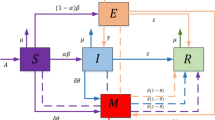
Abstract
Adverse information can spread through emotional expression to cause public panic and social instability. The network regulators may limit the spread by force silently. This paper aims to capture the effects of public sentiment and forced silence on information propagation. To this end, the paper proposes a class of SFPFNR information propagation models with time delays and a forced silence function on a heterogeneous network. In addition, event-triggered impulsive control mechanism is designed. Combined with forced silence, the paper creates a dual control mechanism. Next, the mean-field principle is used to calculate the basic reproduction number \(R_{0}\) and then prove the existence of the equilibrium point \(E^{*}\). By constructing the Lyapunov function and applying the comparison principle, the global and local stability of the system are then discussed. Besides, we perform extensive numerical simulations to verify the theoretical conclusions. The results show that time delays do not affect system stability, and negative emotions are crucial for large-scale information transmission. Finally, the model is applied to the actual case and shows a significant improvement in prediction accuracy compared with the SIR model. The RMSE decreases from 0.3234 to 0.0664. Therefore, the model can guide social media management and information dissemination regulation.
Graphical abstract


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Luo, Z. Cao, D. Zeng, Q. Zhang, A dissemination model based on psychological theories in complex social networks. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 14, 519–531 (2022)
J. Liu, Y. Yu, P. Ji, D. Liu, Information dissemination model in rural live broadcasting under blockchain in the era of artificial intelligence. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 4590578 (2022)
X.-J. Li, C. Li, X. Li, The impact of information dissemination on vaccination in multiplex networks. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 65, 172202 (2022)
D.J. Daley, D.G. Kendall, Epidemics and rumours. Nature 204, 1118 (1964)
D.P. Maki, M. Thompson, Mathematical models and applications: with emphasis on the social life, and management sciences, in, 1973.
D. Zanette, Criticality behavior of propagation on small-world networks. Phys. Rev. E 64, 050001 (2001)
D.H. Zanette, Dynamics of rumor propagation on small-world networks. J. Phys. Rev. E Stat. 65, 041908 (2002)
Y. Zhang, J. Zhu, Dynamics of a rumor propagation model with stochastic perturbation on homogeneous social networks. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 17, 031005 (2022)
F. Yin, X. Xia, Y. Pan, Y. She, X. Feng, J. Wu, Sentiment mutation and negative emotion contagion dynamics in social media: a case study on the Chinese Sina Microblog. Inform. Sci. 594, 118–135 (2022)
C.-Y. Sang, S.-G. Liao, Modeling and simulation of information dissemination model considering user’s awareness behavior in mobile social networks. Phys. A 537, 122639 (2020)
A.I.E. Hosni, K. Li, S. Ahmad, Minimizing rumor influence in multiplex online social networks based on human individual and social behaviors. Inf. Sci. 512, 1458–1480 (2020)
H. Chen, C. Ai, B. Chen, Y. Zhao, K. Lai, L. He, Z. Liu, The research on propagation modeling and governance strategies of online rumors based on behavior–attitude. Int. Res. 32, 620–639 (2021)
C.-Y. Sang, S.-G. Liao, Modeling and simulation of information dissemination model considering user’s awareness behavior in mobile social networks. Physica A. 537, 122639 (2020)
F. Yin, X. Xia, X. Zhang, M. Zhang, J. Lv, J. Wu, Modelling the dynamic emotional information propagation and guiding the public sentiment in the Chinese Sina-microblog. Appl. Math. Comput. 396, 125884 (2021)
J. Chen, H. Ma, S. Yang, SEIOR rumor propagation model considering hesitating mechanism and different rumor-refuting ways in complex networks. Mathematics 11, 283 (2023)
W. Pan, W. Yan, Y. Hu, R. He, L. Wu, Dynamic analysis of a SIDRW rumor propagation model considering the effect of media reports and rumor refuters. Nonlinear Dyn. 111, 3925 (2022)
L. Dong, B. Li, G. Zhang, Analysis on a diffusive SI epidemic model with logistic source and saturation infection mechanism. B. Malays. Math. Ssci. So. 45, 1111–1140 (2022)
B. Xie, M. Liu, L. Zhang, Bifurcation analysis and optimal control of SEIR epidemic model with saturated treatment function on the network. Math. Biosci. Eng. 19, 1677–1696 (2022)
L. Zhu, W. Liu, Z. Zhang, Delay differential equations modeling of rumor propagation in both homogeneous and heterogeneous networks with a forced silence function. Appl. Math. Comput. 370, 124925 (2020)
Y. Dong, L.A. Huo, L. Zhao, An improved two-layer model for rumor propagation considering time delay and event-triggered impulsive control strategy. Chaos Sol. Fract. 164, 11271 (2022)
L. Zhu, W. Zheng, X. Zhang, Bifurcation analysis of a reaction-diffusion rumor spreading model with nonsmooth control. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 32, 2250109 (2022)
J. Hu, L. Zhu, M. Peng, Analysis of turing patterns and amplitude equations in general forms under a reaction–diffusion rumor propagation system with Allee effect and time delay. Inf. Sci. 596, 501–519 (2022)
L. Zhu, G. Guan, Y. Li, Nonlinear dynamical analysis and control strategies of a network-based SIS epidemic model with time delay. Appl. Math. Modell. 70, 512–531 (2019)
S. Chen, H. Jiang, L. Li, J. Li, Dynamical behaviors and optimal control of rumor propagation model with saturation incidence on heterogeneous networks. Chaos Sol. Fract. 140, 110206 (2020)
L. Zhu, H. Zhao, Dynamical behaviours and control measures of rumour-spreading model with consideration of network topology. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 48, 2064–2078 (2017)
X. Yue, L. Huo, Analysis of the stability and optimal control strategy for an ISCR rumor propagation model with saturated incidence and time delay on a scale-free network. Mathematics 10, 3900 (2022)
Y. Zhou, J. Zhang, C. Zhu, H. Wang, Modelling and analysis of rumour propagation based on stochastic optimal control. Alex. Eng. J. 61, 12869–12880 (2022)
Y. Xia, H. Jiang, Z. Yu, S. Yu, X. Luo, Dynamic analysis and optimal control of a reaction-diffusion rumor propagation model in multi-lingual environments. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 521, 126967 (2023)
K. Kandhway, J. Kuri, Optimal control of information epidemics modeled as Maki Thompson rumors. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 19, 4135–4147 (2014)
S. Yu, Z. Yu, H. Jiang, X. Mei, J. Li, The spread and control of rumors in a multilingual environment. Nonlinear Dyn. 100, 2933–2951 (2020)
M.H. DarAssi, M.A. Safi, B. Al-Hdaibat, A delayed SEIR epidemic model with pulse vaccination and treatment. Nonlinear Stud. 25, 521 (2018)
S. Yu, Z. Yu, H. Jiang, J. Li, Dynamical study and event-triggered impulsive control of rumor propagation model on heterogeneous social network incorporating delay. Chaos Sol. Fract. 145, 110806 (2021)
J.P. LaSalle, Stability theory for ordinary differential equations. J. Differ. Equ. 4, 57–65 (1968)
Z. Yang, D. Xu, Stability analysis and design of impulsive control systems with time delay. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 52, 1448–1454 (2007)
X. Tong, H. Jiang, J. Qiu, X. Luo, S. Chen, Dynamic analysis of the IFCD rumor propagation model under stochastic disturbance on heterogeneous networks. Chaos Sol. Fract. 173, 113637 (2023)
Y. Ma, Y. Cui, M. Wang, A class of delay SIQR-V models considering quarantine and vaccination: validation based on the COVID-19 perspective. Results Phys. 31, 104990 (2021)
B. Cao, G. Guan, S. Shen, L. Zhu, Dynamical behaviors of a delayed SIR information propagation model with forced silence function and control measures in complex networks. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 138, 402 (2023)
S. Lenhart, J.T. Workman, Optimal Control Applied to Biological Models (CRC Press, Place, 2007)
L.H. Zhu, W.S. Liu, Z.D. Zhang, Delay differential equations modeling of rumor propagation in both homogeneous and heterogeneous networks with a forced silence function. Appl. Math. Comput. 370, 124925 (2020)
B.W. Cao, G. Guan, S.L. Shen, L.H. Zhu, Dynamical behaviors of a delayed SIR information propagation model with forced silence function and control measures in complex networks. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 138, 402 (2023)
S.S. Chen, H.J. Jiang, L. Li, J.R. Li, Dynamical behaviors and optimal control of rumor propagation model with saturation incidence on heterogeneous networks. Chaos Sol. Fract. 140, 110206 (2020)
U.L. Abbas, R.M. Anderson, J.W. Mellors, Potential impact of antiretroviral chemoprophylaxis on HIV-1 transmission in resource-limited settings. PLoS ONE 2, e875 (2007)
D. Atilano-Barbosa, L. Paredes, F. Enciso, E.H. Pasaye, R.E. Mercadillo, Moral emotions when reading quotidian circumstances in contexts of violence: an fMRI study. Adapt. Behav. 30, 119–145 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 71701036).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could influence the work presented in this paper.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Y., Xie, L., Liu, S. et al. Dynamical behaviors and event-triggered impulsive control of a delayed information propagation model based on public sentiment and forced silence. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 138, 979 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04589-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04589-8