Abstract
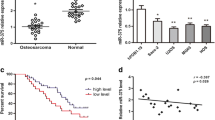
Osteosarcoma is the most common type of bone cancer, with a peak incidence in the early childhood. The relationship between microRNAs (miRNAs) and cancer development attracted more and more attention over the last few years. Members of the miRNA-29 family, including miRNA-29a, miRNA-29b, and miRNA-29c were shown to participate in the development of rhabdomyosarcoma and hepatocarcinogenesis. Here, it has been demonstrated miRNA-29a and miRNA-29b expression levels to be downregulated in most of the osteosarcoma tissues (23 from 30). Besides, miRNA-29a displayed ability to induce apoptosis in both U2OS and SAOS-2 osteoblastic cells. While miRNA-29 members induced apoptosis through p53 gene activation, the effect of miRNA-29a on osteoblastic cells was independent on p53 expression level. Moreover, Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 were earlier demonstrated to be the direct targets of miRNA-29 in many types of cancer tissues and cancers. In both U2OS and SAOS-2 osteoblastic cell types, overexpression of miRNA-29a also downregulated Bcl-2 and Mcl-1, while silencing of miRNA-29a increased their expression. In addition, enhanced expression of miRNA-29a increased the expression of two tumor suppressor genes, E2F1 and E2F3. In summary, data obtained highlight the role of miRNA-29a in the regulation of osteoblastic cell apoptosis by silencing Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 and inducing E2F1 and E2F3 expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambros V. 2004. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 431, 350–355.
Bartel D.P. 2004. MicroRNAs, genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116, 281–297.
Rogaev E.I., Borinskaia S.A., Islamgulov D.V., Grigorenko A.P. 2008. Human microRNA in norm and pathology. Mol. Biol. (Moscow). 42, 668–680.
Calin G.A., Croce C.M. 2006. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nature Rev. Cancer. 6, 857–866.
Negrini M., Nicoloso M.S., Calin G.A. 2009. MicroRNAs and cancer: New paradigms in molecular oncology. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 21, 470–479.
Braconi C., Kogure T., Valeri N., Huang N., Nuovo G., Costinean S., Negrini M., Miotto E., Croce C.M., Patel T. 2011. MicroRNA-29 can regulate expression of the long non-coding RNA gene MEG3 in hepatocellular cancer. Oncogene. 30, 1–7.
Garzon R., Heaphy C.E.A., Havelange V., Fabbri M., Volinia S., Tsao T., Zanesi N., Kornblau S.M., Marcucci G., Calin G.A., Andreeff M., Croce C.M. 2009. MicroRNA 29b functions in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 17, 5331–5341.
Ottaviani G., Jaffe N. 2010. The epidemiology of osteosarcoma. Cancer Treat. Res. 152, 3–13.
Janeway K.A., Grier H.E. 2010. Sequelae of osteosarcoma medical therapy: A review of rare acute toxicities and late effects. Lancet Oncol. 11, 670–678.
Tao J., Chen S., Lee B. 2010. Alteration of Notch signaling in skeletal development and disease. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1192, 257–268.
Iorio M.V., Ferracin M., Liu C.G., Veronese A., Spizzo R., Sabbioni S., Magri E., Pedriali M., Fabbri M., Campiglio M., Ménard S., Palazzo J.P., Rosenberg A., Musiani P., Volinia S., Nenci I., Calin G.A., Querzoli P., Negrini M., Croce C.M. 2005. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 65, 7065–7070.
Pekarsky Y., Santanam U., Cimmino A., Palamarchuk A., Efanov A., Maximov V., Volinia S., Alder H., Liu C.G., Rassenti L., Calin G.A., Hagan J.P., Kipps T., Croce C.M. 2006. Tcl1 expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia is regulated by miR-29 and miR-181. Cancer Res. 66, 11590–11593.
Porkka K.P., Pfeiffer M.J., Waltering K.K., Vessella R.L., Tammela T.L.J., Visakorpi T. 2007. MicroRNA expression profiling in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 67, 6130–6135.
Mott J.L., Kobayashi S., Bronk S.F., Gores G.J. 2007. miR-29 regulates Mcl-1 protein expression and apoptosis. Oncogene. 26, 6133–6140.
Stamatopoulos B., Meuleman N., Haibe-Kains B., Saussoy P., van den Neste E., Michaux L., Heimann P., Martiat P., Bron D., Lagneaux L. 2009. MicroRNA-29c and microRNA-223 downregulation has in vivo significance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and improves disease risk stratification. Blood. 113, 5237–5245.
Wang H., Garzon R., Sun H., Ladner K.J., Singh R., Dahlman J., Cheng A., Hall B.M., Qualman S.J., Chandler D.S., Croce C.M., Guttridge D.C. 2008. NF-kappaB-YY1-miR-29 regulatory circuitry in skeletal myogenesis and rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Cell. 14, 369–381.
Fabbri M., Garzon R., Cimmino A., Liu Z.F., Zanesi N., Callegari E., Liu S., Alder H., Costinean S., Fernandez-Cymering C., Volinia S., Guler G., Morrison C.D., Chan K.K., Marcucci G., Calin G.A., Huebner K., Croce C.M. 2007. MicroRNA-29 family reverts aberrant methylation in lung cancer by targeting DNA methyltransferases 3A and 3B. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 104, 15805–15810.
Park S.Y., Lee J.H., Ha M., Nam J.W., Kim V.N. 2008. miR-29 miRNAs activate p53 by targeting p85alpha and CDC42. Nature Struct. Mol. Biol. 16, 23–29.
Lu J., Getz G., Miska E.A., Alvarez-Saavedra E., Lamb J., Peck D., Sweet-Cordero A., Ebert B.L., Mak R.H., Ferrando A.A., Downing J.R., Jacks T., Horvitz H.R., Golub T.R. 2005. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 435, 834–838.
Volinia S., Calin G.A., Liu C.G., Ambs S., Cimmino A., Fabio P., Visone R., Iorio M., Roldo C., Ferracin M., Prueitt R.L., Yanaihara N., Lanza G., Scarpa A., Vecchione A., Negrini M., Harris C.C., Croce C.M. 2006. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103, 2257–2261.
Sieghart W., Losert D., Strommer S., Cejka D., Schmid K., Rasoul-Rockenschaub S., Bodingbauer M., Crevenna R., Monia B.P., Peck-Radosavljevic M., Wacheck V. 2006. Mcl-1 overexpression in hepatocellular carcinoma: A potential target for antisense therapy. J. Hepatol. 44, 151–157.
Zekri A.R.N., Bahnassy A.A., Abdel-Wahab S.A., Khafagy M.M., Loutfy S.A., Radwan H., Shaarawy S.M. 2009. Expression of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in relation to apoptotic genes in Egyptian liver disease patients associated with HCV-genotype-4. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 24, 416–428.
Yip K.W., Reed J.C. 2008. Bcl-2 family proteins and cancer. Oncogene. 27, 6398–406.
Zheng N., Fraenkel E., Pabo C.O., Pavletich N.P. 1999. Structural basis of DNA recognition by the heterodimeric cell cycle transcription factor E2F-DP. Genes Dev. 13, 666–674.
Zwicker J., Liu N., Engeland K., Lucibello F.C., Müller R. 1996. Cell cycle regulation of E2F site occupation in vivo. Science. 271, 1595–1597.
Ogawa H., Ishiguro K., Gaubatz S., Livingston D.M., Nakatani Y. 2002. A complex with chromatin modifiers that occupies E2F- and Myc-responsive genes in G0 cells. Science. 296, 1132–1136.
Xiong Y., Fang J.H., Yun J.P., Yang J., Zhang Y., Jia W.H., Zhuang S.M. 2010. Effects of microRNA-29 on apoptosis, tumorigenicity, and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 51, 836–845.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
W. Zhang and J.-X. Qian contributed equally to this work.
W. Zhang and J.-X. Qian are the co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Qian, J.X., Yi, H.L. et al. The microRNA-29 plays a central role in osteosarcoma pathogenesis and progression. Mol Biol 46, 557–562 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893312040139
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893312040139