Abstract
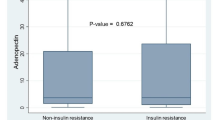
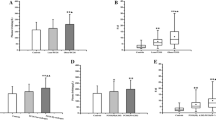
Overproduction of proinflammatory factors is associated with obesity and diabetes. Interleukin (IL)-18 as a member of IL-1 cytokine family is increased in obese, in diabetic, and even in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) patients. In the present study we evaluated the association of serum IL-18 levels with insulin resistance in PCOS women. Forty-two PCOS women and 38 control subjects were enrolled in this study and matched with respect to age and body mass index (BMI). Serum IL-18 levels and hormones were measured for all subjects. Furthermore, euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp test was performed in selected 30 PCOS women and 11 control subjects. Serum IL-18 levels were elevated in PCOS women compared with the control (p=0.003). IL-18 levels were positively correlated with homeostasis model assessment index (HOMA) β index, which assesses β cell function (p=0.035), but were inversely correlated with clamp indices, which best-represent insulin resistance status: M, Clamp ISIS100, and MCRg values (p=0.006, 0.010, and 0.009 respectively). No correlation was found between IL-18 and age, BMI, waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), lipid profile, dehydroepiandrosterone-sulfate (DHEAS), sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG), or fasting insulin levels. In conclusion, in the present study, serum IL-18 levels were significantly increased in PCOS women and firmly associated with insulin resistance displayed by euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp test. It indicates that IL-18 may be a contributing factor linking inflammation and insulin resistance in PCOS women.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Okamura, H., Tsutsi, H., Komatsu, T., Yutsudo, M., and Hakura, A (1995). Nature 378, 88–91.
Dinarello, C. A. (2000). Eur. Cytokine. Netw. 11, 483–486.
Gerdes, N., Sukhova, G. K., Libby, P., and Reynolds, R. S. (2002). J. Exp. Med. 195, 245–257.
Dinarello, C. A. (1999). Methods 19, 121–132.
Nakanishi, K., Hoshimoto, T., Tsutsui, H., and Okamura, H. (2001). Annu. Rev. Immunol. 19, 423–474.
Skurk, T., Kolb, H., Muller-Scholze, S., Rohrig, K., Hauner, H., and Herder, C. (2005). Eur. J. Endocrinol. 152, 863–868.
Mallat, Z., Corbaz, A., Scoazec, A., and Bersnard, S. (2001). Circulation 104, 1598–1603.
Mallat, Z., Corbaz, A., and Scoazec, A. (2001). Circ. Res. 89, e41-e45.
Festa, A., D'Agostino, R. Jr., Howard, G., Mykkänen L, Tracy, R. P., and Haffner, S. M. (2002). Circulation 102, 42–47.
Chen, J., Wildman, R. P., Hamm, L. L., et al. (2004). Diabetes Care 27, 2960–2965.
Sayin, N. C., Gucer, F., Balkanli-Kaplan, P., et al. (2003). J. Reprod. Med. 48, 165–170.
Escobar-Morreale, H. F., Botella-Carretero, J. I., Villaendas, G., Sancho, J., and Millán, J. L. S. (2004). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89, 806–811.
Esposito, K., Pontillo, A., Ciotola, M., et al. (2002). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 87, 3864–3866.
Tsilchorozidou, T., Overton, C., and Conway, G. S. (2004). Clin. Endocrinol. 60, 1–17.
Salehi, M., Bravo-Vera, R., Sheikh, A., Gouller, A., and Poretsky, L. (2004). Metabolism 53, 358–376.
Cibula, D., Škrha, J., Hill, M., and Fanta, M. (2002). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 87, 5821–5825.
Kanazawa, M., Yoshiike, N., Osaka, T., Numba, Y., Zimmet, P., and Inoue, S. (2002). Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 11(Suppl.), S732-S737.
Blankenberg, S., Tiret, L., Bickel, C., and Peetz, D. (2002). Circulation 105, r143-r149.
McInnes, I. B., Gracie, J. A., Leung, B. P., Wei, X. Q., and Liew, F. Y. (2000). Immunol. Today 21, 312–315.
Aso, Y., Wakabayashi, S., Okumura, K., Inukai, T., and Takebayashi, K. (2003). Diabetes Care 26, 2622–2627.
Goodarzi, M. O. and Korenman, S. G. (2003). Fertil. Steril. 80, 255–258.
Orio, F. Jr., Palomba, S., Cascella, T., Simone, B. D., Biase, S. D., and Russo, T. (2004). J. Clin. Endocr. Metab. 89, 4588–4593.
Lakhani, K., Seifalian, A.M., and Hardiman, P. (2002). Circulation 106, 81–85.
Kelly, C. C., Lyall, H., Petrie, J. R., and Gould, G. W. (2001). J. Clin. Endocr. Metab. 86, 2453–2455.
Krook, H., Wallstrom, J., and Sandler, S. (1999). Autoimmunity 29, 263–267.
The Rotterdam ESHRE/ASRM-Sponsored PCOS Conseusus Workshop Group. (2004). Fertil. Steril. 81, 19–25.
Defronzo, R. A., Tobin, J. D., and Andres, R. (1979). Am. J. Physiol. 237, E214-E223.
Soonthornpun, S., Setasuban, W., and Thamprasit, A. (2003). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 88, 1019–1023.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Yf., Yang, Ys., Hong, J. et al. Elevated serum levels of interleukin-18 are associated with insulin resistance in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Endocr 29, 419–423 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:29:3:419
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:29:3:419