Abstract
Background
L1 cell adhesion molecule (L1CAM), which belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily, has recently been observed in a variety of human malignancies. However, its clinical implication in gastric cancer remains unclear. The aim of this study was to explore the role of L1CAM in gastric cancer and to analyze its correlation with tumor progression and prognosis.
Methods
L1CAM expression was measured in human gastric cancer cell lines and knockdown was conducted using siRNA. Cell proliferation, invasion and migration ability was assessed in vitro. The downstream pathway of L1CAM was explored by western blot analysis. L1CAM expression was measured in 112 pairs of human gastric cancer and adjacent noncancerous tissues using real-time quantitative RT-PCR, and the correlation with clinicopathological features and prognosis was analyzed.
Results
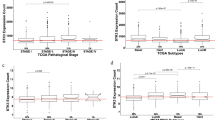
L1CAM downregulation by siRNA significantly decreased cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in gastric cancer cell lines. Phosphorylated ERK levels began to decline more rapidly in L1CAM knockdown cells compared with parental cells. L1CAM overexpression was significantly correlated with local tumor cell growth (P = 0.041), distant metastasis (P = 0.047), and tumor stage (P = 0.031). The overall survival in patients with high L1CAM expression was significantly shorter than that of patients with low L1CAM expression (P = 0.02).
Conclusions
L1CAM overexpression may be a critical prognostic factor in patients with gastric cancer, and was strongly associated with tumor proliferation, migration, and invasion through the ERK pathway. L1CAM might be an attractive therapeutic molecular target for the treatment of gastric cancer patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90.
Sakuramoto S, Sasako M, Yamaguchi T, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy for gastric cancer with S-1, an oral fluoropyrimidine. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:1810–20.
Koizumi W, Narahara H, Hara T, et al. S-1 plus cisplatin versus S-1 alone for first-line treatment of advanced gastric cancer (SPIRITS trial): a phase III trial. Lancet Oncol. 2008;9:215–21.
Moos M, Tacke R, Scherer H, et al. Neural adhesion molecule L1 as a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily with binding domains similar to fibronectin. Nature. 1988;334:701–3.
Thies A, Schachner M, Moll I, et al. Overexpression of the cell adhesion molecule L1 is associated with metastasis in cutaneous malignant melanoma. Eur J Cancer. 2002;38:1708–16.
Fogel M, Gutwein P, Mechtersheimer S, et al. L1 expression as a predictor of progression and survival in patients with uterine and ovarian carcinomas. Lancet. 2003;362:869–75.
Bondong S, Kiefel H, Hielscher T, et al. Prognostic significance of L1CAM in ovarian cancer and its role in constitutive NF-kappaB activation. Ann Oncol. 2012;23:1795–802.
Boo Y-J, Park J-M, Kim J, et al. L1 expression as a marker for poor prognosis, tumor progression, and short survival in patients with colorectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14:1703–11.
Tischler V, Pfeifer M, Hausladen S, et al. L1CAM protein expression is associated with poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer. 2011;10:127.
Gavert N, Conacci-Sorrell M, Gast D, et al. L1, a novel target of beta-catenin signaling, transforms cells and is expressed at the invasive front of colon cancers. J Cell Biol. 2005;168:633–42.
Shtutman M, Levina E, Ohouo P, et al. Cell adhesion molecule L1 disrupts E-cadherin-containing adherens junctions and increases scattering and motility of MCF7 breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2006;66:11370–80.
Schaefer AW, Kamiguchi H, Wong EV, et al. Activation of the MAPK signal cascade by the neural cell adhesion molecule L1 requires L1 internalization. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:37965–73.
Silletti S, Yebra M, Perez B, et al. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)-dependent gene expression contributes to L1 cell adhesion molecule-dependent motility and invasion. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:28880–8.
Cheng L, Lemmon S, Lemmon V. RanBPM is an L1-interacting protein that regulates L1-mediated mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. J Neurochem. 2005;94:1102–10.
Izumoto S, Ohnishi T, Arita N, et al. Gene expression of neural cell adhesion molecule L1 in malignant gliomas and biological significance of L1 in glioma invasion. Cancer Res. 1996;56:1440–4.
Suzuki T, Izumoto S, Fujimoto Y, et al. Clinicopathological study of cellular proliferation and invasion in gliomatosis cerebri: important role of neural cell adhesion molecule L1 in tumour invasion. J Clin Pathol. 2005;58:166–71.
Stoeck A, Gast D, Sanderson MP, et al. L1-CAM in a membrane-bound or soluble form augments protection from apoptosis in ovarian carcinoma cells. Gynecologic Oncol. 2007; 104:461–9.
Wolterink S, Moldenhauer G, Fogel M, et al. Therapeutic antibodies to human L1CAM: functional characterization and application in a mouse model for ovarian carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2010; 70:2504–15.
Gavert N. Expression of L1-CAM and ADAM10 in human colon cancer cells induces metastasis. Cancer Res. 2007;67:7703–12.
Meier F, Busch S, Gast D, et al. The adhesion molecule L1 (CD171) promotes melanoma progression. Int J Cancer. 2006;119:549–55.
Geismann C, Morscheck M, Koch D, et al. Up-regulation of L1CAM in pancreatic duct cells is transforming growth factor beta1- and slug-dependent: role in malignant transformation of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 2009;69:4517–26.
Sebens Muerkoster S, Werbing V, Sipos B, et al. Drug-induced expression of the cellular adhesion molecule L1CAM confers anti-apoptotic protection and chemoresistance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells. Oncogene. 2007;26:2759–68.
Kodera Y, Nakanishi H, Ito S, et al. Expression of L1 cell adhesion molecule is a significant prognostic factor in pT3-stage gastric cancer. Anticancer Res. 2009;29:4033–9.
Raveh S, Gavert N, Ben-Ze’ev A. L1 cell adhesion molecule (L1CAM) in invasive tumors. Cancer Lett. 2009;282:137–45.
Siesser PF, Maness PF. L1 cell adhesion molecules as regulators of tumor cell invasiveness. Cell Adh Migr. 2009;3:275–7.
Hai J, Zhu C-Q, Bandarchi B, et al. L1 cell adhesion molecule promotes tumorigenicity and metastatic potential in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:1914–24.
Gavert N, Ben-Shmuel A, Raveh S, Ben-Ze’ev A. L1-CAM in cancerous tissues. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2008;8:1749–57.
Kohno M, Pouyssegur J. Targeting the ERK signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Ann Med. 2006;38:200–11.
Gavert N, Ben-Shmuel A, Lemmon V, et al. Nuclear factor-kappa B signaling and ezrin are essential for L1-mediated metastasis of colon cancer cells. J Cell Sci. 2010;123:2134–42.
Ebeling O, Duczmal A, Aigner S, et al. L1 adhesion molecule on human lymphocytes and monocytes: expression and involvement in binding to alpha v beta 3 integrin. Eur J Immunol. 1996;26:2508–16.
Arlt MJE, Novak-Hofer I, Gast D, et al. Efficient inhibition of intra-peritoneal tumor growth and dissemination of human ovarian carcinoma cells in nude mice by anti-L1-cell adhesion molecule monoclonal antibody treatment. Cancer Res. 2006;66:936–43.
Gast D, Riedle S, Issa Y, et al. The cytoplasmic part of L1-CAM controls growth and gene expression in human tumors that is reversed by therapeutic antibodies. Oncogene. 2008;27:1281–9.
Schafer H, Dieckmann C, Korniienko O, et al. Combined treatment of L1CAM antibodies and cytostatic drugs improve the therapeutic response of pancreatic and ovarian carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2012;319:66–82.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig. S1
Silencing of L1CAM by siRNA knockdown in representative cell lines. The mRNA levels of L1CAM in L1CAM and parental KATOIII, MKN1, MKN74, SC-6-JCK and MKN28 cells were confirmed by real-time PCR with GAPDH serving as a loading control (a). The protein levels of L1CAM in these cells were confirmed by western blot analysis with β-actin as a loading control (b, c). Cont: Control (PPT 388 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, T., Yamada, S., Tanaka, C. et al. Overexpression of L1CAM is Associated with Tumor Progression and Prognosis via ERK Signaling in Gastric Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 21, 560–568 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-013-3246-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-013-3246-5