Abstract
Electrolyte supplements may be used to prevent changes in electrolyte balance during hypokinesia (diminished movement). The aim of this study was to measure the effect of potassium (K) supplements on K balance during prolonged hypokinesia (HK).
Studies were done during 30 d of a pre-HK period and during 364 d of an HK period. Forty male athletes aged 25.1±4.4 yr were chosen as subjects. They were divided equally into four groups: unsupplemented ambulatory control subjects (UACS), unsupplemented hypokinetic subjects (UHKS), supplemented hypokinetic subjects (SHKS) and supplemented ambulatory control subjects (SACS). The SHKS and UHKS groups were kept under an average walking distance of 0.7 km/d. The SACS and SHKS groups were supplemented daily with 50.0 mg elemental potassium chloride (KCl) per kilogram body weight.
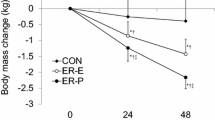
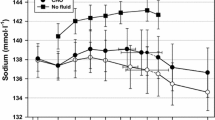
The K balance, fecal K excretion, urinary K, sodium (Na), and chloride (Cl) excretion, plasma K, Na, and Cl concentration, plasma renin activity (PRA) and plasma aldosterone (PA) concentration, anthropometric characteristics and peak oxygen uptake were measured. Negative K balance, fecal K excretion, urinary K, Na, and Cl excretion, plasma K, Na, and Cl concentration, and PRA and PA concentration increased significantly (p≤0.01), whereas body weight and peak oxygen uptake decreased significantly in the SHKS and UHKS groups when compared with SACS and UACS groups. However, the measured parameters changed much faster and much more in SHKS group than UHKS group. By contrast, K balance, fecal, urinary, and plasma K, plasma hormones, body weight, and peak oxygen uptake did not change significantly in the SACS and UACS groups when compared with the baseline control values.
It was concluded that prolonged HK induces a significant negative K balance associated with increased plasma K concentration and urinary and fecal K excretion. However, negative K balance appeared much faster and was much greater in the SHKS group than UHKS group. Thus, K supplementation was not effective in preventing negative K balance during prolonged HK.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. V. Fedorov and L. A. Grishanina, Nitrogen metabolism in animals exposed to hypodynamia, Kosmicheskaya Biol. 1, 43–48 (1967).
I. V. Fedorov, A. V. Chernyy, and A. I. Fedorov, Synthesis and catabolism of tissue proteins during hypodynamia and resumption of muscular activity, Fiziol. Zh. SSR. 63, 1128–1133 (1977).
Y. G. Zorbas, G. E. Verentsov, and Y. F. Federenko, Renal excretion of end products of protein metabolism in urine of endurance trained subjects during restriction of muscular activity, Panminerva Med. 37, 109–114 (1995).
V. P. Krotov, Kinetics and regulation of fluid-electrolyte metabolism in animals and human beings during hypokinesia, Ph.D. thesis, “Interkosmos” Council, Academy of Sciences USSR and Directorate of Kosmic Biology and Meditsine, Ministry of Health USSR, Moscow (1978).
A. I. Grigor’yev, Regulation of fluid-electrolyte metabolism and renal function in man during kosmic flights, Ph.D. thesis, “Interkosmos” Council, Academy of Sciences USSR and Directorate of Kosmic Biology and Meditsine, Ministry of Health USSR, Moscow (1980).
Y. G. Zorbas, N. I. Abratov, and C. B. Stoikolescu, Renal excretion of potassium in men under hypokinesia and physical exercise with chronic hyperhydration, Urologia 53, 229–238 (1988).
Y. G. Zorbas, K. A. Naexu, and Y. F. Federenko, Effect of potassium and calcium loading on healthy subjects under hypokinesia and physical exercise with fluid and salt supplements, Acta Astronaut. 36, 183–189 (1995).
Y. G. Zorbas, K. A. Naexu, and Y. F. Federenko, Potassium changes in trained subjects after potassium loading and during restriction of muscular activity and chronic hyperhydration, Biol. Trace Element Res. 53, 233–245 (1996).
J. H. Lohman, A. F. Roche, and R. Martorell (eds.), Anthropometric Standardization Reference Manual, Human Kinetics, Champaign, IL (1988).
J. Brozek, F. Grande, J. T. Anderson, and A. Keys, Densitometric analysis of body composition, Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 110, 113–140 (1963).
T. M. Lobova, Blood and tissue lipids in hypokinetic rats, Kosmicheskaya Biol. 7, 32–35 (1973).
Yu. P. Ryl’nikov, Hypokinetic effect on the lipid composition of blood tissues of rabbits of different age, Kosmicheskaya Biol. 8, 8–13 (1974).
Y. G. Zorbas and V. M. Petrovskiy, Carbohydrate and lipid metabolism of the heart and liver in rabbits under hypokinetic stress, in Pathogenesis of Stress-Induced Heart Disease, R. E. Beamish, V. Panagia, and N. S. Dhalla, eds., Martinus Nijhoff, Boston, pp 397–404 (1984).
Y. G. Zorbas, A. L. Ivanov, and M. F. Fukuhara, Blood and lipids metabolism in rats under hypokinesia, Mater. Med. Polona 22, 275–279 (1990).
V. A. Tishler, V. M. Zatsiorskiy, and V. N. Seluyanov, Study of mass-inertia characteristics of human body segments during six month hypokinesia by gamma scanning method, Kosmicheskaya Biol. 15, 36–42 (1981).
Y. G. Zorbas, V. R. Bobylev, and A. N. Naexu, Physical exercise in preserving men’s body mass under hypokinesia, Int. J. Rehab. Res. 12, 326–330 (1989).
Y. G. Zorbas, V. R. Bobylev, A. N. Marketi, and Y. F. Federenko, Body mass changes in endurance trained volunteers during prolonged restriction of muscular activity and chronic hyperhydration, Sports Med. Training Rehab. 4, 167–176 (1993).
Ye. V. Gushevas and R. Yu. Tashpulatov, Effect of flights of differing duration on protein composition of cosmonauts blood, Kosmicheskaya Biol. 14, 13–17 (1980).
Y. G. Zorbas, Y. Y. Yaroshenko, O. L. Georgeascu and M. N. Tanaka, Haemoglobin mass in men after hypokinesia and physical exercise with chronic hyperhydration, Model. Simul. Control 21, 43–56 (1990).
Y. G. Zorbas, A. L Ivanov, and Y. K. Imura, Changes in total body potassium, haemoglobin and bromine space after hypokinesia and physical exercise, Mater. Med. Polona 22, 3–303 (1990).
Y. G. Zorbas and I. O. Matvedev, Man’s desirability in performing physical exercises under hypokinesia, Inter. J. Rehab. Res. 9, 1970–1974 (1986).
Y. G. Zorbas, I. O. Matvedev, and V. R. Bobylev, Men’s working capacity under hypokinesia and physical exercise, Model. Simul. Control 18, 37–50 (1988).
V. T. Bakhteyeva, Distinction of potassium excretion by the kidneys of vertebrates, and cellular mechanisms of secretion of potassium, Ph.D. thesis, “Interkosmos” Council, Academy of Sciences USSR and Directorate of Kosmic Biology and Meditsine, Ministry of Health USSR, Moscow (1975).
Yu. V. Natochin, Regulation of potassium by the kidney of animals, Fiziol. Zh. SSSR 48, 1278–1286 (1974).
A. V. Chernyy, Effect of hypodynamia on animals reactions to administration of glucose, epinephrine and insulin referable to some parameters of carbohydrate metabolism, Ph.D. thesis, “Interkosmos” Council, Academy of Sciences USSR and Directorate of Cosmic Biology and Medicine, Ministry of Health USSR, Yaroslav (1974).
B. D. Rose, Clinical Physiology of Acid-Base and Electrolyte Disorders, 2nd ed., McGraw-Hill, New York (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zorbas, Y.G., Kakurin, V.J., Afonin, V.B. et al. Potassium supplements’ effect on potassium balance in athletes during prolonged hypokinetic and ambulatory conditions. Biol Trace Elem Res 78, 93–112 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:78:1-3:93
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:78:1-3:93