Abstract
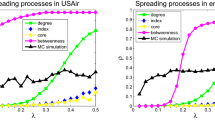
In the study of disease spreading on empirical complex networks in SIR model, initially infected nodes can be ranked according to some measure of their epidemic impact. The highest ranked nodes, also referred to as “superspreaders”, are associated to dominant epidemic risks and therefore deserve special attention. In simulations on studied empirical complex networks, it is shown that the ranking depends on the dynamical regime of the disease spreading. A possible mechanism leading to this dependence is illustrated in an analytically tractable example. In systems where the allocation of resources to counter disease spreading to individual nodes is based on their ranking, the dynamical regime of disease spreading is frequently not known before the outbreak of the disease. Therefore, we introduce a quantity called epidemic centrality as an average over all relevant regimes of disease spreading as a basis of the ranking. A recently introduced concept of phase diagram of epidemic spreading is used as a framework in which several types of averaging are studied. The epidemic centrality is compared to structural properties of nodes such as node degree, k-cores and betweenness. There is a growing trend of epidemic centrality with degree and k-cores values, but the variation of epidemic centrality is much smaller than the variation of degree or k-cores value. It is found that the epidemic centrality of the structurally peripheral nodes is of the same order of magnitude as the epidemic centrality of the structurally central nodes. The implications of these findings for the distributions of resources to counter disease spreading are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.M. Anderson, R.M. May, Infectious Diseases of Humans: Dynamics and Control (Oxford University Press, 1991)
M.J. Keeling, P. Rohani, Modeling Infectious Diseases in Humans and Animals (Princeton University Press, 2008)
R. Pastor-Satorras, A. Vespignani, Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 3200 (2001)
R. Albert, A.L. Barabási, Rev. Mod. Phys. 74, 47 (2002)
M.E.J. Newman, SIAM Rev. 45, 167 (2003)
S.N. Dorogovtsev, A.V. Goltsev, J.F.F. Mendes, Rev. Mod. Phys. 80, 1275 (2008)
N.C. Grassly, C. Fraser, Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 6, 477 (2008)
S. Boccaletti, V. Latora, Y. Moreno, M. Chavez, D.U. Hwang, Phys. Rep. 424, 175 (2006)
M. Youssef, R. Kooij, C. Scoglio, J. Comput. Sci. 2, 286 (2011)
V. Colizza, A. Barrat, M. Barthelemy, A.J. Valleron, A. Vespignani, PLoS Med. 4, 95 (2007)
V. Colizza, A. Barrat, M. Barthelemy, A. Vespignani, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 2015 (2006)
V. Colizza, A. Vespignani, Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 148701 (2007)
M. Kitsak et al., Nat. Phys. 6, 888 (2010)
L.C. Freeman, Social Networks 1, 215 (1979)
N.E. Friedkin, Am. J. Soc. 96, 1478 (1991)
K. Klemm, M.A. Serrano, V.M. Eguiluz, M. San Miguel, Sci. Rep. 2, 292 (2012)
Z. Shen et al., Emerg. Infect. Dis. 10, 256 (2004)
J.O. Lloyd-Smith, S.J. Schreiber, P. Kopp, W.M. Getz, Nature 438, 355 (2005)
S. Bansal, B.T. Grenfell, L.A. Meyers, J. R. Soc. Interface 4, 879 (2007)
W.O. Kermack, A.G. McKendrick, Proc. R. Soc. London A 115, 700 (1927)
A. Lancic, N. Antulov-Fantulin, M. Sikic, H. Stefancic, Physica A 390, 65 (2011)
E. Volz, L.A. Meyers, J. R. Soc. Interface 6, 233 (2009)
I.B. Schwartz, L.B. Shaw, Physics 3, 17 (2010)
M.E.J. Newman, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 98, 404 (2001)
D.J. Watts, S.H. Strogatz, Nature 393, 440 (1998)
M.E.J. Newman, http://www-personal.umich.edu/mejn/netdata/.
A. Grabowski, N. Kruszevska, R.A. Kosiński, Phys. Rev. E 78, 066110 (2008)
D.G. Gibson et al., Science 329, 52 (2010)
V.T. Vredenburg, R.A. Knapp, T.S. Tunstall, C.J. Briggs, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 9689 (2010)
G.A. Forster, C.A. Gilligan, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 4984 (2007)
R.E. Rowthorn, R. Laxminarayan, C.A. Gilligan, J. R. Soc. Interface 6, 1135 (2009)
A. Grabowski, M. Rosińska, Eur. Phys. J. B 85, 248 (2012)
A. Grabowski, M. Rosińska, Acta. Phys. Pol. B 37, 1521 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Šikić, M., Lančić, A., Antulov-Fantulin, N. et al. Epidemic centrality — is there an underestimated epidemic impact of network peripheral nodes?. Eur. Phys. J. B 86, 440 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2013-31025-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2013-31025-5