Abstract
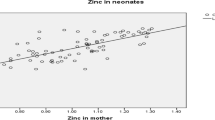
The objective of the present study was to evaluate the potential effects of zinc, copper, and selenium on placental cadmium transport. From November 2002 through January 2003, a total of 47 healthy pregnant women from Da-Ye City, Hubei Province in central China participated in the study. Their age, parity, gestational age, pregnancy history, and lifestyle data were obtained by questionnaire interview. The placental, whole-blood, and cord blood levels of cadmium were determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICP-MS), whole-blood zinc was measured by flame atomic absorption spectrometry (F-AAS), whole-blood copper by ICP-MS, and selenium was by atomic fluorescence spectrophotometry (AFS). The cord blood cadmium concentration (0.020–1.48 μg/L) was significantly lower than in maternal blood (0.80–25.20 μg/L, p<0.01). The placental cadmium concentration was from 0.082 to 3.97 μg/g dry weight. Multiple linear regression analysis indicated that lower levels of maternal blood copper were significantly associated with higher cadmium concentrations in cord blood. Placental cadmium in women with lower levels of maternal blood zinc was significantly higher than in those with normal zinc levels. The placental cadmium level in women with lower whole-blood selenium was significantly lower than in subjects with normal selenium levels. It was concluded that the essential elements copper, selenium, and zinc might significantly affect placental cadmium transport.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Järup, Cadmium overload and toxicity, Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 17, 35–39 (2002).
T. Jin, Q. Kong, T. Ye, et al., Environmental epidemiology: human health impacts caused by cadmium, Chin. J. Environ. Occun. Med., 19, 10–16 (2002) (in Chinese).
S. Cai, L. Yue, T. Jin, and G. Nordberg, Renal dysfunction from cadmium contamination of irrigation water: dose-response analysis in a Chinese population, Bull. World Health Org. 76, 153–159 (1998).
E. F. Madden and B. A. Fowler, Mechanisms of nephrotoxicity from metal combinations: a review, Drug Chem. Toxicol., 23, 1–12 (2000).
M. Berglund, A. Akesson, P. Bjellerup, and M. Vahter, Metal-bone interactions, Toxicol. Lett. 112–113, 219–225 (2000).
T. Alfven, C. G. Elinder, M. D. Carlsson, et al., Low-level cadmium exposure and osteoporosis, J. Bone Miner. Res. 15, 1579–1586 (2000).
G. Nordberg, T. Jin, A. Bernard, et al., Low bone density and renal dysfunction following environmental cadmium exposure in China, Ambio, 31, 478–481 (2002).
T. L. Sorell and J. H. Graziano, Effect of oral cadmium exposure during pregnancy on maternal and fetal zinc metabolism in the rat, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 102, 537–545 (1990).
L. Shen, Q. Fan, X. Ding, and T. Jin, Influence of cadmium exposure during gestation and lactation on the growth and development of the second generation in rats, J. Health Toxicol. 15, 197–200 (2001) (in Chinese).
B. Baranski, Effect of exposure of pregnant rats to cadmium on prenatal and postnatal development of the young, J. Hyg. Epidemiol. Microbiol. Immunol., 29, 253–262 (1984).
S. Zhou, H. Jiang, Z. Shi, Q. Xu, C. Yan, and J. He, Study of effects of cadmium on development of the second generation and kidney function in rats, J. Health Toxicol. 4, 14–17 (1990) (in Chinese).
D. Holt and M. Webb, Comparison of some biochemical effects of teratogenic doses of mercuric mercury and cadmium in the pregnant rat, Arch. Toxicol. 58, 249–254 (1986).
I. Desi, L. Nagymajtenyi, and H. Schulz, Behavioral and neurotoxicological changes caused by cadmium treatment of rats during development, J. Appl. Toxicol. 18, 63–70 (1998).
L. Nagymajtenyi, H. Schulz, and I. Desi, Behavioural and functional neurotoxicological changes caused by cadmium in a three-generational study in rats, Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 16, 691–699 (1997).
U. Fagher, T. Laudanski, A. Schütz, M. Sipowicz, and M. Akerlund, The relationship between cadmium and lead burdens and preterm labor, Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 40, 109–114 (1993).
M. Nishijo, H. Nakagawa, R. Honda, et al., Effects of maternal exposure to cadmium on pregnancy outcome and breast milk, Occup. Environ. Med. 59, 394–397 (2002).
C. D. Salpietro, S. Gangemi, P. L. et al., Cadmium concentration in maternal and cord blood and infant birth weight: a study on healthy non-smoking women, J. Perinat. Med. 30, 395–399 (2002).
R. M. Jacobs, A. O. Jones, M. R. Fox, et al., Effects of dietary zinc, manganese, and copper on tissue accumulation of cadmium by Japanese quail, Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 172, 34–38 (1983).
P. C. Tewari, D. N. Kachru, and S. K. Tandon, Influence of copper and iron on subacute cadmium intoxication in protein-malnourished rats, Environ. Res. 41, 53–60 (1986).
L. B. Nehru and M. P. Bansal, Effect of selenium supplementation on the glutathione redox system in the kidney of mice after chronic cadmium exposures, J. Appl. Toxicol. 17, 81–84 (1997).
R. A. Goyer, Toxic and essential metal interactions, Annu. Rev. Nutr., 17, 37–50 (1997).
M. A. Peraza, F. Ayala-Fierro, D. S. Barber, E. Casarez, and L. T. Rael, Effects of micronutrients on metal toxicity, Environ. Health Perspect. 106, 203–216 (1998).
G. V. Iyengar, Revaluation of the trace element content in reference man, Radiat. Phys. Chem. 51, 545–560 (1998).
I. Baranowska, Lead and cadmium in human placentas and maternal and neonatal blood (in a heavily polluted area) measured by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry, Occup. Environ. Med. 52, 229–232 (1995).
K. Osman, A. Åkesson, M. Berglund, et al., Toxic and essential elements in placentas of Swedish women, Clin. Biochem. 33, 131–138 (2000).
B. Sarkar, Metal-protein interactions in transport, accumulation, and excretion of metals, Biol. Trace Element Res. 21, 136–144 (1989).
W. Y. Boadi, S. Yannai, J. Urbach, J. M. Brandes, and K. H. Summer, Transfer and accumulation of cadmium, and the level of metallothionein in perfused human placentae, Arch. Toxicol. 65, 318–323 (1991).
T. L. Blalock, M. A. Dunn, and R. J. Cousins, Metallothionein gene expression in rats: tissue-specific regulation by dietary copper and zinc, J. Nutr. 118, 222–228 (1988).
I. Bremner, J. N. Morrison, A. M. Wood, and J. R. Arthur, Effects of changes in dietary zinc, copper and selenium supply and of endotoxin administration on metallothionein I concentrations in blood cells and urine in the rat, J. Nutr. 117, 1595–1602 (1987).
T. A. Gasiewicz and J. C. Smith, Properties of the cadmium and selenium complex formed in rat plasma in vivo and in vitro, Chem. Biol. Interact. 23, 171–183 (1978).
L. Jamba, B. Nehru, and M. P. Bansal, Redox modulation of selenium binding proteins by cadmium exposures in mice, Mol. Cell. Biochem. 177, 169–175 (1997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Zhao, Y., Wang, J. et al. Effects of zinc, copper, and selenium on placental cadmium transport. Biol Trace Elem Res 102, 39–49 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:102:1-3:039
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:102:1-3:039