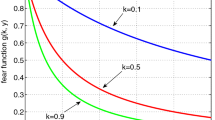
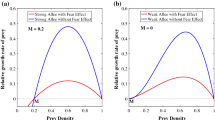
Abstract
In this paper, we consider a two-species predator–prey model with fading memory, where the growth rate of prey species is subject to predation induced fear. Growth rate of predator species depends not only on the present density of prey but also on the past densities with diminishing impact. As the societal activities and behavioral practices influence carrying capacity of any species, we consider the density dependent carrying capacity of prey species instead of a constant. As fear on growth rate and societal activities on carrying capacity entail some time lags to show their effect, so we incorporate two delay parameters to corroborate this in the modeling phenomenon. Feasibility criteria of equilibria and their stability analysis are carried out. We observe that fear parameter and predation rate have destabilizing effect on the system’s dynamics, whereas parameter representing intensity of fading memory has stabilizing impact. We also distinguish stability and instability regions in different parametric planes. With increasing value of production factor from negative to positive, stability region decreases. The system also shows multiple stability switching phenomenon with respect to delay parameters. Solutions show chaotic behavior for a range of fear response delay both in the absence and presence of other delay parameter.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
A.J. Lotka, Elements of physical biology (Williams and Wilkins Company, Baltimore, 1925)
V. Volterra, Variations and fluctuations of the number of individuals in animal species living together. Anim. Ecol. 409–448 (1926)
M. Farkas, Stable oscillations in a predator-prey model with time lag. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 102, 175–188 (1984)
R.M. May, Stability and complexity in model ecosystems (Princeton University Press, Princeton, 2019)
M. Verma, A.K. Misra, Modeling the effect of prey refuge on a ratio-dependent predator-prey system with the Allee effect. Bull. Math. Biol. 80(3), 626–656 (2018)
P. Del Monte-Luna, B.W. Brook, M.J. Zetina-Rejyn, V.H. Cruz-Escalona, The carrying capacity of ecosystems. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 13, 485–495 (2004)
V.I. Yukalov, E.P. Yukalova, D. Sornette, Punctuated evolution due to delayed carrying capacity. Phys. D 238, 1752–1767 (2009)
M.C. Allen, M. Clinchy, L.Y. Zanette, Fear of predators in free-living wildlife reduces population growth over generations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 119(7), e2112404119 (2022)
M. Clinchy, M.J. Sheriff, L.Y. Zanette, Predator-induced stress and the ecology of fear. Funct. Ecol. 27(1), 56–65 (2013)
M.J. Sheriff, S.D. Peacor, D. Hawlena, M. Thaker, Non-consumptive predator effects on prey population size: a dearth of evidence. J. Anim. Ecol. 89(6), 1302–1316 (2020)
L.Y. Zanette, A.F. White, M.C. Allen, M. Clinchy, Perceived predation risk reduces the number of offspring songbirds produce per year. Science 334, 1398–1401 (2011)
M.J. Sheriff, C.J. Krebs, R. Boonstra, The sensitive hare: sublethal effects of predator stress on reproduction in snowshoe hares. J. Anim. Ecol. 78(6), 1249–1258 (2009)
J.P. Suraci, M. Clinchy, L.M. Dill, D. Roberts, L.Y. Zanette, Fear of large carnivores causes a trophic cascade. Nat. Commun. 7, 10698 (2016)
F. Hua, K.E. Sieving, R.J. Fletcher Jr., C.A. Wright, Increased perception of predation risk to adults and offspring alters avian reproductive strategy and performance. Behav. Ecol. 25(3), 509–519 (2014)
J.W. Laundre, L. Hernandez, K.B. Altendorf, Wolves, elk, and bison: reestablishing the ‘landscape of fear‘ in Yellowstone National Park U.S.A. Can. J. Zool. 79, 1401–1409 (2001)
X. Wang, L. Zanette, X. Zou, Modelling the fear effect in predator-prey interactions. J. Math. Biol. 73(5), 1179–1204 (2016)
P. Cong, M. Fan, X. Zou, Dynamic of three-species food chain model with fear effect. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 99, 105809 (2021)
M. Hossain, N. Pal, S. Samanta, Impact of fear on an eco-epidemiological model. Chaos Solit. Fractals 134, 109718 (2020)
B. Mondal, S. Roy, U. Ghosh, P.K. Tiwari, A systematic study of autonomous and nonautonomous predator-prey models for the combined effects of fear, refuge, cooperation and harvesting. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 137, 724 (2022)
S. Pal, P. Panday, N. Pal, A.K. Misra, J. Chattopadhyay, Dynamical behaviors of a constant prey refuge ratio-dependent prey-predator model with Allee and fear effects. Int. J. Biomath. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1142/S1793524523500109
S.K. Sasmal, Population dynamics with multiple Allee effects induced by fear factors: a mathematical study on prey-predator interactions. Appl. Math. Model 64, 1–14 (2018)
P.K. Tiwari, M. Verma, S. Pal, Y. Kang, A.K. Misra, A delay nonautonomous predator-prey model for the effects of fear, refuge and hunting cooperation. J. Biol. Syst. 29(04), 927–969 (2020)
K. Gopalsamy, Stability and oscillations in delay differential equations of population dynamics (Springer Science & Business Media, Cham, 1992)
N. Macdonald, Timedelay in prey-predator models-II. Bifurcation Theor. Math. Biosci. 33, 227–234 (1977)
Y. Kuang, Delay differential equations (University of California Press, Berkeley, 2012)
N. Macdonald, Timedelay in prey-predator models. Math. Biosci. 28, 321–330 (1976)
S. Ruan, On nonlinear dynamics of predator-prey models with discrete delay. Math. Model. Nat. Phenom. 4(2), 140–188 (2009)
B. Dubey, S.K. Sasmal, Chaotic dynamics of a plankton-fish system with fear and its carry over effects in the presence of a discrete delay. Chaos Solit. Fractals 160, 112245 (2022)
K. Chakraborty, S. Haldar, T.K. Kar, Global stability and bifurcation analysis of a delay induced prey-predator system with stage structure. Nonlinear Dyn. 73(3), 1307–1325 (2013)
S. Kundu, S. Maitra, Dynamics of a delayed predator-prey system with stage structure and cooperation for preys. Chaos Solit. Fractals 114, 453–460 (2018)
Y. Song, W. Xiao, X. Qi, Stability and Hopf bifurcation of a predator-prey model with stage structure and time delay for the prey. Nonlinear Dyn. 83(3), 1409–1418 (2016)
B. Dubey, A. Kumar, Dynamics of prey-predator model with stage structure in prey including maturation and gestation delays. Nonlinear Dyn. 96, 2653–2679 (2019)
D. Hu, Y. Li, M. Liu, Y. Bai, Stability and Hopf bifurcation for a delayed predator-prey model with stage structure for prey and Ivlev-type functional response. Nonlinear Dyn. 99(4), 3323–3350 (2020)
D. Jana, R. Agrawal, R.K. Upadhyay, Top-predator interference and gestation delay as determinants of the dynamics of a realistic model food chain. Chaos Solit. Fractals 69, 50–63 (2014)
R. Xu, Global dynamics of a predator-prey model with time delay and stage structure for the prey. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 12(4), 2151–2162 (2011)
B. Dubey, A. Kumar, Stability switching and chaos in a multiple delayed prey-predator model with fear effect and anti-predator behavior. Math. Comput. Simul. 188, 164–192 (2021)
S.K. Nazmul, P.K. Tiwari, S. Pal, M. Martcheva, A delay non-autonomous model for the combined effects of fear, prey refuge, and additional food for predator. J. Biol. Dyn. 15(1), 580–622 (2021)
S. Pal, A. Gupta, A.K. Misra, B. Dubey, Chaotic dynamics of a stage-structured prey-predator system with hunting cooperation and fear in presence of two discrete delays. J. Biol. Syst. 31(2), 611–642 (2023)
P. Panday, N. Pal, S. Samanta, J. Chattopadhyay, Delay induced multiple stability switch and chaos in a predator-prey model with fear effect. Math. Comput. Simul. 172, 134–158 (2020)
J.D. Murray, Mathematical biology I. An introduction (Springer, Cham, 2002)
B. Sahoo, S. Poria, Dynamics of predator-prey system with fading memory. Appl. Math. Comput. 347, 319–333 (2019)
R. Castro, W. Sierra, E. Stange, Bifurcations in a predator-prey model with general logistic growth and exponential fading memory. Appl. Math. Model. 45, 134–147 (2007)
A. Gokce, The influence of past in a population system involving intraspecific competition and Allee effect. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 137, 200 (2022)
J.D. Ferreira, C.A.T. Alazar, P.C.C. Tabares, Weak Allee effect in a predator-prey model involving memory with a hump. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 14, 536–548 (2013)
E. Reimondo, T. Sisk, T.C. Thiemer, Effects of introduced bison on wetlands of the Kaibab Plateau, Arizona. The Colorado Plateau VI: science and management at the landscape scale (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 2015), pp.120–135
N.C. Pati, B. Ghosh, Delayed carrying capacity induced subcritical and supercritical Hopf bifurcations in a predator-prey system. Math. Comput. Simul. 195, 171–196 (2022)
V.I. Yukalov, E.P. Yukalova, D. Sornette, Extreme events in population dynamics with functional carrying capacity. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 205, 313–354 (2012)
C.S. Holling, Some characteristics of simple types of predation and parasitism. Can. Entomol. 91, 385–398 (1959)
M. Farkas, A. Farkas, G. Szabo, Multiparameter bifurcation diagrams in predator-prey models with time lag. J. Math. Biol. 26, 93–103 (1988)
A.K. Misra, R.K. Rai, Y. Takeuchi, Modeling the effect of time delay in budget allocation to control an epidemic through awareness. Int. J. Biomath. 11(2), 1850027 (2018)
D. Adak, N. Bairagi, R. Hakl, Chaos in delay-induced Leslie-Gower prey-predator-parasite model and its control through prey harvesting. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 51, 102998 (2020)
K.K. Choudhary, B. Dubey, A non-autonomous approach to study the impact of environmental toxins on nutrient-plankton system. Appl. Math. Comput. 458, 128236 (2023)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the anonymous referees for their critical reviews and constructive suggestions that improved the quality and presentation of the paper. Soumitra Pal is thankful to the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research(CSIR), Government of India for providing financial support in the form of senior research fellowship (File.No. 09/013(0915)/2019-EMR-I) and Ashvini Gupta acknowledges the senior research fellowship received from University Grant Commission, New Delhi, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pal, S., Gupta, A., Misra, A.K. et al. Complex dynamics of a predator–prey system with fear and memory in the presence of two discrete delays. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 138, 984 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04614-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04614-w