Abstract
Introduction
Timing of autologous reconstruction relative to postmastectomy radiation therapy (PMRT) is debated. Benefits of immediate reconstruction must be weighed against a possibly heightened risk of complications from flap irradiation. We reviewed flap outcomes after single operation plus PMRT in a large institutional cohort.
Methods
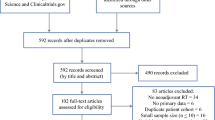
Medical records were reviewed for women who underwent simultaneous mastectomy–autologous reconstruction with PMRT from 2007 to 2016. Primary endpoints were rates and types of radiation-related flap complications and reoperations, whose predictors were assessed by multivariable analysis. A p value < 0.10 was deemed significant to avoid type II error. Non-parametric logistic regression generated a model of PMRT timing associated with probabilities of complications and reoperations.
Results
One-hundred and thirty women underwent 208 mastectomy reconstruction operations, with a median follow up of 35.1 months (interquartile range 23.6–56.5). Forty-seven (36.2%) women experienced radiation-related complications, commonly fat necrosis (44.1%) and chest wall asymmetry (28.8%). Complications were higher among women who received PMRT < 3 months after surgery (46.8% for < 3 months vs. 29.3% for ≥ 3 months; p = 0.06), most of whom received neoadjuvant chemotherapy, and among women treated with internal mammary nodal (IMN) radiation (65.2% vs. 26.4%; p < 0.01); IMN radiation remained strongly associated in multivariable analysis (odds ratio [OR] 5.24; p < 0.01). Thirty-two (24.6%) women underwent 70 reoperations, commonly fat grafting (51.9%) and fat necrosis excision (17.1%). Reoperations were higher among women who received PMRT < 3 months after surgery (48.9 for < 3 months vs. 36.6 for ≥ 3 months; p = 0.19), which was significantly associated in multivariable analysis (OR 0.42; p = 0.08 for ≥ 3 months). The probabilities of complications and reoperations were lowest when PMRT was administered ≥ 3 months after surgery.
Conclusions
Among a large institutional cohort, immediate autologous reconstruction was associated with similar rates of adverse flap outcomes as historically reported alternatively sequenced protocols. IMN radiation increased risk, while PMRT ≥ 3 months after surgery decreased risk. Additional studies are needed to elaborate the impact of IMN radiation and early PMRT in immediate versus delayed autologous reconstruction.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN). NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology for Breast Cancer, Version 1.2019. Available at: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast.pdf. Accessed 22 Mar 2019.
Recht A, Comen EA, Fine RE, et al. Postmastectomy radiotherapy: an American Society of Clinical Oncology, American Society for Radiation Oncology, and Society of Surgical Oncology focused guideline update. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2016;6:219–34.
Hellman S. Stopping metastases at their source. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:996–7.
Overgaard M, Hansen PS, Overgaard J, et al. Postoperative radiotherapy in high-risk premenopausal women with breast cancer who receive adjuvant chemotherapy. Danish Breast Cancer Cooperative Group 82b Trial. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:949–55.
Overgaard M, Jensen MB, Overgaard J, et al. Postoperative radiotherapy in high-risk postmenopausal breast-cancer patients given adjuvant tamoxifen: Danish Breast Cancer Cooperative Group DBCG 82c randomised trial. Lancet. 1999;353:1641–8.
Ragaz J, Olivotto IA, Spinelli JJ, et al. Locoregional radiation therapy in patients with high-risk breast cancer receiving adjuvant chemotherapy: 20-year results of the British Columbia randomized trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97:116–26.
Recht A, Edge SB, Solin LJ, et al. Postmastectomy radiotherapy: clinical practice guidelines of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:1539–69.
Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative. Effect of radiotherapy after mastectomy and axillary surgery on 10-year recurrence and 20-year breast cancer mortality: meta-analysis of individual patient data for 8135 women in 22 randomised trials. Lancet. 2014;383:2127–35.
Olivotto IA, Whelan TJ, Parpia S, et al. Interim cosmetic and toxicity results from RAPID: a randomized trial of accelerated partial breast irradiation using three-dimensional conformal external beam radiation therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(32):4038–45.
Burt LM, Ying J, Poppe MM, et al. Risk of secondary malignancies after radiation therapy for breast cancer: comprehensive results. Breast. 2017;35:122–9.
Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Estimating the Risks of Breast Cancer Radiotherapy: evidence from modern radiation doses to the lungs and heart and from previous randomized trials. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(15):1641–9.
Darby SC, Ewertz M, McGale P, et al. Risk of ischemic heart disease in women after radiotherapy for breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(11):987–98.
Henson KE, McGale P, Taylor C, Darby SC. Radiation-related mortality from heart disease and lung cancer more than 20 years after radiotherapy for breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2013;108(1):179–82.
Jagsi R, Momoh AO, Qi J, et al. Impact of radiotherapy on complications and patient-reported outcomes after breast reconstruction. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017;110(2):157–65.
Ho AY, Hu ZI, Mehrara BJ, Wilkins EG. Radiotherapy in the setting of breast reconstruction: types, techniques and timing. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:742–53.
Billig J, Jagsi R, Qi J, et al. Should immediate autologous breast reconstruction be considered in women who require post-mastectomy radiation therapy? A prospective analysis of outcomes. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;139:1279–88.
Zhong T, Hu J, Bagher S, et al. A comparison of psychological response, body image, sexuality, and quality of life between immediate and delayed autologous tissue breast reconstruction: a prospective long-term outcome study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016;138(4):772–80.
Kelley BP, Ahmed R, Kidwell KM, et al. A systematic review of morbidity associated with autologous breast reconstruction before and after exposure to radiotherapy: are current practices ideal? Ann Surg Oncol. 2014;21:1732–8.
Berbers J, Baardwijk AV, Houben R, et al. Reconstruction: Before or after postmastectomy radiotherapy? A systematic review of the literature. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50:2752–62.
Kronowitz SJ, Hunt KK, Kuerer HM, et al. Delayed-immediate breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004;113:1617–28.
Tran NV, Chang DW, Gupta A, et al. Comparison of immediate and delayed free TRAM flap breast reconstruction in patients receiving postmastectomy radiation therapy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001;108:78–82.
Schaverien MV, Macmillan RD, McCulley SJ. Is immediate autologous breast reconstruction with postoperative radiotherapy good practice? A systematic review of the literature. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2013;66:1637–51.
Veld EH, Long C, Sue G, et al. Analysis of aesthetic outcomes and patient satisfaction after delayed-immediate autologous breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 2018;80(5):303–7.
Yoon AP, Alfred P, Qi J, et al. Outcomes of immediate versus delayed breast reconstruction: results of a multicenter prospective study. Breast. 2018;37:72–9.
ACS-NSQIP. American College of Surgeon National Surgical Quality Improvement Program. Available at: https://www.facs.org/~/media/files/quality%20programs/nsqip/nsqip_puf_userguide_2017.ashx. Accessed 22 March 2019.
Fischer JP, Wes AM, Tuggle CT, et al. Risk analysis and stratification of surgical morbidity after immediate breast reconstruction. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;217:780–7.
Moore DS, McCabe GP, Craig BA. Introduction to the practice of statistics, 8th edn. New York: W.H. Freeman and Company; 2018.
Atisha D, Alderman AK, Lowery JC, et al. Prospective analysis of long-term psychosocial outcomes in breast reconstruction: two-year postoperative results from the Michigan breast reconstruction outcomes study. Ann Surg. 2008;247(6):1019–28.
Hu ES, Pusic, AL, Waljee, JF. Patient-reported aesthetic satisfaction with breast reconstruction during the long-term survivorship period. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;124(1):1–8.
Sullivan S, Fletcher D, Isom C, Isik F. True incidence of all complications following immediate and delayed breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008;122(1):19–28.
Beugels J, Hoekstra LT, Tuinder SM. Complications in unilateral versus bilateral deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flap breast reconstructions: a multicentre study. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2016;69(9):1291–8.
Singh P, Hoffman K, Schaverien MV, et al. Neoadjuvant radiotherapy to facilitate immediate breast reconstruction: a systematic review and current clinical trials. Ann Surg Oncol. 2019;26:3312–20.
Zhang L, Jin K, Wang X, et al. The impact of radiotherapy on reoperation rates in patients undergoing mastectomy and breast reconstruction. Ann Surg Oncol. 2019;26(4):961–8.
Hofer S. Damen T, Mureau M, et al. A critical review of perioperative complications in 175 free deep inferior epigastric perforator flap breast reconstructions. Ann Plast Surg. 2007;59(2):137–42.
Shechter S, Arad E, Inbal A, et al. DIEP flap breast reconstruction complication rate in previously irradiated internal mammary nodes. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2018;34(06):399–403.
Sadideen H, Cleator S, McNaught P, et al. The safety of early adjuvant internal mammary lymph node irradiation following mastectomy and immediate autologous reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2018;141(3):467e–8e.
Tsoutsou PG, Koukourakis MI, Azria D, Belkacémi Y. Optimal timing for adjuvant radiation therapy in breast cancer: A comprehensive review and perspectives. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2009;71(2):102–16.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Brigid K. Killelea, was a member of the Advisory Board for Genentech, August 2017, to discuss data from the APHINITY trial; however, she does not believe this represents a conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heller, D.R., Zhuo, H., Zhang, Y. et al. Surgical Outcomes of Mastectomy with Immediate Autologous Reconstruction Followed by Radiation. Ann Surg Oncol 28, 2169–2179 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-020-09122-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-020-09122-0