Abstract
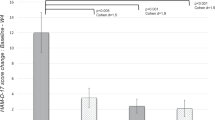
This study investigated the relationship between major depressive disorder (MDD) and neuroinflammation biomarkers. Included 28 patients that were diagnosed with MDD and 22 healthy individuals as the control group. Antidepressant drug therapy was started for depression patients. Venous blood was drawn from the control group and pre-treatment MDD patients for measuring levels of inflammatory markers. Inflammatory marker levels were measured again after 8 weeks of antidepressant medication in MDD patients. The severity of depression was determined by the Hamilton Depression Scale (HDS). Serum levels of IL-1, IL-2, IL-6 and haptoglobin were significantly different between the pre-treatment patients and control groups (P < 0.05), but no significant difference in CRP and sedimentation levels (P > 0.05). Pre- and post-treatment of patient group levels of IL-1, IL-2, IL-6 and haptoglobin significantly different (P < 0.05), whereas CRP levels and sedimentation were not significantly different (P > 0.05). Mean HDS score of pre- and posttreatment in patients group was significantly different (P < 0.05). All participants in the patient group responded to the antidepressant treatment. We found that inflammatory mechanisms occur in MDD and antidepressant therapy affects this process. Inflammatory cytokines IL-1, IL-2 and IL-6, as well as the APR’s haptoglobin are elevated significantly in MDD.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Capuron, L., and Miller, A.H., Pharmacol. Ther., 2011, vol. 130, no. 2, pp. 226–238.
Raison CL, Cowles MK, and Miller AH., Kaplan&Sadock’s Comprehensive Textbook of Psychiatry, 9th edition, 2009, pp. 175–197.
Tuğlu C., and Kara S.H., Klin. Psikofarmakol. Bülteni (Bull. Clin. Psychopharmacol.), 2003, vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 142–150
Dinan, T.G., Curr. Opin. Psychiatry, 2009, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 32–36.
Seidel, A., Arolt, V., Hunstiger, M., Rink, L., Behnisch, A., and Kirchner, H., Scand. J. Immunol., 1995, vol. 41, no. 6, pp. 534–538.
Kushner, I., Ann. NY Acad. Sci., 1982, vol. 389, pp. 39–48.
Gabay, C., and Kushner, I., N. Engl. J. Med., 1999, vol. 340, no. 6, pp. 448–454.
Schiepers, O.J., Wichers, M.C., and Maes, M., Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry, 2005, vol. 29, no. 2, pp. 201–217.
Gümrü, S., and Arıcıoğlu, F., Journal of Marmara University Institute of Health Sciences, 2012, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 103–107.
Krishnadas, R. and Cavanagh, J., J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry, 2012, vol. 83, no. 5, pp. 495–502.
Raedler, T.J., Curr. Opin. Psychiatry, 2011, vol. 24, no. 6, pp. 519–525.
Doksat, M.K., Klin. Psikofarmakol. Bul., 2003, vol. 13, pp. 97–108.
Miller, A.H., Maletic, V., and Raison, C.L., Biol. Psychiatry, 2009, vol. 65, no. 9, pp. 732–741.
Jones, K.A. and Thomsen, C., Mol. Cell. Neurosci., 2013, vol. 53, pp. 52–62.
Doksat, K. and Savrun, M., Yeni Symposium, 2002, vol. 40, pp. 90–99.
Maes, M., Ringel, K., Kubera, M., Berk, M., and Rybakowski, J., J. Affect Disord., 2012, vol. 136, no. 3, pp. 386–392.
Hannestad, J., DellaGioia, N., and Bloch, M., Neuropsychopharmacology, 2011, vol. 36, no. 12, pp. 2452–2459.
Howren, M.B., Lamkin, D.M., and Suls, J., Psychosom. Med., 2009, vol. 71, no. 2, pp. 171–186.
Dowlati, Y., Herrmann, N., Swardfager, W., Liu, H., Sham, L., Reim, E. K., and Lanctôt, K. L., Biol. Psychiatry, 2010, vol. 67, no. 5, pp. 446–457.
Maes, M., Scharp, S., Grootel, V.L., Uyttenbroeck, W., Cooreman, W., Cosyns, P., and Suy, E., J. Affect. Disord., 1992, vol. 24, no. 3, pp. 183–192.
Chavda, N., Kantharia, N.D., Jaykaran, J. Pharmacol. Pharmacother., 2011, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 11–16.
Vargas, H.O., Nunes, S.O.V., de Castro, M.R.P., Vargas, M.M., Barbosa, D.S., Bortolasci, C.C., Venugopal, K., Dodd, S., and Berk, M., Neurosci. Lett., 2013, vol. 544, pp. 136–140.
Janssen, D.G., Caniato, R.N., Verster, J.C., and Baune, B.T., Hum. Psychopharmacol., 2010, vol. 25, no. 3, pp. 201–215.
Kocabaşoğlu, N., Konuk, N., Öztürk, S., and Bayar, R., Yeni Symposium, 2000, vol. 36, pp. 83–87.
Hocaoglu, C., Kural, B., Aliyazıcıoglu, R., Deger, O., and Cengiz, S., Metab. Brain Dis., 2012, vol. 27, no. 4, pp. 425–430.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors thank Dr. Alper Sınan who helped in the statistical analysis of the study. Antalya Training and Research Hospital Ethics Committee Provided the kits of cytokines (IL-1,IL-2,IL-6) and acute phase reactants (Haptoglobin, CRP, ESR) that we use in the biochemistry laboratory for our study.
Funding
No external funding was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest. The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korkut, S., Kulaksizoglu, S. The Relationship of Antidepressant Therapy with Neuroinflammatory Changes and Inflammatory Response in Major Depressive Disorder. Neurochem. J. 15, 477–481 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1819712421040061
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1819712421040061