Abstract
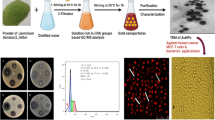
Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) have peaked interests in many researches in these recent years due to their advantageous application in modern health care applications. Therefore, we successfully synthesized ZnO NPs by Acacia luciana flower extract as stabilizing, reducing and capping agent, to investigate the antiproliferative potential and apoptosis induction in breast cancer cell lines. The involvements of Acacia luciana bioactive compounds in the stabilization of the ZnO NPs were confirmed by FTIR analysis. FESEM and EDS instruments confirmed that biosynthesized nanoparticles have an irregular morphology and mostly composed of Zn, C, and O respectively. The TEM and zeta potential instruments confirmed that biosynthesized nanoparticles have slight negative charges with particle size of 40 nm. The survivorship of MCF-7 cells were examined by MTT assay and revealed that ZnO NPs inhibited cell viability in a dose- and time-dependent effect with IC50 value of 3.1 µg/mL after 72 h exposure. Also, as a novel work onto ZnO NPs obtained by Acacia extracts, the Bak1/Bclx expression ratio was elucidated utilizing RT-PCR technique. The results demonstrated that ZnO NPs could enhance the expression ratio; therefore they have the potential to induce apoptosis in breast cancer cells via mitochondria-mediated apoptotic pathway.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Abbreviations: FESEM, field emission scanning electron microscopy; EDS, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy; TEM, transmission electron microscopy; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; ZnO NPs, zinc oxide nanoparticles.
REFERENCES
Anand, G.T., Renuka, D., Ramesh, R., Anandaraj, L., Sundaram S.J., Ramalingam, G., Magdalane, C.M., Bashir, A., Maaza, M., and Kaviyarasu, K., Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticle using Prunus dulcis (Almond Gum) for antimicrobial and supercapacitor applications, Surfaces Interfaces, 2019, vol. 17, p. 100376.
Jang, S.J., Yang, I.J., Tettey, C.O., Kim, K.M., and Shin, H.M., In-vitro anticancer activity of green synthesized silver nanoparticles on MCF-7 human breast cancer cells, Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2016, vol. 68, pp. 430–435.
Aziz, R.A..A., anak Bronny, B.G., and Alam, S., Zinc oxide nanoparticle synthesis with banana peel extract from jackfruit banana: effects of temperature, Int. J. Technol. Res. Eng., 2019.
Vanaja, M., Paulkumar, K., Baburaja, M., Rajeshkumar, S., Gnanajobitha, G., Malarkodi, C., Sivakavinesan, M., and Annadurai, G., Degradation of methylene blue using biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles, Bioinorg. Chem. Appl., 2014, vol. 2014, no. 1, art. 742346.
Manna, J., Begum, G., Kumar, K.P., Misra, S., and Rana, R.K., Enabling antibacterial coating via bioinspired mineralization of nanostructured ZnO on fabrics under mild conditions, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2013, vol. 5, no. 10, pp. 4457–4463.
Boroumand Moghaddam, A., Moniri, M., Azizi, S., Abdul Rahim, R., Bin Ariff, A., Navaderi, M., and Mohamad, R., Eco-friendly formulated zinc oxide nanoparticles: induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in the MCF-7 cancer cell line, Genes, 2017, vol. 8, no. 10, p. 281.
Sardashti, A.R., Valizadeh, J., and Majd, M.H., Chemical constituents of the flower oil of Acacia luciana from Iran, Int. J. Agricult. Crop Sci., 2015, vol. 8, no. 3, p. 395.
Barsaiya, M. and Singh, D.P., Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and their broad-spectrum antimicrobial effects, J. Pure Appl. Microbiol., 2018, vol. 12, no. 4, pp. 2123–2134.
Alarifi, S., Ali, H., and Saad Alkahtani, M.S.A., Regulation of apoptosis through bcl-2/bax proteins expression and DNA damage by nano-sized gadolinium oxide, Int. J. Nanomed., 2017, vol. 12, no. 4, p. 541.
Sargazi, A., Barani, A., and Heidari Majd, M., Synthesis and apoptotic efficacy of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles using Аcacia luciana flower extract in MCF-7 breast cancer cells: activation of Bak1 and Bclx for cancer therapy, BioNanoScience, 2020, vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 683–689.
Khan, S.A., Noreen, F., Kanwal, S., Iqbal, A., and Hussain, G., Green synthesis of ZnO and Cu-doped ZnO nanoparticles from leaf extracts of Abutilon indicum, Clerodendrum infortunatum, Clerodendrum inerme, and investigation of their biological and photocatalytic activities, Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2018, vol. 8, pp. 46–59.
Miri, A., Mahdinejad, N., Ebrahimy, O., Khatami, M., and Sarani, M., Zinc oxide nanoparticles: Biosynthesis, characterization, antifungal and cytotoxic activity, Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2019, vol. 104, p. 109981.
Sargazi, A., Kamali, N., Shiri, F., and Heidari Majd, M., Hyaluronic acid/polyethylene glycol nanoparticles for controlled delivery of mitoxantrone, Artificial Cells, Nanomed. Biotechnol., 2018, vol. 46, no. 3, pp. 500–509.
Mansouri-Torshizi, H., Zareian-Jahromi, S., Gha-hghaei, A., Shahraki, S., Khosravi, F., and Heidari Majd, M., Palladium(II) complexes of biorelevant ligands. Synthesis, structures, cytotoxicity and rich DNA/HSA interaction studies, J. Biomol. Struct. Dynam., 2018, vol. 36, no. 11, pp. 2787–2806.
Sargazi, A., Azhoogh, M., Allahdad, S., and Heidari Majd, M., Evaluation of supramolecule conjugated magnetic nanoparticles as a simultaneous carrier for methotrexate and tamoxifen, J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol., 2018, vol. 47, pp. 115–122.
Shahraki, S., Shiri, F., Majd, M.H., and Razmara, Z., Comparative study on the anticancer activities and binding properties of a hetero metal binuclear complex [Co(dipic)2Ni(OH2)5] · 2H2O (dipic = dipicolinate) with two carrier proteins, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 2017, vol. 145, pp. 273–282.
Sargazi, A., Shiri, F., Keikha, S., and Majd, M.H., Hyaluronan magnetic nanoparticle for mitoxantrone delivery toward CD44-positive cancer cells, Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces, 2018, vol. 171, pp. 150–158.
Shahraki, S., Majd, M.H., and Heydari, A., Novel tetradentate Schiff base zinc(II) complex as a potential antioxidant and cancer chemotherapeutic agent: Insights from the photophysical and computational approach, J. Mol. Struct., 2019, vol. 1177, pp. 536–544.
Barar, J., Kafil, V., Majd, M.H., Barzegari, A., Khani, S., Johari-Ahar, M., Asgari, D., Cokous, G., and Omidi, Y., Multifunctional mitoxantrone-conjugated magnetic nanosystem for targeted therapy of folate receptor-overexpressing malignant cells, J. Nanobiotechnol., 2015, vol. 13, no. 1.
Akhtar, M.J., Ahamed, M., Kumar, S., Khan, M.M., Ahmad, J., and Alrokayan, S.A., Zinc oxide nanoparticles selectively induce apoptosis in human cancer cells through reactive oxygen species, Int. J. Nanomed., 2012, vol. 7, p. 85.
Yip, N., Fombon, I., Liu, P., Brown, S., Kannappan, V., Armesilla, A., Xu, B., Cassidy, J., Darling, J., and Wang, W., Disulfiram modulated ROS–MAPK and NFκB pathways and targeted breast cancer cells with cancer stem cell-like properties, Br. J. Cancer, 2011, vol. 104, no. 10, p. 1564.
Alsammarraie, F.K., Wang, W., Zhou, P., Mustapha, A., and Lin, M., Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using turmeric extracts and investigation of their antibacterial activities, Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces, 2018, vol. 171, pp. 398–405.
Umar, H., Kavaz, D., and Rizaner, N., Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Albizia lebbeck stem bark, and evaluation of its antimicrobial, antioxidant, and cytotoxic activities on human breast cancer cell lines, Int. J. Nanomed., 2019, vol. 14, p. 87.
Barsaiya, M. and Singh, D.P., Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and their broad-spectrum antimicrobial effects, J. Pure Appl. Microbiol., 2018, vol. 12, no. 4, pp. 2123–2134.
Pung, S., Ong, C., Isha, K.M., and Othman, M., Synthesis and characterization of Cu-doped ZnO nanorods, Sains Malaysiana, 2014, vol. 43, no. 2, pp. 273–281.
Yuan, Y.-G., Zhang, S., Hwang, J.-Y., and Kong, I.-K., Silver nanoparticles potentiates cytotoxicity and apoptotic potential of camptothecin in human cervical cancer cells, Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev., 2018, vol. 2018, art. 6121328. https://doi.org/10.31857/10.1155/2018/6121328
Yuan, Y.-G. and Gurunathan, S., Combination of graphene oxide–silver nanoparticle nanocomposites and cisplatin enhances apoptosis and autophagy in human cervical cancer cells, Int. J. Nanomed., 2017, vol. 12, p. 6537.
Sirelkhatim, A., Mahmud, S., Seeni, A., Kaus, N.H.M., Ann, L.C., Bakhori, S.K.M., Hasan, H., and Mohamad, D., Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism, Nano-Micro Lett., 2015, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 219–242.
Zhang, H., Chen, B., Jiang, H., Wang, C., Wang, H., and Wang, X., A strategy for ZnO nanorod mediated multi-mode cancer treatment, Biomaterials, 2011, vol. 32, no. 7, pp. 1906–1914.
Jeng, H.A. and Swanson, J., Toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles in mammalian cells, J. Environ. Sci. Health A, 2006, vol. 41, no. 12, pp. 2699–2711.
Souza, R.C.D., Haberbeck, L.U., Riella, H.G., Ribeiro, D.H., and Carciofi, B.A., Antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized by solochemical process, Braz. J. Chem. Eng., 2019, vol. 36, no. 2, pp. 885–893.
Shobha, N., Nanda, N., Giresha, A.S., Manjappa, P., Sophiya, P., Dharmappa, K., and Nagabhushana, B., Synthesis and characterization of Zinc oxide nanoparticles utilizing seed source of Ricinus communis and study of its antioxidant, antifungal and anticancer activity, Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2019, vol. 97, pp. 842–850.
Sukri, S.N.A.M., Shameli, K., Wong, M.M.-T., Teow, S.-Y., Chew, J., and Ismail, N.A., Cytotoxicity and antibacterial activities of plant-mediated synthesized zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles using Punica granatum (pomegranate) fruit peels extract, J. Mol. Struct., 2019, vol. 1189, pp. 57–65.
El-Shorbagy, H.M., Eissa, S.M., Sabet, S., and El-Ghor, A.A., Apoptosis and oxidative stress as relevant mechanisms of antitumor activity and genotoxicity of ZnO-NPs alone and in combination with N-acetyl cysteine in tumor-bearing mice, Int. J. Nanomed., 2019, vol. 14, p. 3911.
Wang, L., Chen, C., Guo, L., Li, Q., Ding, H., Bi, H., and Guo, D., Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce murine photoreceptor cell death via mitochondria-related signaling pathway, Artificial Cells, Nanomed., Biotechnol., 2018, vol. 46, supl. 1, pp. 1102–1113.
Sun, L., Yuan, Q., Xu, T., Yao, L., Feng, J., Ma, J., Wang, L., Lu, C., and Wang, D., Pioglitazone improves mitochondrial function in the remnant kidney and protects against renal fibrosis in 5/6 nephrectomized rats, Front. Pharmacol., 2017, vol. 8, p. 545.
Susnow, N., Zeng, L., Margineantu, D., and Hockenbery, D.M., Bcl-2 family proteins as regulators of oxidative stress, Semin. Cancer Biol., 2009, pp. 42–49.
Bauer, C., Hees, C., Sterzik, A., Bauernfeind, F., Mak’Anyengo, R., Duewell, P., Lehr, H.-A., Noess-ner, E., Wank, R., and Trauzold, A., Proapoptotic and antiapoptotic proteins of the Bcl-2 family regulate sensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells toward gemcitabine and T-cell–mediated cytotoxicity, J. Immunother., 2015, vol. 38, no. 3, pp. 116–126.
Bai, D.-P., Zhang, X.-F., Zhang, G.-L., Huang, Y.-F., and Gurunathan, S., Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce apoptosis and autophagy in human ovarian cancer cells, Int. J. Nanomed., 2017, vol. 12, p. 6521.
Meyer, K., Rajanahalli, P., Ahamed, M., Rowe, J.J., and Hong, Y., ZnO nanoparticles induce apoptosis in human dermal fibroblasts via p53 and p38 pathways, Toxicol. In Vitro, 2011, vol. 25, no. 8, pp. 1721–1726.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors thank the Deputy of Research and Technology of Zabol University of Medical Sciences for all support provided.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
This study was approved by the ethical committee of Zabol University of Medical Sciences (IR.ZBMU.REC.1398.088). There is no duplicate publication, fraud, plagiarism, or concerns about animal or human experimentation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, M., Majd, M.H. Evaluation of Induced Apoptosis by Biosynthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells Using Bak1 and Bclx Expression. Dokl Biochem Biophys 500, 360–367 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1607672921050148
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1607672921050148