in permeability by factors of up to 105. After saturation with liquid water, the permeability was nearly independent of temperature. The increases in permeability were due to a large decrease in the ability of the bentonite to swell in water. Calculations suggest that swelling of bentonite exposed to water vapor at 250°C was not sufficient to fill the pore spaces. If the pore spaces are filled, the mixture will form an effective barrier against flow, diffusion, and transport of colloids.
The results suggest that if bentonite-based canister packing material is exposed even briefly to water vapor at high temperatures in a high-level nuclear waste repository, its performance will be seriously impaired. The problem will be less severe if the proportion of bentonite is high and the material is highly compacted. Previous results show significant degradation of bentonite by water vapor at temperatures as low as 150°C. This suggests that in some repositories, backfill in tunnels and drifts may also be affected.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. C. Allen, D. L. Lane, R. A. Palmer, and R. G. Johnston, “Experimental Studies of Packing Material Stability,” Materials Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. v.26, p. 105–112, Elsevier (1984).
R. Couture, “Steam Rapidly Reduces the Swelling Capacity of Bentonite,” in preparation; R. Couture in “Nuclear Technology Programs Quarterly Progress Report, April–June 1984,” Argonne National Laboratory, Argonne, IL, ANL-84-57.
D. J. Bradley et al., “Nuclear Waste Package Materials Testing Report, Basaltic and Tuffaceous Environments,” Battelle Pacific Northwest Laboratory, Richland, WA, PNL-4452 (1983).
J. L. Krumhansl, “Observations Regarding the Stability of Bentonite Backfill in a High-Level Waste Repository in Rock Salt,” Sandia National Laboratories, Albuquerque, NM, SAND-33-1293J (1984).
Donald Moore, Baroid Corp., oral communication 1984).
R. Couture and R. Bane, in “Nuclear Technology Programs Quarterly Progress Report, January–March 1984,” Argonne National Laboratory, Argonne, IL, ANL-84-37 (1984).
R. Couture and M. Seitz, in “NRC Nuclear Waste Geochemistry 1983,” U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission, Washington, D.C., NUREG/CP-0052 1984).
K. Norrish, Disc. Faraday Soc. 18, 120–134 1954).
Paul L. Chambré and Thomas H. Pigford, “Prediction of Waste Performance in a Geologic Repository,” Materials Res. Soc. Symp. Proc., v. 26, p. 985–1008, Elsevier 1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Couture, R.A. Rapid Increases in Permeability and Porosity of Bentonite-Sand Mixtures Due to Alteration by Water Vapor. MRS Online Proceedings Library 44, 515–522 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-44-515
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-44-515