Abstract
Objective
T-cell lymphomas (TCLs) classically have a poorer response to therapy when compared with B-cell lymphomas and account for only 10–15% of all lymphoid malignancies. Hepatosplenic TCLs are a rare subset of this group that usually present with hepatosplenomegaly, B-symptoms, and only rarely with lymphadenopathy.
Background
This disease process, also known as gamma/delta (γ/δ) TCL because of the expression of the T-cell receptor γ/δ chain, tends to present in young male patients. Hepatosplenic TCLs have recently gained notoriety because of the realization that patients with long-term treatment of some immunomodulators can develop this potentially fatal disease. These facts are exacerbated by the fact that patients with this disease rarely enjoy remissions of more than brief duration with common chemotherapeutic agents or bone marrow transplants. A novel agent, pralatrexate, has recently been found to have a dramatic activity in this patient population with refractory/relapsed disease. Unfortunately, patients with hepatosplenic TCL often present with thrombocytopenia and this new agent is contraindicated in these patients because of the potential exacerbation of thrombocytopenia with this agent.
Methods
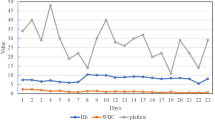
Because of this we attempted a laparoscopic-assisted splenectomy in one patient with grade 4 thrombocytopenia.
Results
Postoperatively the patient’s thrombocytopenia resolved, permitting him to begin treatment with this potentially life-saving agent.
Conclusion
Due to the lethality of this disease and potential efficacy of new therapies, we believe splenectomy should be considered in patients with hepatosplenic lymphoma in an effort to improve the treatment options and survival of patients with this challenging disease.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
O’Connor OA. Pralatrexate: an emerging new agent with activity in T-cell lymphomas Curr Opin Oncol. 2006;18(6):591–7.
Weidmann E. Hepatosplenic T cell lymphoma. A review on 45 cases since the first report describing the disease as a distinct lymphoma entity in 1990 Leukemia. 2000;14(6):991–7.
Moleti ML, Testi AM, Giona F, et al. Gamma-delta hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma. Description of a case with immunophenotypic and molecular follow-up successfully treated with chemotherapy alone Leuk Lymphoma. 2006;47(2):333–6.
Sallah S, Smith SV, Lony LC, Woodard P, Schmitz JL, Folds JD. Gamma/delta T-cell hepatosplenic lymphoma: review of the literature, diagnosis by flow cytometry and concomitant autoimmune hemolytic anemia Ann Hematol. 1997;74(3):139–42.
Veres G, Baldassano RN, Mamula P. Infliximab therapy for pediatric Crohn’s disease Expert Opin Biol Ther. Dec 2007;7(12):1869–80.
Veres G, Baldassano RN, Mamula P. Infliximab therapy in children and adolescents with inflammatory bowel disease Drugs. 2007;67(12):1703–23.
O’Connor OA, Hamlin P. New drugs for the treatment of advanced-stage diffuse large cell lymphomas Semin Hematol. Oct 2006;43(4):251–61.
O’Connor OA, Hamlin PA, Portlock C, et al. Pralatrexate, a novel class of antifol with high affinity for the reduced folate carrier-type 1, produces marked complete and durable remissions in a diversity of chemotherapy refractory cases of T-cell lymphoma Br J Haematol. 2007;139(3):425–8.
Rosh JR, Gross T, Mamula P, Griffiths A, Hyams J. Hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma in adolescents and young adults with Crohn’s disease: a cautionary tale? Inflamm Bowel Dis. Aug 2007;13(8):1024–30.
Mackey AC, Green L, Liang LC, Dinndorf P, Avigan M. Hepatosplenic T cell lymphoma associated with infliximab use in young patients treated for inflammatory bowel disease J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. Feb 2007;44(2):265–7.
Isaacson PG. Primary splenic lymphoma Cancer Surv. 1997;30:193–212.
Chen JH, Chan DC, Lee HS, et al. Spontaneous splenic rupture associated with hepatosplenic gammadelta T-cell lymphoma J Formos Med Assoc. 2005;104(8):593–6.
Farcet JP, Gaulard P, Marolleau JP, et al. Hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma: sinusal/sinusoidal localization of malignant cells expressing the T-cell receptor gamma delta Blood. Jun 1 1990;75(11):2213–9.
Gumbs AA, Bouhanna P, Bar-Zakai B, Briennon X, Gayet B. Laparoscopic partial splenectomy using radiofrequency ablation. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech. 2008;18(4):611–3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1245/s10434-009-0566-6
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gumbs, A.A., Zain, J. & O’Connor, O.A. Importance of Early Splenectomy in Patients with Hepatosplenic T-Cell Lymphoma and Severe Thrombocytopenia. Ann Surg Oncol 16, 2014–2017 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-009-0470-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-009-0470-0