Abstract
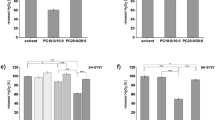
The effect of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), docosahexaenoic acid (22:6n-3; DHA) and arachidonic acid (20:4n-6; AA), on apoptotic cell death was evaluated based on DNA fragmentation and caspase-3 activity induced by serum starvation using Neuro-2A and PC-12 cells. The presence of 20:4n-6 in the medium during serum starvation decreased DNA fragmentation and this initial protective effect was diminished with prolonged serum starvation. The observed protective effect of 20:4n-6 was not affected by the inhibitors of cyclooxygenase (COX) and lipoxygenase. Conversely, 22:6n-3 became protective only after the enrichment of cells with this fatty acid at least for 24 h prior to the serum deprivation. DNA fragmentation as well as caspase-3 activity was reduced in 22:6n-3 enriched cells with a concomitant decrease in protein and mRNA levels. During the enrichment period, 22:6n-3 steadily increased its incorporation into PS leading to a significant increase in the total PS content; the protective effect of 22:6n-3 paralleled the PS accumulation. Neither direct exposure of cells to nor enrichment with 18:1n-9 had any protective effect. In conclusion, it is proposed that 20:4n-6 prevents neuronal apoptosis primarily due to the action of nonesterified 20:4n-6 but 22:6n-3, at least in part, through PS accumulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Das U.N. (1999) Essential fatty acids, lipid peroxidation and apoptosis. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 61(3), 157–163
Dumuis A., Sebben M., Haynes L., Pin J.-P., and Bockaert J. (1988) NMDA receptors activate the arachidonic acid cascade system in striatal neurons. Nature 336, 68–70.
Finstad H. S., Myhrstad M. C., Heimli H., Lomo J., Blomhoff H. K., Kolset S. O., and Drevon C. A. (1998) Multiplication and death-type of leukemia cell lines exposed to very long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. Leukemia 12, 921–929.
Garcia M. C., Ward G., Ma Y. C., Salem N. Jr., and Kim H. Y. (1998) Effect of docosahexaenoic acid on the synthesis of phosphatidylserine in rat brain microsomes and C6 glioma cells. J. Neurochem. 70, 24–30.
Ghosh S., Strum J. C., Sciorra V. A., Daniel L., and Bell R. M. (1996) Raf-1 kinase possesses distinct binding domains for phosphatidylserine and phosphatidic acid. Phosphatidic acid regulates the translocation of Raf-1 in 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-stimulated Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 8472–8480.
Hamilton J., Greiner R., Salem N. Jr., and Kim H. Y. (2000) N-3 fatty acid deficiency decreases phosphatidylserine accumulation selectively in neuronal tissues. Lipids 35, 863–869.
Igarashi M. and Miyazawa T. (2000) Do conjugated eicosapentaenoic acid and conjugated docosahexaenoic acid induce apoptosis via lipid peroxidation in cultured human tumor cells? Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 270, 649–656.
Kim H. Y., Wang T. C., and Ma Y. C. (1994) Liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry of phospholipids using electrospray ionization. Anal. Chem. 66, 3977–3982.
Kim H. Y., Edsall L., Garcia M., and Zhang H. (1999) The release of polyunsaturated fatty acids and their lipoxygenation in the brain. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 447, 75–85.
Kim H. Y. and Edsall L. (1999) The role of docosahexaenoic acid (22:6n-3) in neuronal signaling. Lipids 34, S249-S250.
Kim H. Y. and Hamilton J. (2000) Accumulation of docosahexaenoic phosphatidylserine is selectively inhibited by chronic ethanol exposure in C-6 glioma cells. Lipids 35, 187–195.
Kim H. Y., Akbar M., Lau A., and Edsall L. (2000) Inhibition of neuronal apoptosis by docosahexaenoic acid (22:6n-3): role of phosphatidylserine in antiapoptotic effect. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 35,215–35,223.
Kishida E., Yano M., Kasahara M., and Masuzawa Y. (1998) Distinctive inhibitory activity of docosahexaenoic acid against sphingosine-induced apoptosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1391, 401–408.
Mosior, M. and Newton, A. C. (1998) Mechanism of the apparent cooperativity in the interaction of protein kinase C with phosphatidylserine. Biochemistry 37, 17,271–17,279.
Nagata S. (1997) Apoptosis by death factor. Cell 88, 355–365.
Rotstein N., Aveldano M., Barrantes F., Roccamo A., and Politi L. E. (1997) Apoptosis of retinal photoreceptors during development in vitro: protective effect of docosahexaenoic acid. J. Neurochem. 69, 504–513.
Salem N. Jr. (1989) New protective roles for selected nutrients, in Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Molecular and Biochemical Aspects (Spiller, G. and Scala, J., eds.), Alan R. Liss, New York, NY, pp. 109–228.
Strosznajder, J. and Samochocki, M. (1991) Ca(2+)-independent, Ca(2+)-dependent, and carbachol-mediated arachidonicacid release from rat brain cortex membrane. J. Neurochem. 57, 1198–1206.
Yano M., Kishida E., Iwasaki M., Kojo S., and Masuzawa Y. (2000) Docosahexaenoic acid and vitamin E can reduce human monocytic U937 cell apoptosis induced by tumor necrosis factor. J. Nutr. 130, 1095–1101.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, HY., Akbar, M. & Kim, KY. Inhibition of neuronal apoptosis by polyunsaturated fatty acids. J Mol Neurosci 16, 223–227 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:16:2-3:223
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:16:2-3:223