Abstract
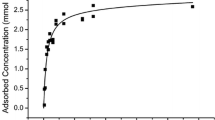
The adsorption of hydroxy-Al by the 2–0•2 µ size fractions of muscovite, biotite, K-depleted micas, vermiculite and montmorillonite was studied. The differences in the amounts of hydroxy-Al adsorbed were apparently related to the expansibility and layer charge of minerals, the ionic saturation and degree of K-depletion, the basicity (OH/Al ratio) of the equilibrating hydroxy-Al solution, and the solution-clay ratio. The CEC reduction was not necessarily proportional to the amount of Al adsorbed because CEC reduction may occur through occupation of cation exchange sites by hydroxy-Al, or through hindrance to the entry of the replacing cation to these sites. Aluminum interlayering generally increases the K/Ca cation exchange selectivity (CES) of Na-vermiculite and K-depleted biotite, whereas the K/Ca CES of Na-montmorillonite was little affected. The basicity of the initial hydroxy-Al solution appeared to affect the K/Ca CES of Na-vermiculite and K-depleted biotite by controlling the amount of hydroxyl-Al adsorbed. The data indicate that in addition to the “propping effect”, hydroxy-Al interlayers may affect the K/Ca CES through the following mechanisms; (1) the “preferential occupation” of Ca adsorbing sites, and/or (2) the “retarding effect” on the entry of the more hydrated Ca ions.
Résumé
On a étudié l’adsorption d’hydroxy-Al par les fractions comprises entre 0,2 et 2 µ des minéraux suivants: muscovite, biotite, micas appauvris en K, vermiculite et montmorillonite. Les différences trouvées dans les quantités d’hydroxy-Al adsorbé sont apparemment reliées à l’aptitude au gonflement et à la charge du minéral, à la saturation ionique et au degré de remplacement du potassium, à la basicité (rapport OH/A1) de la solution d’hydroxy-Al en équilibre, et au rapport solution-argile. La réduction de CEC n’est pas néessairement proportionnelle à la quantité d’aluminium adsorbé du fait que cette réduction de CEC peut provenir soit de l’occupation des sites d’échange cationique par l’hydroxy-Al, soit de l’obstacle créé à l’accès des cations échangeurs à ces sites. L’aluminium placé dans l’espace interfeuillet augmente en général la sélectivité d’échange cationique (CES) K/Ca pour la vermiculite-Na et la biotite appauvrie en K, tandis que la CES K/Ca pour la montmorillonite Na est peu affectée. La basicité de la solution initiale d’hydroxy-Al semble affecter la CES K/Ca de la vermiculite-Na et de la biotite appauvrie en K, en contrôlant la quantité d’hydroxy-Al adsorbé. Les données indiquent qu’en plus d’un “effet de cale”, l’hydroxy-Al interfeuillet peut affecter la CES K/Ca par les mécanismes suivants; (1) occupation préférentielle des sites d’adsorption du calcium, et/ou (2) effet retardateur sur l’entrée des ions Ca plus hydratés.
Kurzreferat
Die Adsorption von Hydroxy-Al durch 2–0•2 µ Grösse Fraktionen von Muskowit, Biotit, K-armem Glimmer, Vermiculit und Montmorillonit wurde untersucht, Die Unterschiede in den Mengen von adsorbiertem Hydroxy-Al standen offenbar in einer Beziehung zu der Expandibilität und Schichtladung der Minerale, der ionischen Sättigung und dem Mass an K-Verarmung, der Basizität (OH/Al Verhältnis) der abgleichenden Hydroxy-Al Lösung und dem Verhältnis Lösung/ Ton. Die Verminderung der CEC war nicht unbedingt proportional der Menge von absorbiertem Al weil ja eine Verminderung der CEC durch Besetzung von Kationenaustauschstellen durch Hydroxy-Al, oder durch Verhinderung des Zutrittes der Ersatzkationen an diese Stellen erfolgen kann. Zwischenlagerung von Aluminium erhöhte im allgemeinen die K/Ca Kationenaustauschselektivität (CES) von Na-Vermiculit and K-armen Biotit, während die K/Ca CES von Na-Montmorillonit wenig berührt war. Die Basizität der ursprünglichen Hydroxy-Al Lösung schien einen Einfluss auf die K/Ca CES von Na-Vermiculit und K-armem Biotit auszuüben durch Steuerung der Menge von adsorbiertem Hydroxy-Al. Die Messwerte deuten daraufhin, dass die Hydroxy-Al Zwischenschichten neben ihrer “Stützwirkung” die K/Ca CES durch die folgenden Mechanismen beeinflussen können: (1) die “Vorzugsbesetzung” von Ca-adsorbierenden Stellen, bzw. (2) die “verzögernde Wirkung” auf den Zutritt der stärker hydratisierten Ca-Ionen.
Резюме
Изучен характер поглощения гидрокси–Аl фракциями 2–0,2 мк мусковита, биотита, слюды с пониженным содержанием К, вермикулита и монтмориллонита. Различия в количестве поглощенного гидрокси–Аl оказались связанными со способностью к разбуханию и зарядом слоев минералов, ионным насыщением и степенью дефицита К, основностью (отношение ОН/Аl) равновесного раствора гидрокси–Аl и отношением раствор — глина. Уменьшение катионно-обменной емкости (КОЕ) не было обязательно пропорционально количеству поглощенного Аl, поскольку уменьшение КОЕ может происходить вследствие заселения положений обменных катионов гидрокси–Аl или является результатом затрудненного вхождения обменных катионов. Внедрение алюминия между слоями обычно увеличивает избирательность катионного обмена K/Са в Na-вермикулите и биотите с дефицитом K, в то время как избирательность катионного обмена K/Са в Na-монтмориллоните изменяется очень незначительно. Основность исходного раствора гидрокси–Аl, как оказалось, влияет на избирательность катионного обмена K/Са в Na-вермикулите и биотите с дефицитом K, контролируя количество поглощенного гидрокси–Аl. Полученные данные свидетельствуют о том, что помимо «эффекта закрепления» межслоевой гидрокси–Аl может воздействовать на избирательность катионного обмена К/Са по следующим механизмам: 1) посредством «предпочтительного заселения» положений адсорбированного Са, и/или 2) вследствие «эффекта замедления» вхождения более гидратированных ионов Са.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexiades, C. A. and Jackson, M. L. (1965) Quantitative determination of vermiculite in soils: Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 29, 522–527.
Carstea, D. D. (1968) Formation of hydroxy-Al and -Fe interlayers in montmorillonite and vermiculite: Influence of particle size and temperature: Clays and Clay Minerals 16, 231–238.
Dixon, J. B. and Jackson, M. L. (1962) Properties of intergradient chlorite-expansible layer silicates of soils: Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 26, 358–362.
Dolcater, D. L., Lotse, E. G., Syers, J. K. and Jackson, M. L. (1968) Cation exchange selectivity of some clay-sized minerals and soil materials: Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 32, 795–798.
Frink, C. R. (1965) Characterization of aluminum interlayers in soil clays: Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 29, 379–382.
Flsu, Pa Ho (1963) Effect of initial pH, phosphate, and silicate on the determination of aluminum with aluminon: Soil Sci. 96, 230–238.
Hsu, Pa Ho and Rich, C. I. (1960) Aluminum fixation in a synthetic cation exchanger: Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 24, 21–25.
Hsu, Pa Ho and Bates, T. F. (1964a) Formation of X-ray amorphous and crystalline aluminum hydroxides: Miner. Mag. 33, 749–768.
Hsu, Pa Ho and Bates, T. F. (1964b) Fixation of hydroxyaluminum polymers by vermiculite: Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 28, 763–769.
Huang, P. M. and Kozak, L. M. (1970) Adsorption of hydroxy-aluminum polymers by muscovite andbiotite: Nature 228, 1084–1085.
Jackson, M. L. (1956) Soil chemical analysis — advanced course: Mimeo. published by the author, Madison, Wise.
Jackson, M. L. (1963) Interlayering of expansible layer silicates in soils by chemical weathering: Clays and Clay Minerals 11, 29–46.
Pratt, P. F. (1965) Digestion with hydrofluoric and perchloric acids for total K and Na: In Methods of Soil Analysis (C. A. Black (Editor-in-Chief)), American Society of Agronomy, Inc., Madison, Wise.
Reed, M. G. and Scott, A. D. (1966) Chemical extraction of potassium from soils and micaceous minerals with solutions containing sodium tetraphenylboron — IV. Muscovite: Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 30, 185–188.
Rich, C. I. (1968) Hydroxy interlayers in expansible layer silicates: Clays and Clay Minerals 16, 15–30.
Rich, C. I. and Black, W. R. (1964) Potassium exchange as affected by cation size, pH, and mineral structure: Soil Sci. 97, 384–390.
Schachtschabel, P. (1940) Untersuchungen über die Sorption der Tonmineralien und organischen Bodenkolloide, und die Bestimmung des Anteils Kolloide an der Sorption in Böden: Kolloid-Beih 51, 199–276.
Schwertmann, U. (1962) Die Selective Kationensorption der Tonfraction einiger Böden aus Sedimenten: Z. Pflanzenernähr Dung. Bodenk. 97, 9–25.
Scott, A. D. and Reed, M. G. (1962) Chemical extraction of potassium from soils and micaceous minerals with solutions containing sodium tetraphenylboron—II. Biotite: Soil Sei. Soc. Am. Proc. 26, 41–45.
Scott, A. D. and Smith, S. J. (1966) Susceptibility of interlayer potassium in micas to exchange with sodium: Clays and Clay Minerals 14, 69–81.
Wiklander, L. (1964) Cation and anion exchange phenomena. In Chemistry of the Soil (Edited by F. E. Bear) p. 163–205. Reinhold, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Contribution No. R62, Saskatchewan Institute of Pedology, Department of Soil Science, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Sask., Canada.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kozak, L.M., Huang, P.M. Adsorption of Hydroxy-Al by Certain Phyllosilicates and its Relation to K/Ca Cation Exchange Selectivity. Clays Clay Miner. 19, 95–102 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.1971.0190205
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.1971.0190205