Abstract
The transcription factors CDX1 and CDX2 are homeobox genes that regulate development of the epithelium of the small and large intestine. A few studies have shown that Cdx2 protein expression is useful in the diagnosis of adenocarcinomas as well as neuroendocrine tumors of the small and large intestine. To examine the utility of Cdx2 in recognizing neuroendocrine tumors of unknown primary sites, we analyzed 224 primary and metastatic neuroendocrine tumors by immunohistochemistry. The specificity of the antibody reaction was confirmed by Western blotting.
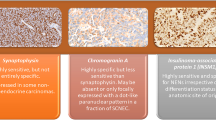
Cdx2 antibody stained all primary and most metastatic midgut carcinoid tumors. A few rectal and pulmonary carcinoids were positive, while gastric carcinoids were negative for Cdx2. One of five small cell carcinomas (20%) of the colon was positive for Cdx2, while all pulmonary small cell carcinomas were negative. Neuroendocrine tumors of the pituitary, parathyroid, medullary thyroid carcinomas, paragangliomas, pheochromocytomas and Merkel cell carcinomas were all negative for Cdx2. Western blot analysis of seven cases showed a 40 kDa band in boht primary and metastatic midgut carcinoid tumors.
These results indicate that Cdx2 can be very useful in recognizing metastatic neuroendocrine carcinomas of unknown primary sites, especially when they are derived from the small intestine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lloyd RV, Osamura RY. Transcription factors in normal and neoplastic pituitary tissues. Review Microsc Res Tech 39:168–181, 1997.
Lau SK, Luthringer DJ, Eisen RN. Thyroid transcription factor-1. A review. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 19:97–102, 2003.
Sebine JN, Malone M. Myogenin and MyoD1 expression in paediatric rhabdomyosarcomas. Review J Clin Pathol 56:412–416, 2003.
Agoff SN, Lamps LW, Philp AT, et al. Thyroid transcription factor-1 is expressed in extrapulmonary small cell carcinomas but not in other extrapulmonary neuroendocrine tumors. Mod Pathol 13:238–242, 2000.
Folpe AL, Gown AM, Lamps LW, et al. Thyroid transcription factor-1: immunohistochemical evaluation in pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors. Mod Pathol 12:5–8, 2000.
Oliveira AM, Tazelaar HD, Myers JL, Erickson LA, Lloyd RV. Thyroid transcription factor-1 distinguishes metastatic pulmonary from well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors of other sites. Am J Surg Pathol 25:815–819, 2001.
Barbareschi M, Murer B, Colby TV, et al. CDX-2 homeobox gene expression is a reliable marker of colorectal adenocarcinoma metastases to the lungs. Am J Surg Pathol 27:141–149, 2003.
Silberg DG, Swain GP, Suh ER, Traber PG. Cdx1 and Cdx2 expression during intestinal development. Gastroenterology 119:961–971, 2000.
Moskaluk CA, Zhang H, Powell SM, Cerilli LA, Hampton GM, Frierson HF, Jr.. Cdx2 protein expression in normal and malignant human tissues: an immunohistochemical survey using tissue microarrays. Mod Pathol 16:913–919, 2003.
LaRosa S, Rigoli E, Uccella S, Capella C. CDX2 is a marker of midgut EC-cell tumors and their metastases. Mod Pathol 17(Supplement 1): 105A (Abstract 434), 2004.
Lin X, Luckasevic T, Silverman JF, et al. Diagnostic Value of CDX-2 and TTF-1 expressions in separating metastatic neuroendocrine neoplasms of unknown origin. Mod Pathol 17 (Supplement 1): 106 (Abstract 435), 2004.
Luckasevic TM, Silverman JF, Medich D, Celebrezze J, Tung MT, Liu YL. Diagnostic value of CDX-2 expression in endocrine neoplasms of gastrointestinal origin. Mod Pathol 17 (Supplement 1): 106A (Abstract 437), 2004.
Barbareshi M, Roldo C, Zamboni G, et al. CDX-2 homeobox gene product expression in neuroendocrine tumors. Its role as a marker of intestinal neuroendocrine tumors. Mod Pathol 17 (Supplement 1): 106 (Abstract 417), 2004.
Subramanian V, Meyer B, Evans GS. The murine Cdx1 gene product localizes to the proliferative compartment in the developing and regenerating intestinal epithelium. Differentiation 64:11–18, 1998.
James R, Kazenwadel J. Homeobox gene expression in the intestinal epithelium of adult mice. J Biol Chem 266:3246–3251, 1991.
Eda A, Osawa H, Satoh K, et al. Aberrant expression of CDX-2 in Barrett’s epithelium and inflammatory esophageal mucosa. J Gastroenterol 38:14–22, 2003.
Almeida R, Silva E, Santos-Silva F, et al. Expression of intestine-specific transcription factors, CDX1 and CDX2, in intestinal metaplasia and gastric carcinomas. J Pathol 199:36–40, 2003.
Werling RW, Yaziji H, Bacchi CE, Gown AM. CDX2, a highly sensitive and specific marker of adenocarcinomas of intestinal origin: an immunohistochemical survey of 476 primary and metastatic carcinomas. Am J Surg Pathol 27:303–310, 2003.
Riss D, Jin L, Qian X, et al. Differential expression of galectin-3 in pituitary tumors. Cancer Res 63:2251–2255, 2003.
Lloyd RV, Vidal S, Jin L, et al. Myosin XVA expression in the pituitary and in other neuroendocrine tissues and tumors. Am J Pathol 159:1375–1382, 2001.
Beck F, Tata F, Chawengsaksophak K. Homebox genes and gut development. Bioessays 22:431–441, 2000.
Lohnes D. The Cdx1 homeodomain protein: an integrator of posterior signaling in the mouse. Bioessays 25:971–980, 2003.
Mitchelmore C, Troelsen JT, Spdsberg N, Sjostrom H, Noren O. Interaction between the homeodomain proteins Cdx2 and HNF1 alpha mediates expression of lactase-phlorizin hydrolase gene. Biochem J 346(Pt 2):529–535, 2000.
Bonhomme C, Duluc I, Martin E, et al. The Cdx2 homeobox gene has a tumour suppressor function in the distal colon in addition to a homeotic role during gut development. Gut 52:1465–1471, 2003.
Pearse AG. The diffuse neuroendocrine system peptides, aminos, placodes and the APUD theory, Prog Brain Res 68:25–31, 1986.
Pearse AG. Calcitonin and the C-cells. Role models for the neuroendocrine system. Bone Miner 16:166–168, 1992.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erickson, L.A., Papouchado, B., Dimashkieh, H. et al. Cdx2 as a marker for neuroendocrine tumors of unknown primary sites. Endocr Pathol 15, 247–252 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1385/EP:15:3:247
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/EP:15:3:247