Abstract
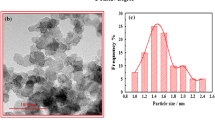
Graphitic carbon nitride was synthesized via thermolysis of urea and then ultrasonic exfoliated from colloidal solution to obtain phase pure ultrafine powder of g-C3N4. It was shown that ultrasonic-assisted exfoliation of the initial graphitic carbon nitride powder leads to an increase in its phase purity (PXRD), a change in the morphology (SEM), a decrease in the band gap from 2.93 eV to 2.85 eV (DRS) and an increase in the specific surface from 58.6 m2/g to 136.7 m2/g (BET). In addition, it was found that the exfoliated g-C3N4 is an effective catalyst for the process of electrocatalytic reforming – the hydrogen evolution from the water-alcohol solution. Based on volamperometry, it was found that the hydrogen overpotential of graphitic carbon nitride is equal to 249 mV (at 10 mA/cm2), and the Taffel slope is 112 mV/dec. The results of cyclic voltammetry of the electrode based on exfoliated g-C3N4 indicate its high stability, which allows us to consider the exfoliated graphitic carbon nitride as a promising basis of materials for electrocatalytic reforming of alcohols.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
X. Chen, Sh. Shen, L. Guo, and S. S. Mao, Chem. Rev. 110, 6503 (2010).
G. Iervolino, V. Vaiano, D. Sannino, L. Rizzo, and V. Palma, Appl. Catal. 207, 182 (2017).
S. Ma, Sh. Chen, A. Soomro, Zhu Min, and W. Xiang, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 43, 3154 (2018).
K. D. Martinson, I. S. Kondrashkova, and V. I. Popkov, Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 90, 1214 (2017).
A. Bachina, V. A. Ivanov, and V. I. Popkov, Nanosyst.: Phys., Chem. Math. 8, 647 (2017).
S. M. Abdel, T. A. Gadallah, M. F. El-shahat, A. M. Ashmawy, and S. I. Hanan, Biochem. Pharmacol. 4, 4165 (2016).
K. S. Kang, C. H. Kim, K. K. Bae, W. Ch. Cho, W. J. Kim, Y. H. Kim, S. H. Kim, and Ch. S. Park, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 35 (568) (2010).
V. I. Popkov, V. P. Tolstoy, and V. N. Nevedomskiy, Heliyon 5, 3 (2019).
I. I. Moiseev, Russ. Chem. Rev. 82, 616 (2013).
D. V. Markovskaya and E. A. Kozlova, Kinet. Catal. 59, 727 (2018).
A. K. Vasilevskaia, V. I. Popkov, A. A. Valeeva, and A. A. Rempel’, Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 89, 1211 (2016).
F. Dong, Z. Zhao, T. Xiong, Z. Ni, W. Zhang, Y. Sun, and W. K. Ho, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5, 11392 (2013).
J. Wen, J. Xie, X. Chen, and X. Li, Appl. Surf. Sci. 391, 72 (2017).
F. Dong, Zh. Wang, Y. Sun, W. K. Ho, and H. J. Zhang, Colloid Interface 401, 70 (2013).
V. P. Tolstoy, L. B. Gulina, A. A. Golubeva, S. S. Ermakov, V. E. Gurenko, D. V. Navolotskaya, N. I. Vladimirova, and A. V. Koroleva, J. Solid State Electrochem. 23, 573 (2019).
V. P. Tolstoy, L. I. Kuklo, and L. B. Gulina, J. Alloys Compd. 786, 198 (2019).
E. S. Bakunin, E. Y. Obraztsova, and A. V. Rukhov, Inorg. Mater.: Appl. Res. 10, 249 (2019).
Y. Zheng, Y. Jiao, Y. Zhu, L. H. Li, Y. Han, Y. Chen, A. Du, M. Jaroniec, and Sh. Zh. Qiao, Nat. Commun. 5, 1 (2014).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The PXRD study was performed on the equipment of the Engineering Center of the Saint-Petersburg State Institute of Technology. The author would like to thank Tomkovich M.V. for help with scanning electron microscopy studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chebanenko, M.I., Zakharova, N.V., Lobinsky, A.A. et al. Ultrasonic-Assisted Exfoliation of Graphitic Carbon Nitride and its Electrocatalytic Performance in Process of Ethanol Reforming. Semiconductors 53, 2072–2077 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S106378261912008X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S106378261912008X