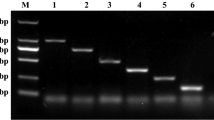
Abstract
Most members of the bacterial family Pasteurellaceae are usually regarded as opportunistic secondary invaders, which under normal conditions might inhabit the mucosal membranes of the upper respiratory and lower genital tracts of mammals and birds (1). Out of the almost 100 species or species-like taxa that might be isolated from mammals, reptiles, and birds, only Pasteurella multocida, Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, and Hemophilus paragallinarum are regarded as major pathogens (1,2) while A. suis, H. somnus, and Mannheimia hemolytica are considered as potential animal pathogens. The pathogenic potential is incompletely known for most taxa, probably due to limitations in their classification and identification, and inappropriate detection methods.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bisgaard, M. (1993) Ecology and significance of Pasteurellaceae in animals. Zbl. Bakt. 279, 7–26.
Bisgaard, M. ( 1995) Taxonomy of the family Pasteurellaceae Pohl 1981, in Haemophilus, Actinobacillus, and Pasteurella (Donachie, W., Lainson, F. A., and Hodgson, J. C., ), Plenum Press, New York, USA, pp. 1–7.
Blackall, P. J. (1999) Infectious coryza: overview of the disease and new diagnostic options. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 12, 627–632.
Harris, F. W. and Janzen, E. D. (1989). The Haemophilus somnus disease complex (Hemophilosis): a review. Can. Vet. J. 30, 816–822.
Ward, A. C. S., Jaworski, M. D., Eddow, J. M., and Corbeil, L. B. (1995) A comparative study of bovine and ovine Haemophilus somnus isolates. Can. J. Vet. Res. 59, 173–178.
Frank, G. H. ( 1989) Pasteurellosis of cattle, in Pasteurella and Pasteurellosis (Adlam, C. and Rutter, J. M., ), Academic Press, London, UK, pp. 197–222.
Gilmour, N. J. L. and Gilmour, J. S. (1989) Pasteurellosis of sheep, in Pasteurella and Pasteurellosis, (Adlam, C. and Rutter, J. M. ), Academic Press, London, UK, pp. 223–262.
Carter, G. R. and De Alwis, M. C. L. (1989) Haemorrhagic septicaemia, in Pasteurella and Pasteurellosis (Adlam, C. and Rutter, J. M. eds.), Academic Press, London, UK, pp. 131–160.
Chanter, N. and Rutter, J. M. ( 1989) Pasteurellosis in pigs and the determinants of virulence of toxigenic Pasteurella multocida, in Pasteurella and Pasteurellosis (Adlam, C., and Rutter, J. M. ), Academic Press, London, UK, pp. 161–195.
Nagai, S., Someno, S. and Yagihashi, T. (1994) Differentiation of toxigenic from nontoxigenic isolates of Pasteurella multocida by PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 32, 1004–1010.
Baalsrud, K. J. (1987) Atrophicrhinitis in goats in Norway. Vet.Rec., 350–353.
DiGiacomo, R. F., Deeb, B. J., Giddens, W. E. Jr., Bernard, B.L., and Chengappa, M.M. (1989) Atrophic rhinitis in New Zealand white rabbits infected with Pasteurella multocida. Am. J. Vet. Res. 50, 1460–1465.
Petersen, S. K. (1990) The complete nucleotide sequence of the Pasteurella multocida toxin gene and evidence for a transcriptional repressor, TxaR. Mol. Microbiol. 4, 821–830.
Christensen, J. P. and Bisgaard, M. (1997) Avian pasteurellosis: taxonomy of the organisms involved and aspects of pathogenesis. Avian Pathol. 26, 461–483.
Amigot, J. A., Torremorell, M. and Pijoan, C. (1998) Evaluation of techniques for the detection of toxigenic Pasteurella multocida strains from pigs. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 10, 169–173.
Townsend, K. M., Hanh, T. X., O’Boyle, D., et al. (2000) PCR detection and analysis of Pasteurella multocida from the tonsils of slaughtered pigs in Vietnam. Vet. Microbiol. 72, 69–78.
Chen, X., Miflin, J. K., Zhang, P. and Blackall, P. J. (1996) Development and application of DNA probes and PCR tests for Haemophilusparagallinarum. Avian Dis. 40, 398–407.
Canto, G. J. and Biberstein, E. L. (1982) Serological diversity in Haemophilus somnus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 15, 1009–1015.
Angen, Ø., Ahrens, P., and Tegtmeier, C. (1998) Development of a PCR test for identification of Haemophilus somnus in pure and mixed cultures. Vet. Microbiol. 63, 39–48.
Tegtmeier, C., Uttenthal, Aa., Friis, N. F., Jensen, N. E., and Jensen H. E. (1999) Pathological and microbiological studies on pneumononic lungs from Danish calves. J. Vet. Med. B 46, 693–700.
Townsend, K. M., Boyce, J. D., Chung, J. Y., Frost, A. J., and Adler, B. (2001) Genetic organization of Pasteurella multocida cap loci and development of a multiplex capsular PCR typing system. J. Clin. Microbiol. 39, 924–929.
Rimler, R. B. and Rhoades, K. R. ( 1989) Pasteurella multocida, in Pasteurella and Pasteurellosis (Adlam, C. and Rutter, J. M., ), Academic Press, London, UK, pp. 37–73.
Townsend, K. M., Frost, A. J., Le, C. W., Papadimitriou, J. M., and Dawkins, H. J. S. (1998) Development of PCR assays for species-and type-specific identification of Pasteurella multocida isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 36, 1096–1100.
Fisher, M. A., Weiser, G. C., Hunter, D. L., Ward, A. C. S. (1999) Use of a polymerase chain reaction method to detect the leukotoxin gene lktA in biogroup and biovariant isolates of Pasteurella hemolytica and P. trehalosi. Am. J. Vet. Res. 60, 1402–1406.
Green, A. L., DuTeau, N. M., Miller, M. W., Triantis, J. M., and Salman, M. D. (1999) Polymerase chain reaction techniques for differentiaitng cytotoxic and noncytotoxic Pasteurella terhalosi form Rocky Mountain bighorn sheep. Am. J. Vet. Res. 60, 583–588.
Miflin, J. K. and Blackall, P. J. (2001) Development of a 23S rRNA based PCR Assay for the identification of Pasteurella multocida. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 33, 216–221.
Kasten, R. W., Carpenter, T. E., Snipes, K. P. and Hirsh, D. C. (1997) Detection of Pasteurella multicida-specific DNA in turkey flocks by use of the polymerase chain reaction. Avian Dis. 41, 676–682.
Brickell, S. K., Thomas, L. M., Long, K. A., Panaccio, M. and Widders, P. R. (1998) Development of a PCR test based on a gene region associated with the pathogenicity of Pasteurella multocida serotype B:2, the causal agent of Haemorrhagic septicaemia in Asia. Vet. Microbiol. 59, 295–307.
Hotzel, H., Erler, W. und Schimmel D. (1997) Nachweis des Dermonekrotoxin-Gens in Pasteurella-multocida-Stämmen mittels Polymerase-Kettenreaktion (PCR). Berl. Münch. Tierärztl. Wschr. 110, 139–142.
Kamp, E. M., Bokken, G. C. A. M., Vermeulen, T. M. M., et al. (1996) A specific and sensitive PCR assay suitable for large-scale detection of toxigenic Pasteurella multocida in nasal and tonsillar swabs specimens of pigs. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 8, 304–309.
Lichtensteiger, C. A., Steenbergen, S. M., Lee, R. M., Polson, D. D. and Vimr, E. R. (1996) Direct PCR analysis for toxigenic Pasteurella multocida. J. Clin. Microbiol. 34, 3035–3039.
Lee, C. W., Wilkie, I. W., Townsend, K. M., and Frost, A. J. (2000) The demonstration of Pasteurella multocida in the alimentary tract of chickens after experimental oral infection. Vet. Microbiol. 72, 47–55.
Tegtmeier, C., Angen, Ø. and Ahrens, P. (2000) Comparison of bacterial cultivation, PCR, in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry as tools for diagnosis of Haemophilus somnus pneumonia in cattle. Vet. Microbiol. 76, 385–394.
Dziva, F., Christensen, H., Olsen, J. E. and Mohan, K. (2002) Random amplification of polymorphic DNA and phenotypic typing of Zimbabwean isolates of Pasteurella multocida. Vet. Microbiol., in press.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F. and Maniatis, T. (1989) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed. CSH Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA.
Leisner, J. J., Pot, B., Christensen, H., et al. (1999) Identification of lactic acid bacteria from Chili Bo, a Malaysian food ingredient. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65, 599–605.
Chen, X., Chen, Q., Zhang, P., Feng, W. and Blackall, P. J. (1998) Evaluation of a PCR test for the detection of Haemophilus paragallinarum in China. Avian Pathol. 27, 296–300.
Appuhamy, S., Parton, R., Coote, J. G. and Gibbs, H. A. (1997) Genomic fingerprinting of Haemophilus somnus by a combination of PCR methods. J. Clin. Microbiol. 35, 288–291.
Petras, S. F., Chidambaram, M., Illyes, E. F., Froshauer, S., Weinstock, G. M. and Reese, C. (1995) Antigenic and virulence properties of Pasteurella hemolytica leukotoxin mutants. Infect. Immunol. 63, 1033–1039
Highlander, S. K., Fedorova, N. D., Dusek, D. M., Panciera, R., Alvarez, L. E. and Rinehart, C. (2000) Inactivation of Pasteurella (Mannheimia) hemolytica leukotoxin causes partial attenuation of virulence in a calf challenge model. Infect. Immunol. 68, 3916–3922.
Murphy, G. L., Whitworth, L. C., Clinkenbeard, K. D. and Clinkenbeard, P.A. (1995) Hemolytic activity of the Pasteurella hemolytica leukotoxin. Infect. Immunol. 63, 3209–3212.
Fedorova, N. D., Highlander, S. K. (1997) Generation of targeted nonpolar gene insertions and operon fusions in Pasteurella hemolytica and creation of a strain that produces and secretes inactive leukotoxin. Infect. Immunol. 65, 2593–2598.
Burrows, L.L., Olah-Winfield, E. and Lo, R. Y. (1993) Molecular analysis of the leukotoxin determinants from Pasteurella hemolytica serotypes 1 to 16. Infect. Immunol. 61, 5001–5007.
Chang, Y. F., Ma, D. P., Shi, J. and Chengappa, M. M. (1993) Molecular characterization of a leukotoxin gene from a Pasteurella hemolytica-like organism, encoding a new member of the RTX toxin family. Infect. Immunol. 61, 2089–2095.
Davies, R. L., Whittam, T. S., and Selander, R. K. (2001) Sequence diversity and molecular evolution of the leukotoxin (lktA) gene in bovine and ovine strains of Mannheimia (Pasteurella) hemolytica. J. Bacteriol. 183, 1394–1404
Biberstein, E. L. and Gills, M. G. (1962) The relationship of the antigenic types of the A and T types of Pasteurella hemolytica. J. Comp. Pathol. 72, 316–320.
Jaworski, M. D., Hunter, D. L. and Ward, A. C. S. (1998) Biovariants of isolates of Pasteurella from domestic and wild ruminants. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 10, 49–55.
Veit, H. P., Wise, D. J., Carter, G. R. and Chengappa, M. M. (1998) Toxin production by Pasteurella granulomatis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 849, 479–484.
Dewhirst, F. E., Paster, B. J., Olsen, I., and Fraser, G. J. (1993) Phylogeny of the Pasteurellaceae as determined by comparison of 16S ribosomal ribonucleic acid sequences. Zbl. Bakt. 279, 35–44.
Townsend, K., Gunawardana, G. A., and Briggs, R. E. (2002) PCR Identification and Typing of Pasteurella Multocida: An Update. Poster 13. International Pasteurellaceae Society Conference. Banff, AB, Canada. May 5-10, 2002.
Jong, M. F. De, Kamp, E., van der Schoot, A., and Banniseth, T. von (1996) Elimination of AR toxinogenic Pasteurella from infected sow herds by a combination of ART vaccination and testing sows with a PCR and ELISA test. Proceedings of the 14th IPVS Congress, Bologna, Italy, 7-10 July 1996. 274
Hunt, M. L., Adler, B. and Townsend, K. M. (2000) The molecular biology of Pasteurella multocida. Vet. Microbiol. 72, 3–25.
Angen, Ø., Ahrens, P. and Leser, T. D. (2001) Development of a PCR test for detection of Haemophilus parasuis. Abstract Z-43. ASM 101 st General Meeting Orlando Florida. ASM, Washington DC, USA.
Van Ostaaijen, J., Frey, J., Rosendal, S., and MacInnes, J. I. (1997). Actinobacillus suis strains isolated from healthy and diseased swine are clonal and carry apxICABD var.suis toxin genes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 35, 1131–1137.
Paul, J. H., and Myers, B. (1982) Fluorometric determination of DNA in aquatic microorganisms by use of Hoechst 33258. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 43, 1393–1399.
Kasten, R. W., Hansen, L. M., Hjinojoza, J., Biebger, D., Ruehl, W. W. and Hirsch, D. C. (1995) Pasteurella multocida produces a protein with homology to the P6 outer membrane protein of Haemophilus influenzae. Infect. Immunol. 63, 989–993.
Christensen, H. Jørgensen, K. and Olsen, J. E. (1999) Differentiation of Campylobacter coli and C. jejuni by length and DNA sequence of the 16S-23S rRNA internal spacer region. Microbiology 145, 99–105.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2003 Humana Press Inc., Totowa, NJ
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Christensen, H., Bisgaard, M., Larsen, J., Elmerdahl Olsen, J. (2003). PCR-Detection of Hemophilus paragallinarum, Hemophilus somnus, Mannheimia (Pasteurella) hemolytica, Mannheimia spp., Pasteurella trehalosi, and Pasteurella multocida. In: Sachse, K., Frey, J. (eds) PCR Detection of Microbial Pathogens. Methods in Molecular Biology™, vol 216. Humana Press. https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-344-5:257
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-344-5:257
Publisher Name: Humana Press
Print ISBN: 978-1-58829-049-6
Online ISBN: 978-1-59259-344-6
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols