Abstract
Background
Staging laparoscopy (SL) is often used to diagnose peritoneal metastasis in patients with advanced gastric cancer, but accurate detection of metastasis can be difficult. We evaluated the usefulness of laparoscopic narrow-band imaging (NBI) versus conventional laparoscopic white-light imaging (WLI) for the diagnosis of peritoneal metastasis.
Methods
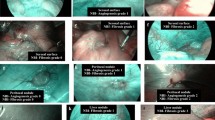
We excised 37 white nodules from the parietal peritoneum of 26 patients with gastric cancer and suspected peritoneal metastasis. The WLI and NBI findings were compared with the pathological findings. All the peritoneal lesions examined were observed as white nodules on WLI. Intranodular vessels were evaluated by WLI and NBI for (1) vessel dilatation, (2) vessel tortuousness, (3) vessel heterogeneity, and (4) brown spots.
Results
Each individual abnormal finding had a diagnostic accuracy of less than 79 % with or without NBI. Detection of any one abnormal finding had a sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of 47.8, 85.7, and 62.2 %, respectively, on WLI and 91.3, 71.4, and 83.8 %, respectively, on NBI, for detection of peritoneal metastasis. Detection of any one abnormal finding on NBI plus clear demarcation of the nodule on WLI had a sensitivity of 91.3 %, specificity of 92.9 %, and accuracy of 91.9 % for detection of peritoneal metastasis. Pathological examination showed that a brown spot detected on NBI correlated with dilated vessels around cancer cells. Vascular endothelial growth factor was expressed in 76.2 % of peritoneal metastases.
Conclusions
NBI was more sensitive for the detection of dilated vessels than WLI. NBI could be a useful tool for the diagnosis of peritoneal metastasis during SL.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Broll R, Weschta M, Windhoevel U, et al. Prognostic significance of free gastrointestinal tumor cells in peritoneal lavage detected by immunocytochemistry and polymerase chain reaction. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2001;386:285–92.
Sugarbaker PH, Yonemura Y. Clinical pathway for the management of resectable gastric cancer with peritoneal seeding: best palliation with a ray of hope for cure. Oncology. 2000;58:96–107.
Lee CC, Lo SS, Wu CW, et al. Peritoneal recurrence of gastric adenocarcinoma after curative resection. Hepatogastroenterology. 2003;50:1720–2.
Ina K, Kataoka T, Takeuchi Y, et al. Pathological complete response induced by the combination therapy of S-1 and 24-h infusion of cisplatin in two cases initially diagnosed as inoperable advanced gastric cancer. Oncol Rep. 2008;20:259–64.
Ishizone S, Maruta F, Saito H, et al. Efficacy of S-1 for patients with peritoneal metastasis of gastric cancer. Chemotherapy. 2006;52:301–7.
Okabe H, Ueda S, Obama K, Hosogi H, Sakai Y. Induction chemotherapy with S-1 plus cisplatin followed by surgery for treatment of gastric cancer with peritoneal dissemination. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16:3227–36.
Tamura S, Miki H, Okada K, et al. Pilot study of intraperitoneal administration of paclitaxel and oral S-1 for patients with peritoneal metastasis due to advanced gastric cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. 2008;13:536–40.
Soma D, Kitayama J, Konno T, et al. Intraperitoneal administration of paclitaxel solubilized with poly(2-methacryloxyethyl phosphorylcholine-co n-butyl methacrylate) for peritoneal dissemination of gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 2009;100:1979–85.
Ishigami H, Kitayama J, Otani K, et al. Phase I pharmacokinetic study of weekly intravenous and intraperitoneal paclitaxel combined with S-1 for advanced gastric cancer. Oncology. 2009;76:311–4.
Ishigami H, Kitayama J, Kaisaki S, et al. Phase I study of biweekly intravenous paclitaxel plus intraperitoneal cisplatin and paclitaxel for gastric cancer with peritoneal metastasis. Oncology. 2010;79:269–72.
Ishigami H, Kitayama J, Kaisaki S, et al. Phase II study of weekly intravenous and intraperitoneal paclitaxel combined with S-1 for advanced gastric cancer with peritoneal metastasis. Ann Oncol. 2010;21:67–70.
Zhu ZG, Tang R, Yan M, et al. Efficacy and safety of intraoperative peritoneal hyperthermic chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer patients with serosal invasion: a long-term follow-up study. Dig Surg. 2006;23:93–102.
Glockzin G, Schlitt HJ, Piso P. Peritoneal carcinomatosis: patients selection, perioperative complications and quality of life related to cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy. World J Surg Oncol. 2009;7:5.
Smyth EC, Shah MA. Role of (1)(8)F 2-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography in upper gastrointestinal malignancies. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17:5059–74.
Contreras CM, Stanelle EJ, Mansour J, et al. Staging laparoscopy enhances the detection of occult metastases in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 2009;100:663–9.
Chang L, Stefanidis D, Richardson WS, Earle DB, Fanelli RD. The role of staging laparoscopy for intraabdominal cancers: an evidence-based review. Surg Endosc. 2009;23:231–41.
Shim JH, Yoo HM, Lee HH, et al. Use of laparoscopy as an alternative to computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans for the detection of recurrence in patients with gastric cancer: a pilot study. Surg Endosc. 2011;25:3338–44.
Jerby BL, Milsom JW. Role of laparoscopy in the staging of gastrointestinal cancer. Oncology (Williston Park). 1998;12:1353–60.
Lehnert T, Rudek B, Kienle P, Buhl K, Herfarth C. Impact of diagnostic laparoscopy on the management of gastric cancer: prospective study of 120 consecutive patients with primary gastric adenocarcinoma. Br J Surg. 2002;89:471–5.
Gono K, Obi T, Yamaguchi M, et al. Appearance of enhanced tissue features in narrow-band endoscopic imaging. J Biomed Opt. 2004;9:568–77.
Muto M, Horimatsu T, Ezoe Y, et al. Narrow-band imaging of the gastrointestinal tract. J Gastroenterol. 2009;44:13–25.
Kaise M, Kato M, Urashima M, et al. Magnifying endoscopy combined with narrow-band imaging for differential diagnosis of superficial depressed gastric lesions. Endoscopy. 2009;41:310–5.
Goda K, Tajiri H, Ikegami M, Urashima M, Nakayoshi T, Kaise M. Usefulness of magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging for the detection of specialized intestinal metaplasia in columnar-lined esophagus and Barrett’s adenocarcinoma. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007;65:36–46.
Nakayoshi T, Tajiri H, Matsuda K, Kaise M, Ikegami M, Sasaki H. Magnifying endoscopy combined with narrow band imaging system for early gastric cancer: correlation of vascular pattern with histopathology (including video). Endoscopy. 2004;36:1080–4.
Yoshida T, Inoue H, Usui S, Satodate H, Fukami N, Kudo SE. Narrow-band imaging system with magnifying endoscopy for superficial esophageal lesions. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004;59:288–95.
Hirata M, Tanaka S, Oka S, et al. Magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging for diagnosis of colorectal tumors. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007;65:988–95.
Kondo K, Kaneko T, Baba M, Konno H. VEGF-C and VEGF-A synergistically enhance lymph node metastasis of gastric cancer. Biol Pharm Bull. 2007;30:633–7.
Kim SJ, Kim HH, Kim YH, et al. Peritoneal metastasis: detection with 16- or 64-detector row CT in patients undergoing surgery for gastric cancer. Radiology. 2009;253:407–15.
Kitayama J, Ishigami H, Yamaguchi H, Yamashita H, Emoto S, Kaisaki S. S-1 plus intravenous and intraperitoneal Paclitaxel for gastric cancer with peritoneal metastasis. Gastrointest Cancer Res. 2012;5:S10–3.
Nekarda H, Gess C, Stark M, et al. Immunocytochemically detected free peritoneal tumour cells (FPTC) are a strong prognostic factor in gastric carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 1999;79:611–9.
Kodera Y, Nakanishi H, Ito S, et al. Quantitative detection of disseminated free cancer cells in peritoneal washes with real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction: a sensitive predictor of outcome for patients with gastric carcinoma. Ann Surg. 2002;235:499–506.
Sakakura C, Takemura M, Hagiwara A, et al. Overexpression of dopa decarboxylase in peritoneal dissemination of gastric cancer and its potential as a novel marker for the detection of peritoneal micrometastases with real-time RT-PCR. Br J Cancer. 2004;90:665–71.
Watanabe A, Taniguchi M, Tsujie H, Hosokawa M, Fujita M, Sasaki S. The value of narrow band imaging endoscope for early head and neck cancers. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008;138:446–51.
Watanabe A, Taniguchi M, Tsujie H, Hosokawa M, Fujita M, Sasaki S. The value of narrow band imaging for early detection of laryngeal cancer. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2009;266:1017–23.
Muto M, Nakane M, Katada C, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma in situ at oropharyngeal and hypopharyngeal mucosal sites. Cancer. 2004;101:1375–81.
Kumagai Y, Inoue H, Nagai K, Kawano T, Iwai T. Magnifying endoscopy, stereoscopic microscopy, and the microvascular architecture of superficial esophageal carcinoma. Endoscopy. 2002;34:369–75.
Yao K, Oishi T, Matsui T, Yao T, Iwashita A. Novel magnified endoscopic findings of microvascular architecture in intramucosal gastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002;56:279–84.
Chiu HM, Chang CY, Chen CC, et al. A prospective comparative study of narrow-band imaging, chromoendoscopy, and conventional colonoscopy in the diagnosis of colorectal neoplasia. Gut. 2007;56:373–9.
Su MY, Hsu CM, Ho YP, Chen PC, Lin CJ, Chiu CT. Comparative study of conventional colonoscopy, chromoendoscopy, and narrow-band imaging systems in differential diagnosis of neoplastic and nonneoplastic colonic polyps. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:2711–6.
Machida H, Sano Y, Hamamoto Y, et al. Narrow-band imaging in the diagnosis of colorectal mucosal lesions: a pilot study. Endoscopy. 2004;36:1094–8.
Fushida S, Oyama K, Kinoshita J, et al. VEGF is a target molecule for peritoneal metastasis and malignant ascites in gastric cancer: prognostic significance of VEGF in ascites and efficacy of anti-VEGF monoclonal antibody. Oncotargets Ther. 2013;6:1445–51.
Yoshikawa T, Tsuburaya A, Miyagi Y, et al. Up-regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha and VEGF mRNAs in peritoneal dissemination of patients with gastric cancer. Anticancer Res. 2006;26:3849–53.
DISCLOSURES
Hirotoshi Kikuchi, Kinji Kamiya, Yoshihiro Hiramatsu, Shinichiro Miyazaki, Masayoshi Yamamoto, Manabu Ohta, Satoshi Baba, and Hiroyuki Konno have no conflicts of interest or funding to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kikuchi, H., Kamiya, K., Hiramatsu, Y. et al. Laparoscopic Narrow-Band Imaging for the Diagnosis of Peritoneal Metastasis in Gastric Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 21, 3954–3962 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-014-3781-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-014-3781-8