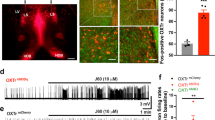
Abstract—Chemogenetic activation of glutamatergic neurons of the prefrontal cortex reduces the manifestations of psychoemotional anxiety during the juvenile period of ontogenesis. This result is the first evidence of feasibility of targeted chemogenetic control of neuronal activity during the early stages of brain development.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Sternson, S.M. and Roth, B.L., Chemogenetic tools to interrogate brain functions, Annu. Rev. Neurosci., 2014, vol. 37, pp. 387–407. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-neuro-071013-014048
Yun, S., et al., Stimulation of entorhinal cortex-dentate gyrus circuitry is antidepressive, Nat. Med., 2018, vol. 24, pp. 658–666. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0002-1
Selleck, R.A., et al., Limited prefrontal cortical regulation over the basolateral amygdala in adolescent rats, Sci. Rep., 2018, vol. 8, p. 17171. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35649-0
Spear, L.P., The adolescent brain and age-related behavioral manifestations, Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev., 2000, vol. 24, pp. 417–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0149-7634(00)00014-2
Zimmermann, K.S., Richardson, R., and Baker, K.D., Maturational changes in prefrontal and amygdala circuits in adolescence: implications for understanding fear inhibition during a vulnerable period of development, Brain Sci., 2019, vol. 9, no. 3. pii: E65. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9030065
Lanshakov, D.A., Drozd, U.S., and Dygalo, N.N., Optogenetic stimulation increases level of antiapoptotic protein Bcl-xL in neurons, Biochemistry (Moscow), 2017, vol. 82, pp. 340–344. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297917030129
Bourin, M. and Hascoët, M., The mouse light/dark box test, Eur. J. Pharmacol., 2003, vol. 463, nos. 1–3, pp. 55–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-2999(03)01274-3
Lanshakov, D.A., Sukhareva, E.V., Kalinina, T.S., and Dygalo, N.N., Dexamethasone-induced acute excitotoxic cell death in the developing brain, Neurobiol. Dis., 2016, vol. 91, pp. 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2016.02.009
Chtarto, A., et al., A next step in adeno-associated virus-mediated gene therapy for neurological diseases: regulation and targeting, Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 2013, vol. 76, no. 2, pp. 217–232. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.12065
Lieb, A., Weston, M., and Kullmann, D.M., Designer receptor technology for the treatment of epilepsy, EBioMedicine, 2019, vol. 43, pp. 641–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.04.059
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (project no. 19-15-00093).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement on the welfare of animals. Experiments on animals were in compliance with the rules of humane treatment of experimental animals (order no. 755 of the USSR Ministry of Health dated August 12, 1977).
Additional information
Translated by M. Batrukova
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dygalo, N.N., Lanshakov, D.A., Komysheva, N.P. et al. Chemogenetic Activation of Glutamatergic Neurons in the Juvenile Rat Cortex Reduces Anxiety. Dokl Biochem Biophys 490, 16–18 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1607672920010056
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1607672920010056