Abstract
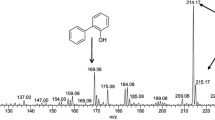
A novel bacterium, Gordonia alkanivorans strain 1B, was isolated from hydrocarbon-contaminated soil. Assessment of the biodegradation of distinct organic sulfur-compounds, such as dibenzothiophene (DBT), benzothiophene (BT), DBT sulfone, and alkylated tiophenic compounds, as the sole source of sulfure was investigated. G. alkanivorans strain 1B was able to remove selectively the sulfur from DBT while keeping intact the remaining carbon-carbon structure. Orthophenyl phenol (2-hydroxybiphenyl) was the only detected metabolic product. The bacterial desulfurization activity was repressed by sulfate. G. alkanivorans straini 1B consumed 310 μM DBT after 120 h of cultivation, corresponding to a specific desulfurization rate of 1.03 μmol/(g of dry cells·h). When an equimolar mixture of DBT/BT was used as a source of sulfur in the growth medium, G. alkanivorans strain 1B assimilated both compounds in a sequential manner, with BT as the preferred source of sulfur. Only when BT concentration was decreased to a very low level was DBT utilized as the source of sulfur for bacterial growth. Thespecific desulfurization overall rates of BT and DBT obtained were 0.954 and 0.813 μmol/(g of dry cells·h), respectively. The newly isolated G. alkanivorans strain 1B has good potential for application in the biodesulfurization of fossil fuels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reichmuth, D. S., Hittle, J. L., Blanch, H. W., and Keasling, J. D. (2000), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 67, 72–79.
Schmidt, M., Siebert, W., and Bagnall, K. W. (1973), The Chemistry of Sulphur Selenium, Tellurium and Polonium: Pergamon Texts in Inorganic Chemistry, vol. 15, Pergamon, Oxford, UK.
Monticello, D. J. (1998), ChemTech 28, 38–45.
Gray, K. A., Mrachko, G. T., and Squires, C. H. (2003), Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 6, 229–235.
Tanaka, Y., Matsui, T., Konishi, J., Maruhashi, K., and Kurane, R. (2002), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 59, 325–328.
Grossman, M. J., Lee, M. K., Prince, R. C., Minak-Bernero V., George, G. N., and Pickering, I. J. (2001), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67, 1949–1952.
Ohshiro, T. and Izumi, Y. (1999), Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 63, 1–9.
Kirimura, K., Furuya, T., Sato, R., Ishii, Y., Kino, K., and Usami, S. (2002), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68, 3867–3872.
Gallagher, J. R., Olson, E. S., and Stanley, D. C. (1993), FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 107, 31–36.
Oldfield, C., Pogrebinsky, O., Simmonds, J., Olson, E. S., and Kulpa, C. F. (1997), Microbiology 143, 2961–2973.
Gilbert, S. C., Morton, J., Buchanan, S., Oldfield, C., and McRoberts, A. (1998), Microbiology 144, 2545–2553.
van Afferden, M., Schacht, S., Klein, J., and Trüper, H. G. (1990), Arch. Microbiol. 153, 324–328.
Kodanna, K., Umehara, K., Shimizu, K., Nakatani, S., Minoda, Y., and Yamada, K. (1973), Agric. Biot. Chem. 37, 45–50.
Konishi, J., Onaka, T., Ishii, Y., and Susuki, M. (2000), FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 187, 151–154.
Kayser, K. J., Cleveland, L., Park, H.-S., Kwak, J.-H., Kolhatkar., A., and Kibane II, J. J. (2002), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 59, 737–745.
Rhee, S. K., Chang, J. H., Chang, Y. K., and Chang, H. N. (1998), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64, 2327–2331.
Chang, J. H., Rhee, S.-K., Chang, Y. K., and Chang, H. N. (1998), Biotechnol. Prog. 14, 851–855.
Kummer, C., Schumann, P., and Stackebrandt, E. (1999), Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 49, 1513–1522.
Ohshiro, T., Suzuki, K., and Izumi, Y. (1996), J. Ferment. Bioeng. 81, 121–124.
Finkel’shtein, Z. I., Baskunov, B. P., Golovlev, E. L., and Golovleva, L. A. (1999), Microbiology 68, 154–157.
Kirimura, K., Furuya, T., Nishii, Y., Ishii, Y., Kino, K., and Usami, S. (2001), J. Biosci. Bioeng. 91, 262–266.
Wang, P. and Krawiec, S. (1994), Arch. Microbiol. 161, 266–271.
Tanaka, Y., Onaka, T., Matsui, T., Maruhashi, K., and Kurane, R. (2001) Curr Microbiol. 43, 187–191.
Kobayashi, M., Onaka, T., Ishii, Y., Konishi, J., Takaki, M., Okada, H., Ohta, Y., Koizumi, K., and Suzuki, M. (2000), FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 187, 123–126.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alves, L., Salgueiro, R., Rodrigues, C. et al. Desulfurization of dibenzothiophene, benzothiophene, and other thiophene analogs by a newly isolated bacterium, Gordonia alkanivorans strain 1B. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 120, 199–208 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:120:3:199
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:120:3:199