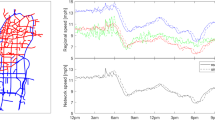
Abstract.
Traffic is highly influenced by network structure and human behaviour. Small changes in the human behaviour can lead to huge changes in the load of a traffic network. Current transportation models do not, and most of them cannot, research such random behaviour but always calculate a steady state. In our multi-agent transport simulation, we frequently observe seemingly random “network breakdowns”, huge traffic jams that spread over a big part of the network, making a normal traffic flow impossible. This paper describes the investigations that were performed on the results of our large-scale multi-agent transport simulations in an attempt to contribute to the better understanding of the dynamic processes in such simulations and, hopefully, better understanding and modelling of the real-world.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Computational Science – ICCS 2007: 7th International Conference, Vol. 4487–4490 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, edited by Y. Shi, G.D. v. Albada, J. Dongarra, P.M.A. Sloot (Springer New York, 2007)
U. Harder, M. Paczuski, Physica A, 361(1), 329 (2006)
J.P. Eckmann, E. Moses, D. Sergi, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci., 101(40), 14333 (2004)
TRANSIMS www page: TRansportation ANalysis, SIMulation System, http://transims.tsasa.lanl.gov/, accessed 2008, (Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, NM)
MATSIM www page: MultiAgent Transport SIMulation; http://matsim.org/, accessed 2008
DYNAMIT/MITSIM www page: http://mit.edu/its, accessed 2008
DYNASMART www page, http://www.dynasmart.com/, accessed 2007
R.J.F. Rossetti, R. Liu, in Applications of Agent Technology in Traffic and Transportation, edited by F. Klügl, A. Bazzan, S. Ossowski, Whitestein, Series in Software Agent Technologies and Autonomic Computing (Birkhäuser, 2005), pp. 88–93
J. Esser, Simulation von Stadtverkehr auf der Basis zellularer Automaten, Ph.D. thesis, University of Duisburg, Germany, 1998. See also http://www.traffic.uni-duisburg.de
D. Helbing, Rev. Mod. Phys. 73, 1067 (2001)
D. Chowdhury, L. Santen, A. Schadschneider, Phys. Rep. 329, 199 (2000)
W. Knospe, L. Santen, A. Schadschneider, M. Schreckenberg, J. Phys. A: Math. Gen., 33, L477 (2000)
O. Biham, A. Middleton, D. Levine, Phys. Rev. A 46(10), R6124 (1992)
F.C. Martínez, J.A. Cuesta, J.M. Molera, R. Brito, Phys. Rev. E 51(2), R835 (1995)
T. Nagatani, Phys. Rev. E 59(5), 4857 (1999)
P. Bak, C. Tang, K. Wiesenfeld, Phys. Rev. A 38(1), 364 (1988)
P. Bak, K. Sneppen, Phys. Rev. Lett. 71(24), 4083 (1993)
D. Helbing, M. Schönhof, D. Kern, New J. Phys. 4(33), 1 (2002)
Proceedings of the Workshop on Human Behaviour and Traffic Networks, edited by N. Schrockenberg, R. Selten (Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, 2004), pp. 1–21
C. Gawron, Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 9(3), 393 (1998)
N. Cetin, A. Burri, K. Nagel, in Proceedings of Swiss Transport Research Conference (STRC), Monte Verita, CH, 2003. Earlier version, with inferior performance values: Transportation Research Board Annual Meeting 2003 paper number 03-4272
W.S. Vickrey, Amer. Econom. Rev. 59(2), 251 (1969)
R. Arnott, A. De Palma, R. Lindsey, Am. Econom. Rev. 83(1), 161 (1993)
D. Charypar, K. Nagel, Transportation 32(4), 369 (2005)
M. Balmer, B. Raney, K. Nagel, in Progress in activity-based analysis, edited by H.J.P. Timmermans (Elsevier, Oxford, UK, 2005), pp. 91–114
M. Ben-Akiva, S.R. Lerman, Discrete choice analysis (The MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 1985)
R Development Core Team, R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria, 2007. ISBN 3-900051-07-0
C.G. Langton, in Artificial Life II, Santa Fe Institute Studies in the Science of Complexity, Vol. 10, edited by C.G. Langton et al. (Addison-Wesley, Redwood Citz, CA, 1992), pp. 41–92
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rieser, M., Nagel, K. Network breakdown “at the edge of chaos” in multi-agent traffic simulations. Eur. Phys. J. B 63, 321–327 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2008-00153-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2008-00153-6