Abstract
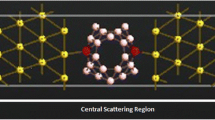
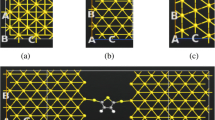
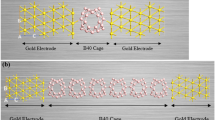
A substantial amount of researches have been carried out on the electron transport properties of gold surfaces. In order to study the role of linkage in the conductive properties of a molecular wire, different linkers such as sulfur, nitrogen, oxygen, CS, SH, NS, and CN are considered in our study. It is found that nitrogen or sulfur linkages can bond Au covalently to cis- and trans-butadiene, whereas on the other hand, oxygen linkage with the same shows a weak interaction and a non-covalent character. Further, this research is also an attempt to study the dependence of the molecular electronic structure of gold-molecule complexes on the external electric field. In addition, electronic conduction has been investigated from the perspective of alteration in shape of molecular orbitals and the development of the HOMO-LUMO gap of moleculegold complexes under the effect of an electric field.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Aviram and M. A. Ratner, Chem. Phys. Lett., 29, 277–283 (1974).
C. Joachim, J. K. Gimzewski, R. R. Schlittler, et al. Phys. Rev. Lett., 74, 2102–2015 (1995).
T. Oyamada, H. Tanaka, H. Sasabe, et al. Appl. Phys. Lett., 83, 1252–1254 (2003).
L. Ma, S. Pyo, J. Ouyang, et al. Appl. Phys. Lett., 82, 1419–1421 (2003).
D. R. Stewart, D. A. Ohlberg, P. Beck A., et al. Nano Lett., 4, 133–136 (2004).
J. He, L. Ma, J. Wu, and Y. Yang, J. Appl. Phys., 97, 064507 (2005).
C. N. Lau, D. R. Stewart, R. S. Williams, et al. Nano Lett., 4, 569–572 (2004).
L. T. Cai, Y. X. Yao, J. P. Yang, et al. J. Mol. Tour. Chem. Matter., 14, 2905–2909 (2002).
D. L. Allara, T. D. Dunbar, P. S. Weiss, L. A. Bumm, et al. Ann. Acad. Sci., 852, 349–370 (1998).
J. M. Tour, Chem. Rev., 96, 537–553 (1996).
Y. C. Choi, W. Y. Kim, K. S. Park, et al. J. Chem. Phys., 122, 094706 (2005).
P. Hermet, J. L. Bantignies, A. Rahmani, et al. J. Phys. Chem. A, 109, 4202–4207 (2005).
Y. Zhang, Y. Ye, Y. Li, et al. J. Mol. Struct. (Theochem.), 802, 53–58 (2007).
Y. Li, J. Zhao, and G. Yin, Comp. Mater. Sci., 39, 775–781 (2006).
Z. Bayat, S. Daneshnia, and S. J. Mahdizadeh, Physica E, 43, 1569–1575 (2011).
A. Mohajeri and A. Zare, Comp. Mater.Sci., 45, 935–940 (2009).
S. Sitha and A. Bhanuprakash, J. Mol. Struct. (Theochem.), 761, 31–38 (2006).
W. B. Davis, W. A. Svec, M. A. Ratner, et al. Nature, 396, 60–63 (1998).
W. B. Davis, M. A. Ratner, and M. R. Wasielewski, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 123, 7877–7886 (2001).
W. Gao, M. Zhao, and Q. Jiang, Appl. Surface Sci., 255, 9259–9263 (2009).
H. Ke, H. U. Baranger, and W. Yang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 126, 15897–15904 (2004).
L. Yang, J. KangFeng, A. MinRen, et al. Polymer, 47, 1397–1404 (2006).
J. Chen, W. Wang, M. A. Reed, et al. Appl. Phys. Lett., 77, 1224–1226 (2000).
R. J. Magyar, S. Tretiak, Y. Gao, et al. Chem. Phys. Lett., 401, 149–156 (2005).
Y. Li, J. Zhao, X. Yin, et al. Phys Chem. Chem. Phys., 9, 1186–1193 (2006).
U. Bunz, Chem. Rev., 100, 1605–1644 (2000).
M. Moroni, J. Le Moigne, and S. Luzzati, Macromol., 27, 562–571 (1994).
Y. Li, J. Zhao, X. Yin, et al. Phys Chem. Chem. Phys., 9, 1186–1193 (2006).
W. R. Wadt and P. J. Hay, J. Chem. Phys., 82, 284–298 (1985).
Y. Li, G. Yin, J. Yao, and J. Zhao, Comput. Mater. Sci., 42, 638–642 (2008).
Y. Li, J. Zhao, and G. Yin, Comp. Mater. Sci, 39, 775–781 (2006).
X. D. Cui, A. Primak, X. Zarate, et al., Science, 294, 571–574 (2001).
J. Zhao and K. Uosaki, Nano Lett., 2, 137–140 (2002).
M. J. Frisch et al., GAUSSIAN, Gaussian Inc, Wallingford, CT (2004).
P. Delaney, M. Nolan, and J. C. Greer, J. Chem. Phys., 122, 044710-2 (2005).
J. M. Seminario, A. G. Zacarias, and J. M. Tour, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 122, 3015–3020 (2003).
C. Majumder, T. M. Briere, H. Mizuseki, et al. J. Chem. Phys., 117, 7669–7675 (2002).
H. Fueno, M. Hayashi, K. Nin, et al. Curr. Appl. Phys., 6, 939–942 (2006).
J. G. Kushmerick, D. B. Holt, S. K. Pollack, et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 124, 10654/10655 (2002).
K. W. Hipps, Science, 294, 536/537 (2001).
J. M. Beebe, V. B. Engelkes, L. L. Miller, et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 124, 11268/11269 (2002).
Y. Xue, S. Datta, S. Hongy, et al. Phys. Rev. B, 59, R7852 (1999).
C. Majumder, T. M. Briere, H. Mizuseki, et al. J. Chem. Phys., 117, 7669–7675 (2002).
H. Fueno, M. Hayashi, K. Nin, et al. Curr. Appl. Phys., 6, 939–942 (2006).
Y. Ye, M. Zhang, and J. Zhao, J. Mol. Struct. (Theochem.), 822, 12–20 (2007).
Y. Li, J. Zhao, X. Yin, et al. J. Phys. Chem. A, 110, 11130–11135 (2006).
W. Y. Kim, S. K. Kwon, and K. S. Kim, Phys. Rev. B, 76, 033415 (2007).
A. Pecchia, A. DiCarlo, A. Gagliardi, et al. Nano Lett., 4, 2109–2114 (2004).
W. Y. Kim, Y. C. Choi, and K. S. Kim, J. Mater. Chem., 18, 4510–4521 (2008).
W. Y. Kim and K. S. Kim, J. Comput. Chem., 29, 1073–1083 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © 2014 Z. Chamani, Z. Bayat, S. J. Mahdizadeh.
The text was submitted by the authors in English. Zhurnal Strukturnoi Khimii, Vol. 55, No. 3, pp. 557–565, May–June, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chamani, Z., Bayat, Z. & Mahdizadeh, S.J. Theoretical study of the electronic conduction through organic nanowires. J Struct Chem 55, 530–538 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022476614030226
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022476614030226