Abstract
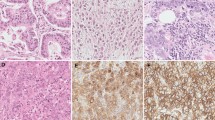
Ovarian cancer (OC) is mostly detected at late stages weighed down with metastasis, and the five-year survival rate of patients is only 30%, which dictates the necessity to develop gentler and more selectively targeted drugs that current chemotherapeutic agents. The search for factors that can influence on the activity of the PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint signaling pathway in tumors is relevant, and microRNAs (miRNAs) play an important role in it. Over the past 5 years, only a few miRNAs (miR-34a, miR-145, and miR-424), which have a regulatory effect on the PD-1/PD-L1 system in OC patients, have been discovered. In present work, the methylation levels of 13 miRNA genes in 26 primary tumors and 19 peritoneal metastases of OC patients were determined and compared with the level of the soluble form of PD-L1 (sPD-L1) in the blood plasma of the same patients. It was shown that the methylation levels of five miRNA genes (MIR124-2, MIR34B/C, MIR9-1, MIR9-3, and MIR339) in tumors are in direct correlation with the sPD-L1 level in the blood plasma. In addition, when analyzing these five genes, a significant association of the methylation level of the MIR9-1 gene with a decrease in the three-year relapse-free survival, and a trend for decrease in the three-year survival rate with the methylation level of the MIR124-2 gene of OC patients were determined. Thus, the first data suggesting the role of inhibitors of the sPD-L1 immune checkpoint for five miRNAs (miR-124, miR-34b, miR-34c, miR-9, miR-339) and the possibility of using hypermethylated MIR9-1 and, presumably, MIR124-2 genes as independent prognostic markers of poor disease-free survival in OC patients were obtained.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Omar H.A., El-Serafi A.T., Hersi F., Arafa E.A., Zaher D.M., Madkour M., Arab H.H., Tolba M.F. 2019. Immunomodulatory microRNAs in cancer: targeting immune checkpoints and the tumor microenvironment. FEBS J. 286 (18), 3540–3557. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.15000
Kushlinskii N.E., Fridman M.V., Morozov A.A., Gershtein E.S., Kadagidze Z.G., Matveev V.B. 2018. Modern approaches to kidney cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Urol. 14 (2), 54–67. https://doi.org/10.17650/1726-9776-2018-14-2-54-67
Korotaeva A.A., Apanovich N.V., Braga E.A., Matveev V.B., Karpukhin A.V. 2019. Current advances in kidney cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Urol. 15 (4), 30–38. https://doi.org/10.17650/1726-9776-2019-15-4-30-38
Wang Q., Lin W., Tang X., Li S., Guo L., Lin Y., Kwok H.F. 2017. The roles of microRNAs in regulating the expression of PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18 (12). pii: E2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122540
Sheng Q., Zhang Y., Wang Z., Ding J., Song Y., Zhao W. 2020. Cisplatin-mediated down-regulation of miR-145 contributes to up-regulation of PD-L1 via the c-Myc transcription factor in cisplatin-resistant ovarian carcinoma cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 200 (1), 45‒52. https://doi.org/10.1111/cei.13406
Loginov V.I., Pronina I.V., Burdennyi A.M., Filippova E.A., Kazubskaya T.P., Kushlinsky D.N., Utkin D.O., Khodyrev D.S., Kushlinskii N.E., Dmitriev A.A., Braga E.A. 2018. Novel miRNA genes deregulated by aberrant methylation in ovarian carcinoma are involved in metastasis. Gene. 662, 28‒36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.04.005
Braga E.A., Loginov V.I., Burdennyi A.M., Filippova E.A., Pronina I.V., Kurevlev S.V., Kazubskaya T.P., Kushlinskii D.N., Utkin D.O., Ermilova V.D., Kushlinskii N.E. 2018. Five hypermethylated microRNA genes as potential markers of ovarian cancer. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 164 (3), 351‒355. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-018-3988-y
Koukourakis M.I., Kontomanolis E., Sotiropoulou M., Mitrakas A., Dafa E., Pouliliou S., Sivridis E., Giatromanolaki A. 2018. Increased soluble PD-L1 levels in the plasma of patients with epithelial ovarian cancer correlate with plasma levels of miR34a and miR200. Anticancer Res. 38 (10), 5739‒5745. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.12912
Xu S., Tao Z., Hai B., Liang H., Shi Y., Wang T., Song W., Chen Y., OuYang J., Chen J., Kong F., Dong Y., Jiang S.W., Li W., Wang P., et al. 2016. miR-424(322) reverses chemoresistance via T-cell immune response activation by blocking the PD-L1 immune checkpoint. Nat. Commun. 7, 11406. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11406
Zuo Y., Zheng W., Liu J., Tang Q., Wang S.S., Yang X.S. 2020. MiR-34a-5p/PD-L1 axis regulates cisplatin chemoresistance of ovarian cancer cells. Neoplasma. 67 (1), 93‒101. https://doi.org/10.4149/neo_2019_190202N106
Shi C., Zhang Z. 2016. The prognostic value of the miR-200 family in ovarian cancer: A meta-analysis. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 95 (5), 505‒512. https://doi.org/10.1111/aogs.12883
Xia L., Zhang W., Gao L. 2019. Clinical and prognostic effects of CDKN2A, CDKN2B and CDH13 promoter methylation in ovarian cancer: A study using meta-analysis and TCGA data. Biomarkers. 24 (7), 700‒711. https://doi.org/10.1080/1354750X.2019.1652685
World Health Organization. 2014. WHO Classification of Tumours of Female Reproductive Organs, 4th ed. Eds. Kurman R.J., Carcangiu M.L., Herrington C.S., Young R.H. Lyon: IARC.
Hattermann K., Mehdorn H.M., Rolf Mentlein R., Schultka S., Held-Feindt J. 2008. A methylation-specific and SYBR-green-based quantitative polymerase chain reaction technique for O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase promoter methylation analysis. Anal. Biochem. 377 (1), 62‒71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2008.03.014
Panagopoulou M., Karaglani M., Balgkouranidou I., Biziota E., Koukaki T., Karamitrousis E., Nena E., Tsamardinos I., Kolios G., Lianidou E., Kakolyris S., Chatzaki E. 2019. Circulating cell-free DNA in breast cancer: size profiling, levels, and methylation patterns lead to prognostic and predictive classifiers. Oncogene. 38 (18), 3387‒3401. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0660-y
van Hoesel A.Q., Sato Y., Elashoff D.A., Turner R.R., Giuliano A.E., Shamonki J.M., Kuppen P.J., van de Velde C.J., Hoon D.S. 2013. Assessment of DNA methylation status in early stages of breast cancer development. Br. J. Cancer. 108 (10), 2033‒2038.
Duan M., Fang M., Wang C., Wang H., Li M. 2020. LncRNA EMX2OS induces proliferation, invasion and sphere formation of ovarian cancer cells via regulating the miR-654-3p/AKT3/PD-L1 axis. Cancer Manag. Res. 12, 2141‒2154. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S229013
Wang Y., Zhang W., Wang Y., Wang S. 2018. HOXD-AS1 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion through miR-608/FZD4 axis in ovarian cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 8 (1), 170‒182.
Dong S., Wang R., Wang H., Ding Q., Zhou X., Wang J., Zhang K., Long Y., Lu S., Hong T., Ren H., Wong K., Sheng X., Wang Y., Zeng Y. 2019. HOXD-AS1 promotes the epithelial to mesenchymal transition of ovarian cancer cells by regulating miR-186-5p and PIK3R3. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 38 (1), 110. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1103-5
Yang Q., Yu Y., Sun Z., Pan Y. 2018. Long non-coding RNA PVT1 promotes cell proliferation and invasion through regulating miR-133a in ovarian cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 106, 61–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.112
Chen Y., Du H., Bao L., Liu W. 2018. LncRNA PVT1 promotes ovarian cancer progression by silencing miR-214. Cancer Biol. Med. 15 (3), 238‒250. https://doi.org/10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2017.0174
Ding Y., Fang Q., Li Y., Wang Y. 2019. Amplification of lncRNA PVT1 promotes ovarian cancer proliferation by binding to miR-140. Mamm. Genome. 30 (7‒8), 217‒225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-019-09808-1
Qu C., Dai C., Guo Y., Qin R., Liu J. 2020. Long non-coding RNA PVT1-mediated miR-543/SERPINI1 axis plays a key role in the regulatory mechanism of ovarian cancer. Biosci. Rep. 40 (6). https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20200800
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Russian Science Foundation (project no. 20-15-00368); the analysis of the sPD-L1 level in the blood plasma of patients was performed within the State Task of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation for 2020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement of compliance with standards of research involving humans as subjects. All procedures performed in the present study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research ethics committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants involved in the study.
Additional information
Translated by D. Novikova
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kushlinskii, N.E., Loginov, V.I., Utkin, D.O. et al. Novel miRNAs as Potential Regulators of PD-1/PD-L1 Immune Checkpoint, and Prognostic Value of MIR9-1 and MIR124-2 Methylation in Ovarian Cancer. Mol Biol 54, 870–875 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893320060072
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893320060072