Abstract.
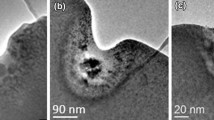
Silver particles in soda-lime glass, less than 10 nm in size, were prepared by ion implantation. The implantation dose was in the range of 0.5 to 2×1016 Ag ions/cm2 and the beam current density was varied from 0.5 to 2μA/cm2. Here, the beam current density strongly influences ion diffusion and particle precipitation as well as compressive stress generation around the particles due to thermal effects resulting from the deceleration of silver ions. Stress relaxation can be achieved by increased dose rates or thermal processing at elevated temperatures. Based on RBS and HREM results, a possible route to homogeneous distribution of Ag nanoparticles within the glass is discussed with respect to their interesting optical properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dubiel, M., Hofmeister, H., Tan, G.L. et al. Silver diffusion and precipitation of nanoparticles in glass by ion implantation. Eur. Phys. J. D 24, 361–364 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2003-00178-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2003-00178-5