Abstract
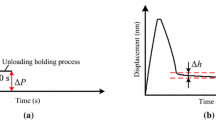
This paper supplies new interpretation of nanoindentation data for silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide based on Raman microanalysis of indentations. For the first time, Raman microspectroscopy analysis of semiconductors within nanoindentations is reported. The given analysis of the load-displacement curves shows that depth-sensing indentation can be used as a tool for identification of pressure-induced phase transformations. Volume change upon reverse phase transformation of metallic phases results either in a pop-out (or a kink-back) or in a slope change (elbow) of the unloading part of the load-displacement curve. Broad and asymmetric hysteresis loops of changing width, as well as changing slope of the elastic part of the loading curve in cyclic indentation can be used for confirmation of a phase transformation during indentation. Metallization pressure can be determined as average contact pressure (Meyer’s hardness) for the yield point on the loading part of the load-displacement curve. The pressure of the reverse transformation of the metallic phase can be measured from pop-out or elbow on the unloading part of the diagram. For materials with phase transformations less pronounced than in Si, replotting of the loaddisplacement curves as average contact pressure versus relative indentation depth is required to determine the transformation pressures and/or improve the accuracy of data interpretation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.R. Clarke, M.C. Kroll, P.D. Kirchner, R.F. Cook, and B.J. Hockey, Phys. Rev. Lett. 60, 2156 (1988).
Y.G. Gogotsi, A. Kailer, and K.G. Nickel, Materials Research Innovations 1, 3 (1997).
A. Kailer, Y.G. Gogotsi, and K.G. Nickel, J. Appl. Phys. 81, 3057 (1997).
G.M. Pharr, W.C. Oliver, and D.S. Harding, J. Mater. Res. 6, 1129 (1991).
G.M. Pharr, W.C. Oliver, R.F. Cook, P.D. Kirchner, M.C. Kroll, T.R. Dinger, and D.R. Clarke, J. Mater. Res. 7, 961 (1992).
G.M. Pharr, W.C. Oliver, and D.R. Clarke, J. Electron. Mater. 19, 881 (1990).
J.J. Gilman, J. Mater. Res. 7, 535 (1992).
S.V. Hainsworth, A.J. Whitehead, and T.F. Page, in Plastic Deformation of Ceramics, edited by R.C. Bradt, C.A. Brookes, and J.L. Routbort (Plenum Press, New York, 1995), p. 173.
J.C. Morris and D.L. Callahan, in Microstructure of Materials, edited by K.M. Krishnan (San Francisco Press, San Francisco, 1992), p. 104.
D.L. Callahan and J.C. Morris, J. Mater. Res. 7, 1614 (1992).
N.V. Novikov, S.N. Dub, Y.V. Milman, I.V. Gridneva, and S.I. Chugunova, Sverkhtverdye Materialy (Superhard Materials) 18, 37 (1996).
S.N. Dub, in Thin Films: Stresses and Mechanical Properties VII, edited by R.C. Cammarata, M. Nastasi, E.P. Busso, and W.C. Oliwer (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 505, Warrendale, PA, 1998), pp. 223–228.
M.I. McMahon and R.J. Nelmes, Phys. Status Solidi B 198, 389 (1996).
J.M. Besson, J.P. Itie, A. Polian, G. Weill, J.L. Masot, and J. Gonzalez, Phys. Rev. B 44, 421 (1991).
J.J. Gilman, Czech J. Phys. 45, 913 (1995).
Y. Gogotsi, M.S. Rosenberg, A. Kailer, and K.G. Nickel, in Proceedings of the Workshop on Tribology Issues and Opportunities in MEMS, edited by B. Bhushan (Kluwer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1998), pp. 431–442.
R.J. Needs and A. Mujica, Phys. Rev. B 51, 9652 (1995).
R.O. Piltz, J.R. Maclean, S.J. Clark, G.J. Ackland, P.D. Hatton, and J. Crain, Phys. Rev. B 52, 4072 (1995).
I.V. Gridneva, Y.V. Milman, and V.I. Trefilov, Phys. Status Solidi A 9, 177 (1972).
E.R. Weppelmann, J.S. Field, and M.V. Swain, J. Mater. Res. 8, 830 (1993).
E.R. Weppelmann, J.S. Field, and M.V. Swain, J. Mater. Sci. 30, 2455 (1995).
M.C. Gupta and A.L. Ruoff, J. Appl. Phys. 51, 1072 (1980).
J. Crain, G.J. Ackland, J.R. Maclean, R.O. Piltz, P.D. Hatton, and G.S. Pawley, Phys. Rev. B 50, 13043 (1994).
P. Haasen and A. Kelly, Acta Metall. Mater. 5, 192 (1957).
V.P. Alekhin, Physica Prochnosti i Plastichnosti Poverkhnostnykh Sloev Materialov (Nauka, Moscow, 1983).
B. Bhushan, A.V. Kulkarni, W. Bonin, and J.T. Wyrobek, Philos. Mag. A 74, 1117 (1996).
T.F. Page, W.C. Oliver, and C.J. McHargue, J. Mater. Res. 7, 450 (1992).
R.J. Nelmes, M.I. McMahon, N.G. Wright, D.R. Allan, and J.S. Loveday, Phys. Rev. B 48, 9883 (1993).
C.S. Menoni, J.Z. Hu, and I.L. Spain, Phys. Rev. B 34, 362 (1986).
C.H. Bates, F. Dachille, and R. Roy, Science 147, 860 (1965).
A. Kailer, Y.G. Gogotsi, and K.G. Nickel, in High Pressure Materials Research, edited by R.M. Wentzcovitch, R.J. Hemley, W.J. Nellis, and P.Y. Yu (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 499, Warrendale, PA, 1998), pp. 225–230.
N.W. Ashcroft and N.D. Mermin, Solid State Physics (Saunders College Publishing, Philadelphia, PA, 1976).
A.B. Chen, A. Sher, and W.T. Yost, in The Mechanical Properties of Semiconductors, edited by K.T. Faber and K. Malloy (Academic Press, London, 1992), Vol. 37, p. 68.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gogotsi, Y.G., Domnich, V., Dub, S.N. et al. Cyclic nanoindentation and Raman microspectroscopy study of phase transformations in semiconductors. Journal of Materials Research 15, 871–879 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2000.0124
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2000.0124