Abstract
Background
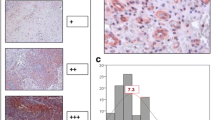
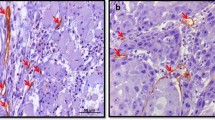
The presence of intratumoral lymphatic vessels (ILVs) and the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor-C (VEGF-C) in tumour cells have been studied as markers of lymphangiogenesis in order to evaluate their role in metastatic dissemination in laryngopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma.
Methods
A retrospective study was performed in 76 patients of N0 laryngopharyngeal carcinoma. with variable tumour size (T1-T4), histological grade, and location (supraglottic, glottic and hypopharyngeal). The presence of ILVs, as revealed by the expression of PA2.26 antigen and VEGF-C expression, were determined by immunohistochemistry (IHC). Low-grade and high-grade lymphangiogenesis were defined by qualitative and quantitative criteria.
Results
Multivariate analysis revealed low-grade ILV and VEGF-C expression to be associated respectively with 30.3- and 16.2-fold higher probabilities of cervical lymph node relapse (P = 0.005 and P = 0.032) and with 16.2- and 8.44-fold shorter disease-free survival (P = 0.009 and P = 0.045).
Conclusions
Low-grade ILV and VEGF-C expression are independent predictive factors of cervical lymph node relapse and shortening of time to relapse in N0 laryngopharyngeal carcinoma.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Bray F, Sankila R, Parkin DM. (1999) EUCAN: Cancer Incidence, Mortality and Prevalence in the European Union, version 4.0. IARC Cancer Base No 4. Lyon, IARC Press
Stacker SA, Baldwin ME, Achen MG. The role of tumor lymphangiogenesis in metastatic spread. FASEB J 2002; 16:922–34
Ruoslahti E. How cancer spreads. Sci Am 1996; 275:72–7
Gallo O, Boddi V, Bottai GV, Parrella F, Fini Storchi O. Treatment of the clinically negative neck in laryngeal cancer patients. Head Neck 1996; 18:566–72
Franchi A, Gallo O, Boddi V, Santucci M. Prediction of occult neck metastases in laryngeal carcinoma: role of proliferating cell nuclear antigen, MIB-1, and E-cadherin immunohistochemical determination. Clin Cancer Res 1996; 2:1801–8
Takes RP, Baatenburg de Jong RJ, Schuuring E, Hermans J, Vis AA, Litvinov SV, van Krieken JH. Markers for assessment of nodal metastasis in laryngeal carcinoma. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1997; 123:412–9
Nathanson SD. Insights into the mechanisms of lymph node metastasis. Cancer 2003; 98:413–23
Greene FL, Page Dl, Fleming ID, et al (2002). AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. TNM, Sixth Edition. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Martín-Villar E, Scholl FG, Gamallo C, et al. Characterization of human PA2.26 antigen (T1α-2, podoplanin), a small membrane mucin induced in oral squamous cell carcinomas. Int J Cancer 2005; 113:899–910
Jussila L, Alitalo K. Vascular growth factors and lymphangiogenesis. Physiol Rev 2002; 82:673–700
Jussila L, Valtola R, Partanen TA, et al. Lymphatic endothelium and Kaposi’s sarcoma spindle cells detected by antibodies against the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3. Cancer Res 1998; 58:1599–1604
Kaipainen A, Korhonen J, Mustonen T, et al. Expression of the fms-like tyrosine kinase 4 gene becomes restricted to lymphatic endothelium during development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92:3566–70
Partanen TA, Arola J, Saaristo A, et al. VEGF-C and VEGF-D expression in neuroendocrine cells and their receptor, VEGFR-3, in fenestrated blood vessels in human tissues. FASEB J 2000; 14:2087–96
Valtola R, Salven P, Heikkila P, et al. VEGFR-3 and its ligand VEGF-C are associated with angiogenesis in breast cancer. Am J Pathol 1999; 154:1381–90
Breiteneder-Geleff S, Soleiman A, Kowalski H, et al. Angiosarcomas express mixed endothelial phenotypes of blood and lymphatic capillaries: podoplanin as a specific marker for lymphatic endothelium. Am J Pathol 1999; 154:385–94
Wigle JT, Oliver G. Prox 1 function is required for the development of the murine lymphatic system. Cell 1999; 98:769–78
Carreira CM, Nasser SM, di Tomaso E, Padera TP, Boucher Y, Tomarev SI, Jain RK. LYVE-1 is not restricted to the lymph vessels: expression in normal liver blood sinusoids and down-regulation in human liver cancer and cirrhosis. Cancer Res 2001; 61:8079–84
Banerji S, Ni J, Wang SX, et al. LYVE-1, a new homologue of the CD44 glycoprotein, is a lymph-specific receptor for hyaluronan. J Cell Biol 1999; 144:789–801
Muñoz-Guerra MF, Marazuela EG, Martín-Villar E, Quintanilla M, Gamallo C. Prognostic significance of intratumoral lymphangiogenesis in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. A study of the early stages. Cancer 2004; 100:553–60
Scholl FG, Gamallo C, Vilaró S, Quintanilla M. Identification of PA2.26 antigen as a novel cell-surface mucin-type glycoprotein that induces plasma membrane extensions and increased motility in keratinocytes. J Cell Sci 1999; 112:4601–13
Rishi AK, Joyce-Brady M, Fisher J, et al. Cloning, characterization, and development expression of a rat lung alveolar type I cell gene in embryonic endodermal and neural derivatives. Dev Biol 1995; 167:294–306
Breiteneder-Geleff S, Matsui K, Soleiman A, et al. Podoplanin, novel 43-kd membrane protein of glomerular epithelial cells, is down-regulated in puromycin nephrosis. Am J Pathol 1997; 151:1141–52
Pepper MS, Tille C, Nasato R, Skobe M. Lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis. Cell Tissue Res 2003; 314:167–77
Lohela M, Saaristo A, Veikkola T, Alitalo K. Lymphangiogenic growth factors receptors and therapies. Thromb Haemost 2003; 90:167–84
Cassella M, Skobe M. Lymphatic vessel activation cancer. Ann NY Acad Sci 2002; 979:120–30
Beasley NJP, Prevo R, Banerji S, et al. Intratumoral lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis in head and neck cancer. Cancer Res 2002; 62:1315–20
O-Charoenrat P, Rhys-Evans P, Eccles SA. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor family members in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma correlates with lymph node metastasis. Cancer 2001; 92:556–68
Neuchrist C, Erovic BM, Handisurya A, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor C and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 expression in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Head Neck 2003; 25: 464–74
Homer JJ, Greenman J, Stafford ND. The expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and VEGF-C in early laryngeal cancer: relationship with radioresistance. Clin Otolaryngol 2001; 26:498–504
Homer JJ, Prentice MG, Cawkwell L, Birchall M, Greenman J, Stafford ND. Angiogenesis and the expression of vascular endothelial growth factors A and C in squamous cell carcinoma of the piriform fossa. Arch Otorlayngol Head Neck Surg 2003; 129:1110–4
He Y, Karpanen T, Alitalo K. Role of lymphangiogenic factors in tumor metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta 2004; 1654:3–12
Mandriota SJ, Jussila L, Jeltsch M, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor-C-mediated lymphangiogenesis promotes tumour metastasis. EMBO J 2001; 20:672–82
Skobe M, Hawighorst T, Jackson DG, et al. Induction of tumor lymphangiogenesis by VEGF-C promotes breast cancer metastasis. Nat Med 2001; 7: 192–8
Mattila MM, Ruohola JK, Karpanen T, Jackson DG, Alitalo K, Härkönen PL. VEGF-C induced lymphangiogenesis is associated with lymph node metastasis in orthotopic MCF-7 tumors. Int J Cancer 2002; 98:946–51
Padera TP, Kadambi A, di Tomaso E, et al. Lymphatic metastasis in the absence of fuctional intratumor lymphatics. Science 2002; 296:1883–6
Krishnan J, Kirkin V, Steffen A, et al. Differential in vivo and in vitro expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C and VEGF-D in tumors and its relationship to lymphatic metastasis in immunocompetent rats. Cancer Res 2003; 63:713–22
He Y, Kozaki K, Karpanen T, Koshikawa K, Yla-Herttuala S, Takahashi T, Alitalo K. Suppression of tumor lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis by blocking vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 signaling. J Natl Cancer Inst 2002; 94:819–25
Skobe M, Hamberg LM, Hawighorst T, Schirner M, Wolf GL, Alitalo K, Detmar M. Concurrent induction of lymphangiogenesis, angiogenesis, and macrophage recruitment by vascular endothelial growth factor-C in melanoma. Am J Pathol 2001; 159:893–903
Jia YT, Li ZX, He YT, Liang W, Yang HC, Ma HJ. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor-C and the relationship between lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10: 3261–3
Sedivy R, Beck-Mannagetta J, Haverkampf C, Battistutti W, Hönigschnabl S. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor-C correlates with the lymphatic microvessel density and the nodal status in oral squamous cell cancer. J Oral Pathol Med 2003; 32:455–60
Alitalo K, Carmeliet P. Molecular mechanisms of lymphangiogenesis in health and disease. Cancer Cell 2002; 1:219–27
Straume O, Jackson DG, Akslen LA. Independent prognostic impact of lymphatic vessel density and presence of low-grade lymphangiogenesis in cutaneous melanoma. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9:250–6
Jain RK, Fenton BT. Intratumoral lymphatic vessels: a case of mistaken identity or malfunction? J Natl Cancer Inst 2002; 94:417–21
Birner P, Schindl M, Obermair A, Breitenecker G, Kowalski H, Oberhuber G. Lymphatic microvessel density as a novel prognostic factor in early-stage invasive cervical cancer. Int J Cancer 2001; 95:23–33
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Rodríguez-Salvanés for reviewing the statistical analyses and Dr. Phil Mason for his invaluable help with the English language.
This work was supported by grants from the Thematic Network for Cooperative Research RESPIRA (Code C003/011; Foundation for Biomedical Research, Hospital Universitario de la Princesa) and the Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias (Code FIS 02/1025).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hinojar-Gutiérrez, A., Fernández-Contreras, ME., González-González, R. et al. Intratumoral Lymphatic Vessels and VEGF-C Expression Are Predictive Factors of Lymph Node Relapse in T1-T4 N0 Laryngopharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 14, 248–257 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-006-9201-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-006-9201-y