Abstract
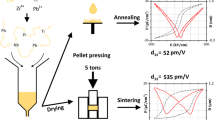
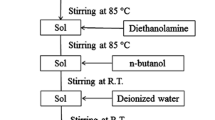
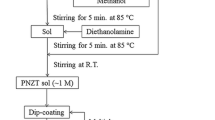
Poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) additives with different molecular weights were used to modify sol-gel precursor solutions for preparing lead zirconate titanate (PZT) thin films. The morphology, crystalline structure, and mechanical and electrical properties of the films were characterized. The relationship between the characteristics of the films and the molecular weight of PEG was investigated. It was observed that the PEG eliminated cracking of the films during multiple pyrolysis treatments. However, with the increase of the PEG molecular weight, the films became less dense, which led to decreased Young’s modulus and dielectric constant and increased coercive field. Our experiments showed that films prepared from sols modified by PEG with a molecular weight of 200 exhibited a dense morphology and excellent mechanical and electric properties without cracking.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.W. Schwartz, Chem. Mater. 9, 2325 (1997).
S.R. Shannigrahi and H.M. Jang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 79, 1051 (2001).
A.I. Kingon and S.K Streiffer, Curr. Opin. Solid State and Mater. Sci. 4, 39 (1999).
D.L. Polla and L.F. Francis, Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 28, 563 (1998).
Ferroelectric Films V, edited by S.B. Desu, R. Ramesh, B.A. Tuttle, R.E. Jones, and I.K. Yoo (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 433, Pittsburgh, PA, 1996).
J. Cheng and Z. Meng, Thin Solid Films 385, 5 (2001).
D. Liu and J.P. Mevissen, Integr. Ferroelectr. 18, 263 (1997).
K. Maki, N. Soyama, S. Mori, and K. Ogi, Jan. J. Appl. Phys. 39, 5421 (2000).
X. Pu, W. Luo, A. Ding, Y. Tian, and P. Qiu, Phys. Status Solidi A 182, R10 (2000).
H. Kozuka, M. Kajimura, T. Hirano, and K. Katayama, J. Sol-Gel Sci. Techol. 19, 205 (2000).
S. Takenaka and H. Kozuka, Appl. Phys. Lett. 79, 3485 (2001).
H.J. Hwang, A. Towata, M. Awano, and M. Toriyama, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 84, 2323 (2001).
X. Li, H. Zhang, F. Chi, S. Li, B. Xu, and M. Zhao, Mater. Sci. Eng., B 18, 209 (1993).
Y. Shimizu and T. Murata, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 80, 2702 (1997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, S., Yao, K., Shannigrahi, S. et al. Effects of poly(ethylene glycol) additive molecular weight on the microstructure and properties of sol-gel-derived lead zirconate titanate thin films. Journal of Materials Research 18, 737–741 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2003.0100
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2003.0100