Abstract
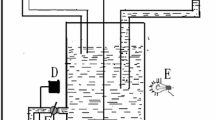
In this study, we investigated the dynamics of a computer simulation of a continuous alcoholic fermentation process combined with a flash column under vacuum. The alcohol was partially extracted in order to maintain its concentration at about 40 kg/m3 in the fermentor. The mathematical model of the fermentation was developed for industrial conditions and considers the effect of the temperature on the kinetic parameters. The performance of the dynamic matrix control algorithm, single input single output and multiple input multiple output, for the control of the extractive process was studied. The concepts of factorial design were used in a simulation study to determine the best control structures for the process.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Dynamic matrix in the DMC algorithm
- b :
-
Coefficients in the step-response model
- C p :
-
Heat capacity (J/[kg·K])
- D=F/V :
-
Dilution rate (h−1)
- E :
-
Activation energy (J/mol)
- f :
-
Weighting factor in the DMC algorithm
- F :
-
Feed stream flow rate (m3/h)
- F c :
-
Cell suspension flow from centrifuge (m3/h)
- F c1 :
-
Cell suspension flow to treatment tank (m3/h)
- F E :
-
Light phase flow rate to flash tank (m3/h)
- F L :
-
Liquid outflow from the vaccum flash tank (m3/h)
- F LR :
-
Liquid phase recycling flow rate (m3/h)
- F LS :
-
Liquid phase flow to rectification column (m3/h)
- F p :
-
Purge flow rate (m3/h)
- F r :
-
Cell recycling flow rate (m3/h)
- F V :
-
Vapor outflow from the vacuum flash tank (m3/h)
- F w :
-
Water flow rate (m3/h)
- F 0 :
-
Fresh medium flow rate (m3/h)
- I :
-
Identity matrix
- J :
-
Performance index
- K i :
-
Equilibrium constant
- K s :
-
Substrate saturation constant (kg/m3)
- n :
-
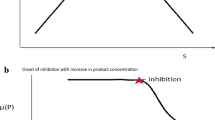
Product inhibition power
- NC :
-
Control horizon in the DMC algorithm
- NP :
-
Prediction horizon in the DMC algorithm
- p :
-
Pressure (Pa)
- p sat i :
-
Vapor pressure (Pa)
- P :
-
Product concentration in the fermentor (kg/m3)
- P F :
-
Product concentration in the feed stream (kg/m3)
- P LR :
-
Product concentration in the light phase from centrifuge (kg/m3)
- P max :
-
Product concentration when cell growth ceases (kg/m3)
- P r :
-
Product concentration in the recycle (kg/m3)
- P v :
-
Product concentration in the vapor phase from flash tank (kg/m3)
- r=L LR/F L :
-
Flash recycle rate
- r p :
-
Kinetic rate of product formation (h−1)
- r s :
-
Kinetic rate of substrate consumption (h−1)
- r x :
-
Kinetic rate of growth (h−1)
- R=F r/F :
-
Cell recycle rate
- R G :
-
Gas constant (8.314 J/[mol·K])
- S :
-
Substrate concentration in the fermentor (kg/m3)
- S F :
-
Substrate concentration in the feed stream (kg/m3)
- S LR :
-
Substrate concentration in the light phase from centrifuge (kg/m3)
- S r :
-
Substrate concentration in the recycle (kg/m3)
- S 0 :
-
Inlet substrate concentration (kg/m3)
- T :
-
Temperature in the fermentor (K)
- T F :
-
Feed stream temperature (K)
- T LR :
-
Light phase temperature (K)
- T r :
-
Recycle temperature (K)
- T w :
-
Water temperature (K)
- T 0 :
-
Inlet temperature of the fresh medium (K)
- x Ei :
-
Component i concentration in the light phase (mol %)
- x i :
-
Component i concentration in the liquid (mol %)
- X :
-
Biomass concentration in the fermentor (kg/m3)
- X c :
-
Cell concentration in the heavy phase from centrifuge (kg/m3)
- X E :
-
Cell concentration in the light phase flow rate to flash tank (kg/m3)
- X F :
-
Cell concentration in the feed stream (kg/m3)
- X LR :
-
Cell concentration in the light phase from centrifuge (kg/m3)
- X r :
-
Cell recycling concentration (kg/m3)
- y :
-
Controlled variable
- y i :
-
Component i concentration in the vapor (mol %)
- Y P/S :
-
Yield constant (kg product/kg substrate)
- Y X/S :
-
Yield constant (kg cell/kg substrate)
- Z :
-
Constant (s−1)
- γ i :
-
Activity coefficient of Component i
- ΔH :
-
Reaction heat (J/kg)
- Δm :
-
Variation in the manipulated variable
- Δmax :
-
Maximum specific growth rate (h−1)
- σ:
-
Density (kg/m3)
References
Ramalingham, A. and Finn, R. K. (1977), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 19, 583–589.
Cysewski, G. R. and Wilke, C. R. (1977), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 19, 1125–1143.
Christen, M., Minier, M., and Renon, H. (1990), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 36, 116–123.
Minier, M. and Goma, G. (1982), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 24, 1565–1579.
Sourirajan, S. (1987), Membrane 12, 367–369.
Ishida, K. and Shimizu, K. (1996), J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 66, 340–346.
Maiorella, B. L., Blanch, H. W., and Wilke, C. R. (1984), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 26, 1003–1025.
Taylor, F., Kurantz, M. J., Goldberg, N., and Craig, J. C. (1998), Biotechnol. Lett. 20, 67–72.
Silva, F. L. H., Rodrigues, M. I., and Maugeri Filho, F. (1999), J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 74, 176–182.
Andrietta, S. R. (1994), DSc thesis, Faculdade de Engenharia de Alimentos, UNICAMP, Campinas, SP, Brazil.
Andrietta, S. R. and Maugeri, F. (1996), in Advances in Bioprocess Engineering, vol. 1, Galindo, E. and Ramirez, O. T., eds., Kluwer Academic, The Netherlands, pp. 47–52.
Alves, J. G. L. F. (1996), DSc thesis, Faculdade de Engenharia de Alimentos, UNICAMP, Campinas, SP, Brazil.
Box, G. E. P., Hunter, W. G., and Hunter, J. S. (1978), Statisties for Experimenters, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Cutler, C. R. and Ramaker, B. L. (1980), Proc. Joint Auto Control Conf., Paper WP5-B, San Francisco.
Luyben, W. L. (1989), Process Modeling, Simulation and Control for Chemical Engineers, 2nd ed., McGraw-Hill, New York.
Dechechi, E. C. (1998), DSc thesis, Faculdade de Engenharia Química, UNICAMP, Campinas, SP, Brazil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costa, A.C., Dechechi, E.C., Silva, F.L.H. et al. Simulated dynamics and control of an extractive alcoholic fermentation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 84, 577–593 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:84-86:1-9:577
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:84-86:1-9:577