Abstract
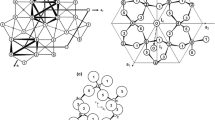
Completeness of exchange of K from muscovite by Ba2+ ions decreased with particle size below 20 µ. Accompanying K exchange at 120°C, using a repeated batch technique, was a marked loss of Si and the formation of boehmite in the finer fractions. Several possible explanations for the unexpected high K retention of fine mica fractions are discussed. The formation of a diffusion-inhibiting surface “skin” is discounted, because equilibrium was obtained more rapidly with the fine fractions than with coarser fractions. The average degree of bending of unit mica layers due to peripheral expansion is probably greater in large particles. With bending, rotation of tetrahedra and shifting of adjacent layers with respect to each other may induce greater release of K and a lower selectivity for this ion. Fault planes may induce preferential expansion of individual layers and initiate interstratification and splitting of particles. Splitting of particles may reduce bending and increase K selectivity.
Résumé
L’achèvement de l’échange du K à partir du muscovite par les ions Ba2+ diminuait pour des dimensions de particule inférieures à 20 µ. L’échange de K à 120°C, au moyen d’une technique de charge répétée, s’accompagnait d’une perte importante de Si ainsi que de la formation de boehmite dans les fractions les plus fines. On discute plusieurs explications possibles de la rétention anormalement élevée des fractions fines de mica. On rejette la possibilité de la formation d’une “peau” à la surface qui empêcherait la diffusion parce que l’équilibre s’obtenait plus rapidement avec les fractions fines qu’avec les fractions plus grossières. Le degré moyen de pliure des couches uniformes de mica en raison de l’expansion périphérique est probablement moins important dans le cas des grandes paricules. Avec la pliure, la rotation des tétrahèdres et le déplacement des couches adjacentes par rapport l’une à l’autre peuvent avoir pour résultat une libérati on plus importante de K et une sélectivité réduite pour cet ion. Des plans de défauts peuvent avoir pour résultat une expansion préférentielle des couches individuelles et initier l’interstratification et la fente des particules. La fente des particules est susceptible de réduire la pliure et d’augmenter la sélectivité au K.
Kurzreferat
Es wurde eine Abnahme in der Vollständigkeit des K-Austausches im Muskowit durch Ba2+ Ionen bei Teilchengrössen von unter 20 µ festgestellt. Bei wiederholtem Satzbetrieb war der K-Austausch bei 120°C von einem deutlichen Si Verlust und einer Bildung von Boehmit in den feineren Fraktionen begleitet. Verschiedene mögliche Erklärungen für die unerwartet hohe Festhaltung des K in feinen Glimmerfraktionen werden erörtert. Die Bildung einer diffusions verhindernden “Oberflächenhaut” kommt nicht in Frage, da sich bei den feinen Fraktionen ein Gleichgewichtszustand schneller einstellt als bei den gröberen Fraktione. Das durchschnittliche Mass der Biegung von Einzelglimmerschichten infolge einer Expansion am Aussenumfang ist vermutlich bei grösseren Teilchen mehr ausgeprägt. Die durch das Biegen bedingte Drehung der Tetraeder und Verschiebung benachbarter Schichten gegeneinander kann eine vermehrte Freigabe von K und geringere Selektivität für dieses Ion zur Folge haben. Fehlerebenen können zu besonderer Expansion einzelner Schichten führen und Zwischenlagerung sowie Abspaltung von Teilchen mit sich bringen. Die Abspaltung von Teilchen kann die Biegung vermindern und die K Selektivität erhöhen.
Резюме
Обмен К+ мусковита на Ва2+ понижается при размере частиц менее 20мк. Параллельно с обменом К при 120°С происходят заметная потеря Si и образование бёмита в более мелких фракциях. Обсуждается возможность удержания К мелкими фракциями слюды. Исключается образование поверхностной «кожи», предотвращающей диффузию, так как равновесие достигается намного быстрее в мелких фракциях, чем в более грубых. Средняя степень изгиба слоев слюды вследствие периферического расширения, вероятно, больше в крупных частицах. По мере изгибания, вращение тетраэдров и относительное смещение соседних слоев могут вызвать большее выделение К и более низкую селективность для этого иона. Плоскости нарушения могут быть причиной преимущественного расширения отдельных слоев и вызывать интерстратификацию, а также расщепление частиц. Последнее может уменьшить изгиб частиц и увеличить селективность в отношении К.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassett, W. A. (1959) The origin of the vermiculite deposit at Libby, Montana: Am. Mineralogist 44, 282–299.
Brown, J., and Rich, C. I. (1968) High resolution electron microscopy of muscovite: Science 161, 1135–1137.
Burns, A. F., and White, J. L. (1963) The effect of potassium removal on the b-dimension of muscovite and dioctahedral soil mica: Proc. 1st Int. Clay Conf. I, 195–201.
Correns, C. W. (1961) The experimental chemical weathering of silicates: Clay Minerals Bull. 4, 249–265.
Haan, F. A. M. de, Bolt, G. H., and Pieters, B. G. M. (1965) Diffusion of potassium-40 into an illite during prolonged shaking: Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 29, 528–530.
Jackson, M. L., and Sherman, G. D. (1953) Chemical weathering of minerals in soils: Advan. Agron. 5, 219–318.
Leonard, R. A., and Weed, S. B. (1967) Influence of the exchangeable ions on the b-dimensions of dioctahedral vermiculite: Clays and Clay Minerals 15, 149–161. [Pergamon Press, New York].
Mortland, M. M. (1958) Kinetics of potassium release from biotite: Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 22, 503–508.
Mortland, M. M., and Lawton, K. (1961) Relationships between particle size and potassium release from biotite and its analogues: Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 25, 473–476.
Radoslovich, E. W. (1963) Cell dimension studies on layer lattice silicates, A summary: Clays and Clay Minerals 11, 225–228. [Pergamon Press, New York].
Raussell-Colom, J. A., Sweatman, T. R., Wells, C. B., and Norrish, K. (1965) Studies in the artificial weathering of mica: In Experimental Pedology, (Edited by E. G. Hellsworth and D. V. Crawford), Butterworths, London, 40–72.
Reed, M. G., and Scott, A. D. (1962) Kinetics of potassium release from biotite and muscovite in sodium tetraphenylboron solutions: Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 26, 437–440.
Reed, M. G., and Scott, A. D. (1966) Chemical extraction of potassium from soils and micaceous minerals with solutions containing sodium tetraphenylboron: IV. Muscovite: Soil Sci. Soc.Am. Proc. 30, 185–188.
Reichenbach, H. Graf von (1968) Cation exchange in the interlayers of expansible layer silicates: Clay Minerals 7, 331–341.
Reichenbach, H. Graf von, and Rich, C. I. (1968) Preparation of dioctahedral vermiculites from muscovite and subsequent exchange properties: Trans. 9th Int. Congr. Soil Sci. 1, 709–719.
Scott, A. D. (1968) Effect of particle size on interlayer potassium exchange in micas: Trans. 9th Int. Congr. Soil Sci. 3, 649–660.
Scott, A. D., and Reed, M. G. (1962a) Chemical extraction of potassium from soils and micaceous minerals with solutions containing sodium tetraphenylboron: II. Biotite: Soil Sci. Soc.Am. Proc. 26, 41–45.
Scott, A. D., and Reed, M. G. (1962b) Chemical extraction of potassium from soils and micaceous minerals with solutions containing sodium tetraphenylboron: III. lllite: Soil Sci. Soc.Am. Proc. 26, 45–48.
Scott, A. D., and Reed, M. G. (1966) Expansion of potassium depleted muscovite: Clays and Clay Minerals 13, 247–261.
Shapiro, L., and Brannock, W. W. (1956) Rapid analysis of silicate rocks: U.S. Geol. Surv. Bull. 1036C, 19–55.
Walker, G. F. (1963) The cation exchange reaction in vermiculite: Proc. 1st Int. Clay Conf. I, 177–181.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Support for this work by a grant (GP-5074) from the National Science Foundation is gratefully acknowledged.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
von Reichenbach, H.G., Rich, C.I. Potassium Release from Muscovite as Influenced by Particle Size. Clays Clay Miner. 17, 23–29 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.1969.0170105
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.1969.0170105