Abstract
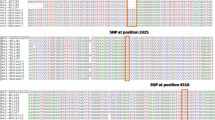
Rice amylose content (AC) is a key determinant for grain end-use quality attributes. The base substitution ((G → T) at +1 loci of the first intron (In1) of Waxy (Wx), a major gene controlling AC in rice, results in decreased AC. A new SNP typing method of Wx In1 based on polymerase chain reaction with confronting two-pair primers (PCR-CTPP) was reported here: first its practicability was confirmed by 23 varieties with known SNP and AC; and then the segregation ratio at target SNP loci were checked and it fitted well for 1: 2: 1 single gene segregation; at last SNP typing and AC assay with 150 mini core collections (MCC) in China showed that average AC of 53 G type varieties (22.5%) was significantly higher than that of 97 T type varieties (13.7%) (p < 0.01) and the target SNP loci explained 77.8% AC variation. So this method could be used to estimate AC of rice variety roughly or in marker-assisted breeding, that is, using variety with known and desired AC as Wx allele donor parent and aided with crossbreed, backcross and marker-assisted selection (MAS) reported here, rice breeders could improve AC of varieties with comprehensively excellent performance to meet special end-products.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergman, C.J., Bhattacharya, K.R., and Ohtsubo, K., Rice end-use quality analysis, Rice Chemistry and Technology, Champagne, E., Ed., St. Paul, MN: American Association of Cereal Chemists, 2004.
Wang, Z., Wu, Z., Xing, Y., et al., Nucleotide sequence of rice waxy gene, Nucleic Acids Res., 1990, vol. 18, no. 19, p. 5898.
Divashuk, M.G., Klimushina, M.V., and Karlov, G.I., Molecular genetic characteristics of the Wx-B1e allele from common wheat and applicability of the DNA markers for its identification, Russ. J. Genet., 2011, vol. 47, no. 12, pp. 1428–1432.
Bligh, H., Larkin, P., Roach, P., et al., Use of alternate splice sites in granule-bound starch synthase mRNA from low-amylose rice varieties, Plant Mol. Biol., 1998, vol. 38, no. 3, pp. 407–415.
Cai, X., Wang, Z., Xing, Y., et al., Aberrant splicing of intron 1 leads to the heterogeneous 5' UTR and decreased expression of waxy gene in rice cultivars of intermediate amylose content, Plant J., 1998, vol. 14, no. 4, pp. 459–465.
Hirano, H., Eiguchi, M., and Sano, Y., A single base change altered the regulation of the Waxy gene at the posttranscriptional level during the domestication of rice, Mol. Biol. Evol., 1998, vol. 15, no. 8, pp. 978–987.
Isshiki, M., Morino, K., Nakajima, M., et al., A naturally occurring functional allele of the rice waxy locus has a GT to TT mutation at the 5’ splice site of the first intron, Plant J., 1998, vol. 15, no. 1, pp. 133–138.
Larkin, P. and Park, W., Transcript accumulation and utilization of alternate and non-consensus splice sites in rice granule-bound starch synthase are temperaturesensitive and controlled by a single-nucleotide polymorphism, Plant Mol. Biol., 1999, vol. 40, no. 44, pp. 719–727.
Ayres, N., McClung, A., and Larkin, P., Microsatellites and a single-nucleotide polymorphism differentiate apparent amylose classes in an extended pedigree of US rice germplasm, Theor. Appl. Genet., 1997, vol. 94, no. 66, pp. 773–781.
Khlestkina, E.K. and Salina, E.A., SNP markers: methods of analysis, ways of development, and comparison on an example of common wheat, Russ. J. Genet., 2006, vol. 42, no. 6, pp. 585–594.
Gostimsky, S.A., Kokaeva, Z.G., and Konovalov, F.A., Studying plant genome variation using molecular markers, Russ. J. Genet., 2005, vol. 41, no. 4, pp. 378–388.
Ashfaq, M. and Khan, A.S., Genetic diversity in basmati rice (Oryza sativa L.) germplasm as revealed by microsatellite (SSR) markers, Russ. J. Genet., 2012, vol. 48, no. 1, pp. 53–62.
Kofiadi, I.A. and Rebrikov, D.V., Methods for detecting single nucleotide polymorphisms: allele-specific PCR and hybridization with oligonucleotide probe, Russ. J. Genet., 2006, vol. 42, no. 1, pp. 16–26.
Neff, M., Neff, J., and Chory, J., dCAPS, a simple technique for the genetic analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms: experimental applications in Arabidopsis thaliana genetics, Plant J., 1998, vol. 14, no. 3, pp. 387–392.
Hamajima, N., PCR-CTPP: a new genotyping technique in the era of genetic epidemiology, Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn., 2002, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 119–123.
Zhang, H., Zhang, D., Wang, M., and Sun, J., A core collection and mini core collection of Oryza sativa L. in China, Theor. Appl. Genet., 2011, vol. 122, no. 1, pp. 49–61.
Dellaporta, S., Wood, J., and Hicks, J., A plant DNA mini preparation: version II, Plant Mol. Biol. Rep., 1983, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 19–21.
Tan, Y., Li, J., Yu, S., et al., The three important traits for cooking and eating quality of rice grains are controlled by a single locus in an elite rice hybrid, Shanyou 63, Theor. Appl. Genet., 1999, vol. 99, no. 3, pp. 642–648.
Cai, X., Liu, Q., Tang, S., et al., Development of a molecular marker for screening the rice cultivars with intermediate amylose content in Oryza sativa subsp. indica, J. Plant Physiol. Mol. Biol., 2002, vol. 28, no. 2, pp. 137–144.
Mao, X., Xiao, X., Chen, J., et al., One-step PCR method for detecting the first base of splice donor of Wx intron 1 in rice, Chin. J. Rice Sci., 2005, vol. 19, no. 3, pp. 285–287.
Sun, L. and Guan, Y., Effect of base mismatch on DNA structure and melting temperature (Tm) [D], China Med. Univ., 2007, pp. 22–24.
Domon, E., Yanagisawa, T., Saito, A., and Takeda, K., Single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping of the barley waxy gene by polymerase chain reaction with confronting two-pair primers, Plant Breed., 2003, vol. 123, no. 3, pp. 225–228.
Mikami, I., Uwatoko, N., Ikeda, Y., et al., Allelic diversification at the Wx locus in landraces of Asian rice, Theor. Appl. Genet., 2008, vol. 116, no. 7, pp. 979–989.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, H., Xu, D., Zhou, L. et al. Development of PCR-based CNP marker of rice Waxy gene with confronting two-pair primers. Russ J Genet 51, 673–676 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795415060034
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795415060034