Abstract
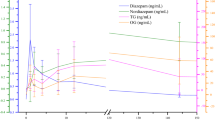
Dizocilpine ([+]-10,11-dihydro-5-methyl-5H-dibenzo[a,d]cyclohepten-5,10-imine), is a potent and selective NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) receptor antagonist, which acts by blocking receptor ion channels. Dizocilpine is pharmacologically related to ketamine and phencyclidine; as such, it has the potential to affect behavior and performance in horses, with particular efficacy at lower concentrations. We now report development of a sensitive method for the detection of dizocilpine and preliminary characterization of its urinary metabolites in the horse. Dizocilpine (MW 221) readily produces a protonated species [M+H]+ in formic acid, and yields a m/z 205 product ion in Multiple Reaction Monitoring (MRM), allowing highly sensitive detection of parent drug. The 17 AMU loss most likely represents an unusual loss of CH5 from the exocyclic methyl group. No unchanged dizocilpine was identified in unhydrolysed urine, and the presence of hydroxymethyl and carboxydizocilpine glucuronide metabolites were supported by observation of m/z 414→238 and 428→235 transitions. Urine samples from horses dosed with dizocilpine (0.0132 and 0.0656 mg kg−1, iv) were hydrolysed with glucuronidase and were found to contain dizocilpine and OH-dizocilpine. Tentatively identified phase I post-hydrolysis compounds include dizocilpine itself, an hydroxymethyl metabolite, two ring-hydroxylated metabolites, a di-hydroxy metabolite, and a carboxy-dizocilpine metabolite. Corresponding Phase II glucuronidated metabolites were also identified as well as a number of combination metabolites and a posssible n-glucuronide metabolite for a total of at least six identifiable urinary glucuronide metabolites. Among the phase I metabolites, the hydroxymethyl metabolite apparently predominated, especially at the 0.0132 mg kg−1 dose. The goal of this research was to identify a target analyte for dizocilpine in post-administration equine urine, so that work may begin on development of a forensically validated qualitative method for this target analyte. Given the likelihood that the doses of dizocilpine used in attempts to influence the behavior or performance of horses, either alone or in combination with other agents, are expected to be in the order of 0.02 mg kg−1 or less, these results suggest selection of the phase I hydroxymethyl metabolite of dizocilpine as the optimal target analyte for regulatory control of dizocilpine in performance horses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hardman JG, Limbird LE (2003) In: Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics: Hardman JG, Limbird LE, Gilman AG (eds.)
Winger G, Hursh SR, Casey KL, Woods JH (2002) J Pharmacol Exp Ther 301:690–697
Elhallaoui M, Laguerre M, Carpy A, Ouazzani FC (2002) J Mol Model 8:65–72
Hassan AA, Schwarzkopf SB (1996) Biol Psychiat 40:744–754
Breese GR, Knapp DJ, Moy SS (2002) Neurosci Biobehav 26:441–455
Rossi S, Yaksh T (2003) J Pharmaceut Biomed 31:243–250
Schwartz PH, Wasterlain CG (1993) J Neurol Sci 115:26–31
Harris LW, Sharp T, Gartlon J, Jones DN, Harrison PJ (2003) Eur J Neurosci 18:1706–1710
Ahmed MM, Yamamoto M, Chikuma T, Rahman MK, Kato T (2003) Neurosci Res 47:177–189
Zhang GH, Yoon YW, Lee KS, Min SS, Hong SK, Park JY, Han HC (2003) Neurosci Lett 351:177–180
Combie J, Blake JW, Nugent E, Tobin T (1982) Clin Chem 28:83–86
Harkins JD, Mundy GD, Stanley S, Woods WE, Rees WA, Thompson KN, Tobin T (1996) Equine Vet J 28:30–37
Foltz RL, Fentiman Jr, AF, Foltz, RB (1980) In: GC-MS Assays for Abused Drugs in Body Fluids: National Institute on Drug Abuse Research Monograph Series, no.32, Rockville, MD, pp 62–89
Bosken J, Lehner AF, Hunsucker A, Harkins JD, Woods WE, Karpiesiuk W, Carter W, Boyles J, Fisher M, Tobin T (2000) Can J Vet Res 64:112–116
Lehner AF, Hughes C, Woods WE, Karpiesiuk W, Harkins JD, Dirikolu L, Holtz C, Bosken J, Carter W, Boyles J, Booze R, Mactutus C, Fisher M, Tobin T (2000) Proceedings of the International Conference of Racing Analysts and Veterinarians 13:420–426
Stevens JC, Fayer JL, Cassidy KC (2001) Drug Metab Dispos 29:289–295
Ghosheh O, Hawes EM (2002) Drug Metab Dispos 30:991–996
Stillwell WG, Sinha R, Tannenbaum SR (2002) Carcinogenesis 23:831–838
Hermann R, Knebel NG, Niebch G, Richards L, Borlak J, Locher M (2003) Eur J Clin Pharmacol 58:795–802
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published as #346 from the Equine Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Program at the Maxwell H. Gluck Equine Research Center and Department of Veterinary Science, University of Kentucky
Published as Kentucky Agricultural Experiment Station Article # 04-14-003 with the approval of the Dean and Director, College of Agriculture and the Kentucky Agricultural Experimental Station
Supported by a grant from the Kentucky Equine Drug Research Council and the Kentucky Racing Commission, Lexington, KY, USA
In Honour of Professor Edward Houghton: A Celebration of 30 Years in Racing Chemistry
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lehner, A., Hughes, C., Harkins, J. et al. Detection and Identification of Dizocilpine and its Major Urinary Metabolites in the Horse: A Preliminary Report. Chromatographia 59 (Suppl 1), S95–S103 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-004-0247-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-004-0247-3